Most organizations thrive on data. And, organizations are doing everything to protect data from unauthorized and corrupt use using data protection strategies. In 2023, it’s all about optimally managing enterprise data protection goals. In this article, we point out the most challenging elements of data protection.
But, first, what is data protection?
Data protection has emerged as the most important facet of disaster recovery for CIOs and CISOs. The meteoric rise in the number of security incidents and ransomware attacks targeting enterprise data has overwhelmed most IT leaders. Today, data protection teams face attacks from all sides, including state-sponsored cyber criminals who are constantly trying to find new vulnerabilities and penetrate data layers with sophisticated tools. For organizations running Kubernetes, protecting data at all costs becomes the biggest challenge.
CIO News: Intel’s Transition of OpenFL Primes Growth of Confidential AI
Data protection is a scientific approach involving three-tiered categories: Backup and Restore, Data Privacy, and Data security. According to SNIA, data protection is the process of securing important data and preventing loss or corruption. It also includes capabilities to restore data in its original state if an attack renders the data “inaccessible or unusable.” Data protection ensures that protected data is available for use and analysis as per legal and regulatory standards.
According to the Ponemon Institute, there are nine elements to establishing IT security governance and building a resolute data protection infrastructure. These are:
- Security posture
- Information management
- Information governance
- Data protection
- Application security
- Detection and recovery
- Third-party risk
- Insider threats.
- Security information and event management (SIEM)
According to the 2022 Kubernetes Adoption Report – commissioned by Portworx by PureStorage, here are the biggest challenges of data protection.
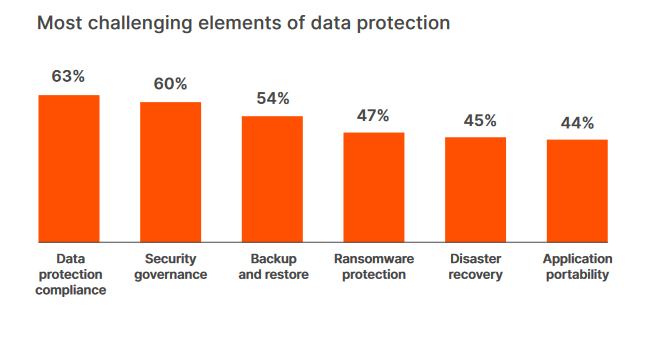
Data protection compliance
Data protection compliance such as GDPR and CCPA provide a standard universal guideline on how companies should collect and store data. This includes personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, e-health records, names, biometric data, birth dates, and contact information. Economically, meeting data protection compliance adds cost to the operations, and failing to meet the standards could dent profits. According to research on how GDPR impact business, GDPR resulted in an 8.1% drop in profit and a 2.2% decline in sales.
Recommended CIO Blogs: Crisis? What Crisis? Managing “Bursty” Data Flows With Event-Driven Architecture Means Retailers…
Therefore, cost-wise, meeting privacy and compliance standards is the biggest challenge for data protection professionals.
Security governance
IT leaders understand the value of having a strong security governance framework within their organization. Yet, it has emerged as a top challenge in data protection. Reason: lack of talent and skills. It takes years of training with cybersecurity professionals to fully understand and cope with ever-shifting paradigms of IT security governance. As newer IT management systems arrive, security governance requires constant collaboration and coordination between experts and IT professionals.
Larger organizations could scale their governance frameworks by adding more tools and automation into the workflow, supervised by AI and machine learning, but for smaller enterprises, managing governance on their own is a big threat.
Backup and restore
The massive influx of SaaS-driven data has put the onus on reliable backup and restore capabilities. Organizations have to perform regular data backup and restore activities to streamline their central assets. The biggest challenge in working with data backup and restore arises with IT leaders realize their data is either missing or corrupt after scheduled tasks are complete. While some organizations may consider lost data or corrupt data as part of the operations, others may have to pay a heavy price for data loss arising from faulty backup and restore operations. It all depends on the type and size of data loss, and the impact it would make on the business operations.
Ransomware protection
Cybercriminals are getting bolder and smarter with sophisticated ransomware targetting activities across the world. In response to such attacks, data organizations are investing heavily in ransomware protection solutions for data protection. It is a big challenge to identify and protect against ransomware as most victims realize the incident happened after being contacted by the criminals.
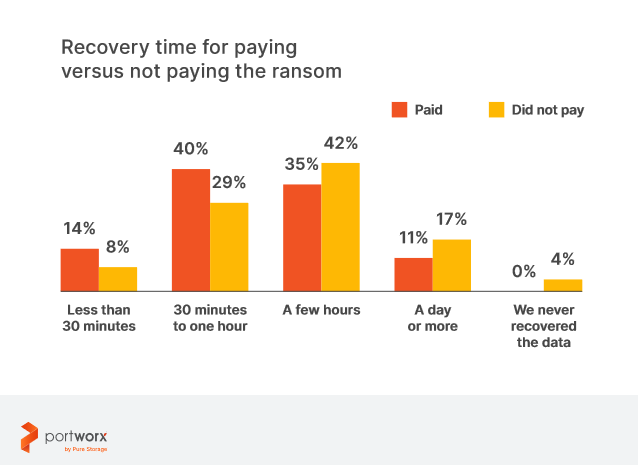
The only way to salvage data from ransomware is by paying the “ransom” to the criminals! However, data protection could help restrict the misuse of the information in critical scenarios. For example, Pure Storage’s Portworx report found 60% of the ransomware victims ended up paying the ransom to release their data. However, there was no assurance that the data would be released fully without misusing it in the future or promising these assets wouldn’t be retargeted in the future. On average, 54% of the companies that paid the ransom amount were able to recover data in less than 60 minutes.
After phishing, ransomware is the most frequent form of cyber attack targeting organizations, And, the incidents peaked during the COVID pandemic months as criminals started using advanced tools and encryption techniques to take advantage of lopsided data protection frameworks. US-based organizations remain the biggest target for ransomware artists, followed by those based in the UK, Canada, and France.
Ransomware protection would continue to be a big challenge for organizations as it is becoming increasingly difficult to connect the outcomes of data protection against ransomware with revenue generation and business profits. It would be an important portfolio for CIOs to convince their CFO about the far-reaching benefits of investing in ransomware protection tools and frameworks for data protection, particularly when ransom bounties are getting higher.
Disaster recovery
The next big challenge in the data protection roadmap is disaster recovery. Disaster recovery is an enterprise-level IT security approach to recover and regain access and functionality of IT assets and resources impacted by catastrophic events or uncontrolled business conditions like state-sponsored military attacks and pandemics. According to VMware, there are five key elements of an effective disaster recovery plan. These are:
Disaster recovery team consisting of experienced IT security and data protection specialists who communicate the best practices in a disaster recovery plan. This team creates and modifies the disaster recovery plan based on requirements, and provides timely information about any incident to employees, vendors, customers, and regulators.
Risk evaluation, depending on the nature of risks and threats that inflict the industry. IT specialists formulate data protection plans and policies after evaluating all the risks.
Asset Labeling and identification, involving clear labeling and organization of critical documents pertaining to IT systems, applications, data infrastructure, software, and people that could get affected by cyber incidents or data incidents. Data protection professionals focus on an Incident Management Plan (IMP) for business continuity and resumption once disaster recovery policies are set in.
Data backups, recovery, and relocation to guide IT teams with standardized strategies, processes, and procedures for handling data protection.
Pro-active simulation, experimentation, and optimization to test if the existing data recovery plans work in critical situations. Data protection teams that frequently test and optimize their disaster recovery strategies are found to be better at handling security breaches.
A full-fledged disaster recovery plan takes months to kick in before showing results. Data protection professionals have to test and find out what strategies work for their organization and if they require Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) provider to help them thwart ransomware attacks or to create new data centers to backup critical infrastructure.
This could be a time-consuming process that runs into weeks and months. Though it could improve customer retention and reduce recovery costs, organizations have to be absolutely clear about their recovery point objective (RPO) and data backups investments before calling in IT experts and data protection professionals to do the job for them. This is a challenge that organizations face during uncertain times and therefore, it requires strategic planning from the onset.
Application portability
77% of enterprise users have reported a significant rise in the use and deployment of Kubernetes in the last 2 years. With time, this trend would only pick up. Currently, companies run 45% of their databases and data services on Kubernetes and by 2025, Kubernetes would play an even larger role in cloud-native application portability for 87% of enterprise users. However, budget constraints and pressure from leadership to embrace digital transformation at a rapid pace are hindering data protection strategies for application portability. Organizations find it hard to overcome the challenges of their cloud-native application portability as they still hesitate in using traditional backup solutions to protect and restore applications on Kubernetes.
According to Portworx by Pure Storage, 38% of the companies do not use data protection built for Kubernetes as they find traditional solutions to be effective in the long run even as 34% connect their data protection to cost constraints. 34% of the companies haven’t matured to a larger Kubernetes deployment that they could scale their data protection strategies straightaway. Only 14% of the companies accepted a lack of executive buy-in to be the reason for not using data protection for their Kubernetes deployment.
Final thoughts
Data protection ensures business continuity for your organization. Frequent or one-off data incidents can have serious ramifications on the organization’s financial health, customer service, revenue generation, and employee trust. A strong data protection strategy enables IT teams to quickly resolve issues and restrict the negative impact on their business. By overcoming the above-mentioned data protection challenges, your organization can reduce customer support calls, lost revenue opportunities, and employee dissatisfaction. What you need today is an end-to-end data protection solution for all your Kubernetes and cloud-native applications. Portwork comes across as a reliable solution for CIOs.


