As technology advances, the risk posed by hackers and cyber attackers escalates. According to the FBI Internet Crime Report, 847,376 complaints of internet-related crimes resulted in financial losses exceeding $6.9 billion, marking a significant increase from the previous year.
Presently, 35% of CISOs utilize AI for security applications, with an anticipated rise to 61% within 12 months. Additionally, 86% believe generative AI will mitigate security skills gaps and talent shortages.
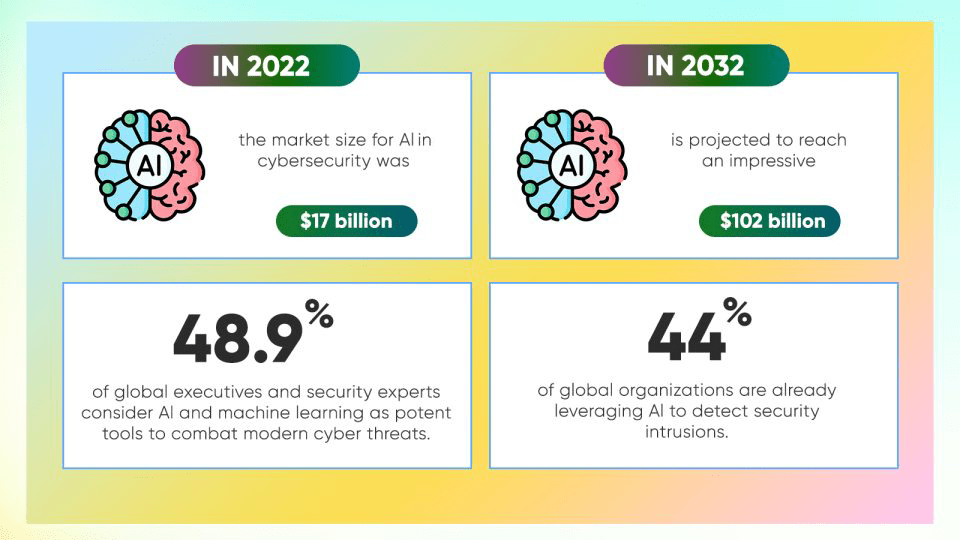
The significance of AI in cybersecurity is evident. Verified Market Research notes that the AI in cybersecurity market was valued at $17 billion in 2022 and is forecasted to reach $102 billion by 2032. This growth aligns with hackers’ adoption of new technologies for malicious purposes.
 Source: Verified Market Research
Source: Verified Market Research
The mounting frequency of cyber-attacks has drawn global attention to the potential role of AI in cybersecurity. A survey by The Economist Intelligence Unit reveals that 48.9% of global executives and security experts view AI and machine learning as effective tools against modern cyber threats. Moreover,
Pillsbury’s report highlights that 44% of global organizations already utilize AI for detecting security intrusions.
Also Read: AI in Cybersecurity a Threat or Not?
AI in cybersecurity establishes inherently secure applications, eliminating user vulnerabilities. By eradicating negative defaults, AI ensures precise issue detection, expedites investigations, and automates response mechanisms. AI-driven solutions, like behavioral biometrics for user verification, foster secure app development, create a safer data ecosystem, and contribute to robust infrastructure.
AI can identify potentially malicious activities and threat actors, enabling organizations to predict and prevent cyber-attacks proactively. Through AI-enabled automated monitoring, systems remain safeguarded 24/7, empowering organizations to protect digital assets preemptively.
Significance of AI in Cybersecurity
The growing complexity of cyber threats, from social engineering to ransomware, challenges conventional defenses’ efficacy in detection and prevention. As organizations grapple with vast data demands analysis for potential risks, bolstering cybersecurity becomes paramount.
“AI is not a silver bullet, but it is a powerful tool that can help us to improve our cybersecurity posture. By using AI to automate tasks, analyze data, and identify patterns, we can free up our security teams to focus on more strategic work.” – John Chambers, CEO of Cisco.
Embracing innovative solutions becomes essential for effectively countering these threats.
Cost Reduction: AI-driven automation significantly reduces costs across cybersecurity operations. Automating routine tasks like log analysis, vulnerability assessments, and patch management diminishes the need for manual intervention, conserving valuable time and human resources. AI’s enhanced threat detection accuracy also drives cost reduction. Traditional security methods often yield false positives or miss threats, leading to wasted resources investigating non-existent issues or overlooking genuine security incidents.
Improved Scalability: Conventional cybersecurity approaches struggle with the immense data volumes in complex, interconnected environments. AI excels in scalability, processing vast data from diverse sources simultaneously. AI algorithms proficiently analyze network traffic logs, system logs, user behaviors, and threat intelligence feeds. This scalability empowers AI to detect subtle cyber threat indicators that might elude human analysts, ensuring a proactive defense stance.
Also Read: AI Integration Roadmap Planning for Cybersecurity Experts
Exploring AI’s Role: 5 Key Applications in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence, designed to mimic human intelligence, holds substantial promise within cybersecurity. AI systems can discern threats, identify novel malware, and fortify the protection of sensitive data, presenting considerable advantages if effectively integrated.
Specific threats slip through undetected, causing significant network damage. To navigate this landscape successfully, businesses must rely on AI and advanced technologies to fortify their cybersecurity defenses in today’s digital era.
This article delves into AI’s manifold applications in cybersecurity, presenting the top 5 use cases for a comprehensive understanding.
1. Advanced Threat Detection and Mitigation
AI excels in threat detection by analyzing diverse data sources for unusual behavior patterns and swiftly identifying potential cyber threats, such as phishing attempts. When a threat is detected, AI triggers real-time alerts and automates incident response actions, limiting the impact of security breaches.
Malware and Phishing Detection
AI-based systems exhibit heightened efficacy compared to legacy methods, achieving security rates of 80% to 92%. These systems differentiate between spam, phishing, and legitimate messages, intercepting suspicious activities and thwarting potential threats.
Security Log Analysis
AI revolutionizes security log analysis by detecting anomalies without known threat signatures. It also identifies potential insider threats by analyzing user behavior across multiple systems.
Endpoint Security
AI-driven endpoint protection dynamically detects threats, including zero-day attacks, by continuously learning from network behavior. It enhances password protection through advanced authentication methods like CAPTCHA and biometrics.
Encryption
AI’s capabilities in breaking strong encryption remain a significant challenge due to the complexity of encryption algorithms like AES and SHA.
Thread Detection in Honeywell
Honeywell’s AI swiftly analyzes industrial control system data, detecting and blocking unusual patterns indicating cyber threats. Continual learning and adaptive responses bolster its capability to recognize and mitigate unauthorized access attempts.
2. Behavioral Analytics for Threat Identification
AI models employing deep learning techniques continuously analyze network behavior, identifying deviations and anomalies. These models self-correct and adapt, enhancing cybersecurity defenses against evolving threats.
User Behavior Analytics in Amazon
Amazon’s AI-powered services like AWS GuardDuty and Inspector revolutionize threat detection by identifying abnormal behavior across various data sources, detecting spikes in API calls, unusual network traffic, and unauthorized access attempts.
3. Real-Time Security Incident Response
AI’s role extends beyond detection, enabling automated responses to diverse cyber threats. Leveraging AI-enhanced cybersecurity solutions allows organizations to optimize incident response times and alleviate the workload on security teams. By analyzing extensive data security and correlating information, AI autonomously generates precise cyber threat responses aligned with technical logs, network traffic patterns, and global threat intelligence.
Advanced Threat Response and Mitigation at Wells Fargo
Wells Fargo‘s cybersecurity strategy centers on an AI-powered threat detection and response platform. This platform harnesses advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze substantial data sets encompassing real-time network traffic, email communications, and files. The AI system identifies patterns and anomalies indicative of malicious activities through this analysis.
Upon detecting potential threats, Wells Fargo’s AI system triggers proactive measures, swiftly blocking malicious traffic or isolating infected files. This immediate response prevents the threat from spreading across the organization’s network, enhancing overall cybersecurity resilience.
4. Proactive Vulnerability Assessment and Management
5. Predictive Threat Intelligence and Analysis
AI significantly contributes to breach risk prediction by providing accurate IT asset inventories encompassing devices, users, and critical system access levels. By amalgamating asset inventory data with threat exposure assessments, AI predicts vulnerable areas prone to cyber breaches.
AI’s diverse data processing capabilities offer security teams a comprehensive view of the organization’s security status. This enhanced situational awareness fosters proactive threat hunting, precise risk evaluations, and prompt incident responses, fortifying the cybersecurity strategy.
Threat Intelligence and Predictive Analytics in PayPal
AI is pivotal in PayPal’s cybersecurity approach, notably in transaction analysis. Given the substantial daily transaction volume, manual fraud detection becomes impractical. AI’s swift processing capabilities efficiently scrutinize each transaction for potential fraudulent indicators.
Additionally, PayPal’s vigilance extends to identifying and blocking malicious websites. AI-driven systems diligently scan websites, identifying malicious content or signs of potential cyber threats and safeguarding users from phishing and scam attempts.
Future Outlook
The future of AI in cybersecurity holds both promise and challenges. AI significantly enhances cybercrime analysis, comprehension, and prevention, instilling greater trust and safety for businesses and their customers. Yet, the intensive resource requirements of AI pose practical challenges, and its potential misuse by cybercriminals heightens concerns. VPNs benefit from AI, leveraging machine learning to shield users from AI-driven online threats.
AI emerges as a critical innovation, augmenting the performance of IT security teams. Cybersecurity training, such as Knowledgehut’s, equips professionals with profound insights into computer networks. The scalability limitations faced by human efforts to secure expansive attack surfaces underscore AI’s crucial role in analyzing threats and bolstering security measures.
Furthermore, AI’s expertise in risk identification, incident response, and preemptive malware detection underscores its potential to fortify security postures. Despite foreseeable challenges, AI remains a driving force propelling cybersecurity, promising organizations a more resilient security framework. For deeper insights, further exploration is recommended.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to psen@itechseries.com]


