According to Capgemini Research Institute, 75% of cybersecurity executives say AI helps them respond faster to breaches. And 69% believe AI is required to respond to cyberattacks effectively. AI revolutionizes cybersecurity, transforming IT professionals’ approach. Advanced AI-powered tools enhance data protection by swiftly recognizing patterns, automating tasks, and detecting anomalies.
According to the latest reports by Dimension Market Research, the Global AI in Cybersecurity Market will reach USD 147.5 billion by 2033. The market is anticipated to register a CAGR of 20.8% from 2023 to 2033.
Ensuring Security Amid AI Evolution
Data privacy and risk management concerns escalate as AI advances for individuals and businesses alike. Regulators are exploring ways to harness AI’s benefits while mitigating potential societal risks. Despite this, comprehensive federal AI legislation is currently absent in the United States.
What implications does this hold for you? How do AI advancements impact your security?
Fortunately, the answer is straightforward: learning new cybersecurity rules is unnecessary. Instead, review your cybersecurity measures, ensuring adherence to best practices in critical areas like passwords, data privacy, personal cybersecurity, and social engineering awareness.
Applying AI to Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence actively monitors, analyzes, detects, and responds to cyber threats in real-time. It analyzes vast amounts of data to detect patterns indicating potential threats and scans the entire network for vulnerabilities to prevent common cyber attacks.
By primarily focusing on behavior patterns, AI establishes a baseline and identifies unusual behaviors to restrict unauthorized access. It aids in prioritizing risks and instantly detecting malware and intrusions.
Implemented effectively, AI is the core of security automation, streamlining operations and freeing up human resources by automating repetitive tasks. It mitigates the risk of human error by minimizing human involvement in tasks and processes.
The Significance of AI in Cybersecurity
As cybercriminal organizations increasingly utilize machine learning, automation, and AI for targeted cyberattacks, the importance of AI in cybersecurity cannot be overstated. The proliferation of threats, including ransomware, poses significant risks to networks.
AI and machine learning empower security analysts by processing vast amounts of data, offering swift insights, and effectively managing daily security alerts and false positives. This enhances team efficiency and productivity, providing an edge against cyber criminals.
The emergence of sophisticated attack vectors such as polymorphic malware and “living-off-the-land” attacks underscores the necessity for modern cybersecurity approaches. Behavior analysis and detection methods are gaining prominence as they focus on identifying malicious behavior rather than solely relying on file-scanning-based anti-virus defenses. When appropriately trained, AI excels in monitoring, detecting, and responding to such malicious behaviors, surpassing human capabilities alone.
Also Read: AI’s Strategic Role in Shaping IT Security
Incorporating AI into Cybersecurity Programs: Best Practices for Leaders
As AI’s role in cybersecurity expands, CISOs and other leaders must guide its integration effectively, ensuring security and efficacy. Here are key strategies for successful implementation:
- Align Strategy with Objectives: Before deploying AI, align its strategy with broader business and security goals. Define outcomes, identify AI’s role in addressing specific cybersecurity challenges, and ensure alignment with overall security strategies.
- Invest in AI Talent: Complement AI with skilled professionals. Recruit experts who understand both cybersecurity and AI technologies. This team will evaluate, implement, and optimize AI solutions effectively. Promote AI literacy to maximize team effectiveness.
- Thoroughly Evaluate Solutions: Diligently assess AI solutions. Consider vendor reputation, model robustness, and commitment to security and privacy. Conduct proof-of-concept trials to gauge integration with existing infrastructure. Ensure alignment with security requirements and regulatory obligations. Mitigate bias through robust data practices and diverse teams.
- Establish Data Governance: Ensure high-quality, diverse, and well-curated data. Develop governance frameworks for data quality, integrity, and privacy. Implement measures for data protection and access control. Choose explainable AI models for transparency.
- Implement Strong Security Measures: Secure AI infrastructure with encryption, authentication mechanisms, and access controls. Regularly update frameworks and dependencies to address vulnerabilities.
Essential Skills for Implementing AI in Cybersecurity
The integration of AI and cybersecurity demands individuals with specialized skill sets. Enterprises and technology firms seek professionals in both domains, capable of effectively applying AI techniques to cybersecurity workflows.
Key roles include data scientists, analysts, and engineers with expertise in machine learning, data modeling, deep neural networks, language modeling, and behavior analysis. Additionally, a strong foundation in cybersecurity principles is imperative.
AI cybersecurity professionals must possess comprehensive knowledge of network security, computer forensics, cryptography, malware detection and defense, and data protection. This multifaceted skill set is essential for successfully implementing AI-driven cybersecurity solutions.
The Role of Industry Standards and Compliance in AI Cybersecurity
Government regulations aren’t the sole drivers shaping AI’s role in cybersecurity; industry-specific standards and compliance frameworks are equally significant. Organizations adhere to these guidelines, which ensure alignment with industry best practices and are subject to continuous evolution.
One pivotal standard is the NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF), launched on January 26, 2023. Developed through collaboration between public and private sectors, it enhances trustworthiness in designing, developing, using, and evaluating AI products and services.
Similarly, the ISO/IEC AWI 27090, currently under development, addresses security threats and failures in AI systems. It aims to deepen organizations’ understanding of security threats to AI systems across their lifecycle and provides strategies for detection and mitigation.
As AI integration in cybersecurity grows, experts stress the urgency of robust, enforceable policies. Advocates call for stringent laws and regulations to govern AI’s ethical and secure use, balancing innovation with necessary regulations as we navigate an increasingly digital future.
AI Applications in Cybersecurity
- Malware detection: AI-powered malware detection applications employ diverse techniques to identify malicious software, including static and dynamic analysis.
- Phishing detection: AI-driven phishing detection solutions utilize machine learning algorithms to scrutinize email content and structure and identify potential phishing attacks.
- Network security: AI-enabled network security encompasses adopting policies, processes, and practices aimed at preventing, detecting, and monitoring unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of computer networks and network-accessible resources.
- Endpoint security: AI-powered endpoint protection employs a dynamic methodology, establishing normal behavior baselines for endpoints and promptly identifying deviations in real time.
- Threat detection: Utilizing AI accelerates threat detection and response, enhancing your network comprehension and enabling swifter identification of potential threats. AI-driven solutions further streamline this process.
Also Read: Cybersecurity Attack Surface Management Trends of 2024
Advantages of AI in Cybersecurity
- Early Threat Detection: AI algorithms, including ML and deep learning models, analyze vast data volumes, identifying patterns for early threat detection. This proactive approach prevents security breaches by spotting anomalies that human analysts might overlook.
- Improved Threat Intelligence: Generative AI automates threat analysis, providing rich insights into potential threats and their behavior. It simplifies the code and network traffic analysis, empowering analysts to understand and address threats efficiently.
- Strengthened Access Control and Password Practices: AI strengthens security measures through advanced authentication mechanisms like biometric authentication. It analyzes login patterns to detect suspicious activities, mitigate insider threats and enhance access control.
- Risk Minimization and Prioritization: AI-powered cybersecurity systems identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks, proactively patching weaknesses to reduce breach risks. Machine learning automates risk assessments, enabling efficient resource allocation and prioritization of mitigation efforts.
- Automated Threat Detection and Response: AI automates threat detection and response processes, blocking malicious IP addresses, shutting down compromised systems, and analyzing emails and web pages for phishing attempts. Real-time monitoring and rapid response times minimize the window for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities, empowering security teams to respond quickly and effectively during incidents.
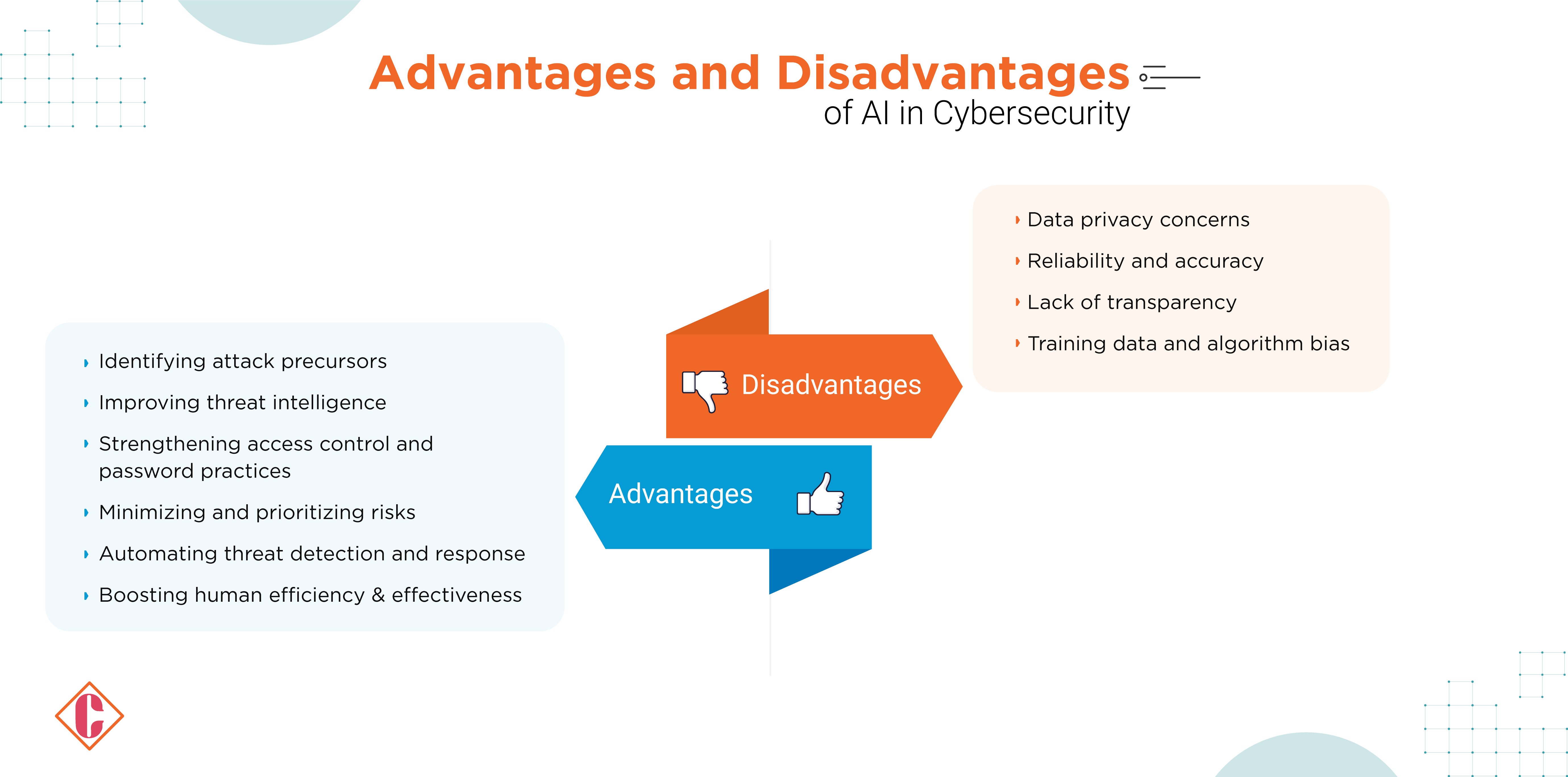
Disadvantages of AI in Cybersecurity
- Data Privacy Concerns: AI systems often require extensive data access, raising privacy risks, particularly when dealing with sensitive personal data. Companies face challenges in balancing user privacy with data utility, necessitating robust AI governance frameworks to mitigate financial and reputational risks.
- Reliability and Accuracy: Despite processing vast amounts of data quickly, AI systems are prone to false positives and negatives, potentially leading to wasted efforts and overlooked threats. Ensuring reliability and accuracy requires investment in data preparation processes to clean and organize datasets, particularly as data poisoning becomes more prevalent.
- Lack of Transparency: Many AI systems, especially deep learning models, operate as black boxes, hindering understanding of their decision-making processes. This opacity impedes cybersecurity experts in validating AI outputs and understanding how AI models arrive at specific decisions, hampering threat identification and mitigation efforts.
- Training Data and Algorithm Bias: Bias in training data and algorithms can significantly impact AI system effectiveness. Training data bias occurs when datasets are not diverse or representative, leading to errors like overlooking certain threats or misidentifying benign behavior as malicious. Conversely, algorithm bias arises from inherent biases in the algorithms themselves, resulting in false positives, alert fatigue, and missed threats.
Also Read: CCPA Essentials: A Guide for IT Security Professionals
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, while AI presents significant opportunities in cybersecurity, it’s crucial to address ethical considerations and implement proper governance to mitigate potential misuse or unintended consequences. AI-based fraud and attack detection systems are expected to remain pivotal in the industry, with developers integrating AI capabilities alongside other cognitive technologies to enhance security protocols. As the proliferation of endpoint devices complicates data flow and increases the difficulty of detecting malicious content, AI’s role in predicting attacks and deploying smart algorithms to recognize such threats becomes indispensable. In essence, AI in cybersecurity serves as a proactive measure to safeguard networks, companies, and production systems from the increasingly sophisticated landscape of cyber threats.
FAQs
1. Will AI dominate cybersecurity?
No, AI will not entirely dominate cybersecurity. While AI will play a significant role, other technologies such as behavioral biometrics, blockchain, and quantum mechanics will also remain prevalent. Human expertise will remain crucial for complex decision-making and problem-solving, including AI’s effective and ethical development, training, deployment, and security. AI is expected to lead to new cybersecurity solutions and careers.
2. Can AI forecast cyber attacks?
Certainly, AI can help predict cyber attacks by analyzing network traffic and system logins to detect unusual patterns indicative of malicious activities and threat actors. However, effective prediction requires training the AI model on a comprehensive data set that accurately represents the current threat landscape and its evolution.
3. What are some examples of AI in cybersecurity?
An instance of AI in cybersecurity is automated cloud remediation. For instance, within the Secureframe platform, Comply AI for Remediation swiftly generates initial remediation guidance as code when a test fails. This enables users to promptly rectify underlying configuration issues in their cloud environment, ensuring compliance with information security requirements.
4. How does AI contribute to threat detection and response?
AI contributes significantly to threat detection and response by analyzing vast data to identify patterns and anomalies that may signify potential threats. AI systems can monitor network activity in real time through machine learning algorithms, enabling proactive threat mitigation and rapid response to security incidents.
5. How can organizations prepare for AI-driven cybersecurity?
Organizations can prepare for AI-driven cybersecurity by investing in skilled personnel who can effectively implement and manage AI systems. They should also prioritize data quality and governance to ensure the accuracy and reliability of AI models. Regular training and updates on emerging threats and AI technologies are essential to stay ahead of cyber adversaries.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]


