As cyber threats grow increasingly complex and frequent, relying on manual network security processes is no longer sufficient. The speed at which vulnerabilities are exploited and new attack methods emerge demands a faster, more reliable approach to network security.
By leveraging automation, businesses can rapidly identify vulnerabilities, configuration issues, and policy gaps, ensuring more consistent security measures and reducing the risk of human error. While we’ve previously examined automation in cloud security, IT/OT integration, and SOC environments, network security automation is a crucial yet often overlooked component.
Why is automating network security so important? How can it boost operational efficiency while minimizing risks? This article explores the core benefits of network security automation, the best tools to invest in, and why it’s essential for organizations looking to stay ahead of ever-evolving threats.
Understanding Network Security Automation: The Essentials
Network Security Automation involves utilizing advanced tools and technologies to automate essential tasks aimed at defending network systems from cyber threats. These tasks can include vulnerability scanning, intrusion detection, incident response, and enforcement of security policies.
The main goal of automation is to minimize manual effort and reduce the time needed to secure networks, while also improving the speed and accuracy of threat detection and response. It ensures consistent application of security policies, reducing human error and strengthening overall security posture.
For organizations with large and complex network infrastructures, managing security manually can be both time-consuming and prone to mistakes. Network security automation becomes invaluable in such environments, particularly in addressing the ongoing shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals.
However, it’s important to note that automation cannot completely replace the need for human oversight. Security experts remain critical in developing security strategies, evaluating risks, and responding to complex threats that require judgment and expertise beyond automation’s capabilities.
How is Network Security different from Endpoint Security?
Network security and endpoint security are both essential components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, but they serve different purposes and offer varying levels of protection.
Network Security refers to the broader set of practices and technologies designed to protect a network infrastructure from a wide range of cyber threats. This includes securing the entire communication network, its devices, and the data that flows through it. Network security often involves tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and encryption protocols to defend against external and internal attacks.
Endpoint Security, on the other hand, focuses specifically on protecting devices (endpoints) that connect to a network, such as laptops, desktops, mobile phones, and IoT devices. The goal is to safeguard these devices from being compromised and used as entry points for attacks. Endpoint security solutions typically include antivirus software, encryption, and device management policies.
While both security measures are crucial, the main difference lies in their coverage. Endpoint security software typically protects about 95% of endpoints, leaving some areas vulnerable. In contrast, network security automation offers comprehensive, 100% coverage across the entire network environment. Ideally, organizations should implement both network security automation tools and endpoint protection software, with the network security automation learning from and complementing the endpoint security to ensure maximum defense.
Also Read: The Arbitrage Opportunity of Small Language Models: Unlocking AI Efficiency and Performance
Why Choose Network Security Automation?
In today’s increasingly complex and dynamic network environments, manual security management is no longer sufficient. Organizations are increasingly turning to network security automation to enhance their security posture, streamline operations, and reduce the burden on their IT teams. As networks grow in scale and sophistication, the risk of human error also rises, making it essential to adopt automated solutions that can provide more reliable and efficient protection.
Network security automation enables continuous security assessments and real-time threat detection, which are critical for defending against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. By automating security tasks, organizations can ensure that security measures are consistently enforced across the entire network, eliminating the gaps often left by manual processes. This proactive approach not only helps in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities faster but also boosts the overall efficiency of security operations.
One of the key benefits of automation is its ability to consistently enforce security policies across all network devices, ensuring compliance with the latest security standards and regulations. This consistency eliminates the variability introduced by manual configurations, reducing the risk of oversight and non-compliance.
Types of Network Security Automation Tools to Improve Efficiency
Network security automation tools are designed to streamline security operations, improve detection and response times, and reduce the manual labor required to maintain a secure network. Below are key types of network security automation tools, along with how they enhance efficiency and reduce human error:
1. Configuration Management Tools
Configuration management tools are essential for automating the setup, maintenance, and modification of network security configurations. These tools ensure that all network devices adhere to corporate policies and compliance requirements. Automation in configuration management eliminates the risk of human error, which is common when manually configuring large networks, where even small misconfigurations can create vulnerabilities.
2. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
SIEM systems aggregate and analyze data across the network in real time to detect potential security incidents by correlating security logs and alerts. These systems automatically identify and prioritize threats, which allows for immediate response, reducing the time between threat detection and mitigation.
3. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) monitor network traffic to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real time. These tools automatically identify patterns that deviate from normal behavior and block malicious traffic or activities.
4. Vulnerability Management Tools
Vulnerability management tools automate the process of identifying, classifying, and mitigating vulnerabilities within network systems and software. These tools scan networks continuously to detect weaknesses, prioritize them based on risk, and automate the deployment of patches or fixes.
Also Read: Making Microsoft SQL Server HA and DR Completely Bulletproof
The Challenges of Automating Network Security at the Infrastructure Layer
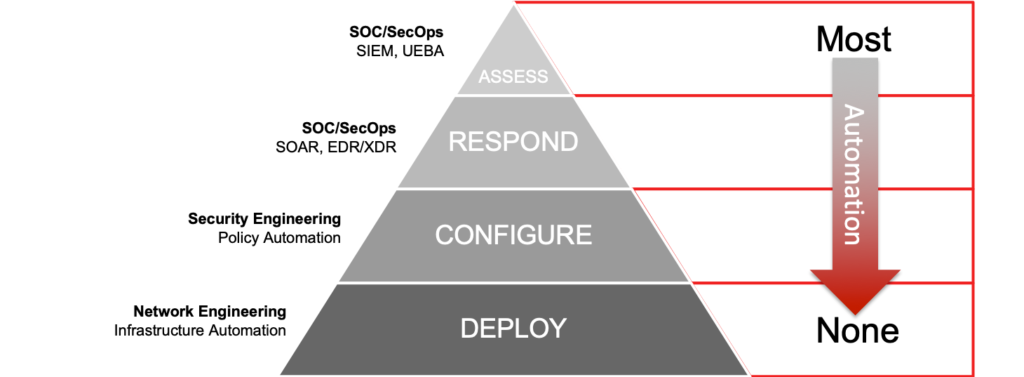
While network security automation has gained significant traction in areas such as threat detection, incident response, and continuous monitoring, it’s not without its challenges. One of the most difficult aspects of automation lies within the Deployment and Configuration layers of the network security protection hierarchy, which forms the infrastructure of an organization’s security architecture.
Although automation tools exist for the Respond and Assess layers, automating the Deploy and Configure layers is still a work in progress. This is where network engineers face a significant challenge: there are no fully integrated solutions or tools readily available that can handle the infrastructure layer out-of-the-box. As a result, organizations are often left to piece together their automation solutions, leading to a DIY nightmare that slows down the adoption of automation at this level.
Conclusion
Network security automation offers transformative advantages, significantly strengthening an organization’s security posture and enhancing operational efficiency. By automating both routine and complex tasks, it minimizes human error—a frequent cause of security vulnerabilities—thereby reducing the likelihood of costly breaches.
Beyond error reduction, automation accelerates the detection and response to security threats, enabling real-time identification and mitigation of risks. This speed is essential in minimizing potential damage and ensuring that an organization remains protected against rapidly evolving cyber threats. Furthermore, automation plays a pivotal role in ensuring regulatory compliance, automatically enforcing security policies and standards across all network devices to meet the latest compliance requirements.
The time and resources saved through security task automation allow IT teams to shift their focus from time-consuming, manual processes to more strategic initiatives. This fosters greater innovation and boosts productivity, driving the overall growth and security of the organization. In an era where cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, adopting network security automation is not just a smart choice—it’s a necessary step toward securing the future of your business.


