With each passing day, we increasingly enter into the digital era where almost everything and anything is done online. From banking to socializing, our ever-increasing reliance on the internet is undeniable. Although the digital revolution has become a blessing in disguise, it is still important to note that this technology has challenges. Cyberattacks and malicious threats have skyrocketed comparatively in recent years; victims’ data has been breached and wealth stolen on the Internet, increasing the incident rate. Cyber insurance has been recognized as the pivotal obligation for companies dealing with Cybersecurity issues.
Also Read: AI Integration Roadmap Planning for Cybersecurity Experts
The skyrocketing demand for cyber insurance has contributed to its being one of the fastest-growing insurance markets. An increasing number of companies in the government and insurance sectors unrelentingly infiltrate daily headlines with information about cyberattacks and have made the government impose strict rules that have made people alert, which in turn has heightened the insurance sector’s awareness of cyber risks. It now goes beyond being a focal subject of IT executives to being a major risk that all red-coded boards ought to have under their focus.
As per the BCG Survey reports, almost 99% of the boards of directors gradually resolve to fight cyber risk, which has become one of the major risks, as so as 80% of CEOs point out cybersecurity as the number one obstacle to corporate growth, — hinting to its great importance Through enforcing stricter regulations, including their global notification demands with heavy penalties, corporations are now required to put in place effective risk management capabilities against the changing risk environments, and they can rely on the help of insurance companies.
Cyber Insurance Explained: Protecting Businesses from Online Threats
Cyber Insurance, also known as Cybersecurity insurance, is a specialized underwrite designed to help businesses afford the risk emanating from cybercrimes such as cyberattacks and data breaches. It compensates for Internet as well as electronic-based risks that impact IT operations, information security, and related rules. However, this category of insurance is of particular importance since typical commercial liability policies are inadequate for the innovative risks that are swarming in this era.
In the same way as physical risks and natural calamities, insurance defends companies financially from cyber attacks and cyber insurance products. Its origins can be traced back to the end of the 1990s, when a steep rise in cyber risks started to evolve, facilitated by the technology dependency phenomenon. Initially, people were insured for data breaches and computer attacks, but cyber insurance has now turned into a wide variety of cybercrimes, like ransomware, cyber extortion, social engineering attacks, and disruptions in business activity due to cybersecurity issues.
The cyber insurance cover is compared with the errors and omissions (E&O) cover, which protects against errors or faults that a company may have in an event where the services they offer are affected. Concurrently, not all cyber insurance policies have E&O included as a unique line but tend to be offered differently. Unlike E&O insurance, which is mainly directed to company service problems, cyber insurance covers third-party data breaches, such as customer card information. It helps protect the company from the increasing cyber-attacks in today’s digital world.
Cyber insurance is the fastest-growing line of business in the insurance industry. A combined assault of daily front-page news items about cyberattacks, increasing government regulation, and insurance industry awareness is raising the cyber risk profile. According to surveys, 99 per cent of all boards of directors discuss cyber risk on a regular basis, and 80 per cent of CEOs consider cyber risk as the number one threat to business growth. As more regulations are adopted, the corporate sector is looking to insurance to offer solutions that can effectively deal with this emerging risk. – Daniel M. Hofmann, Senior Advisor Financial Stability and Insurance Economics, The Geneva Association
Key Features of cyber insurance are:
- Safeguarding against various cyber risks, including viruses, cyber threats, and cyber crimes, whether intentional or otherwise.
- Indemnification of both monetary and legal costs incurred due to various cyber incidents.
- A safety net that even smaller-scale entities can access to face the blow of a cyberattack and minimize losses suffered due to data breaches or leaks of proprietary information.
- Cybersecurity insurance policies are easily available for purchase online and are commonly sold by insurers who already offer other forms of insurance like Errors and Omissions (E&O) insurance, business insurance, general insurance, and commercial property insurance.
Cyber Insurance Coverage Segmentation into Diverse Types of Coverage
1. First Party Expenses:
- This is mandating the compensation of insured entities, resulting in their initial financial losses.
- It has one non-monet for mitigation costs, recovery costs, risks of systems damage and business interruption claims.
2. Regulatory Investigation Coverage:
- Under this coverage, the shareholders meet the expenses connected with looking into the investigations under the regulatory framework.
- It covers all items related to legal payments, bureaucratic expenses, and any other costs associated with professional account auditing services.
3. Privacy and Data Liability Claim:
- This policy is extended to include coverage, which ranks as third-party legal liability ascribed due to an error or a mistake.
- It covers losses associated with privacy infringement, data breaches, network security violations, intellectual property value protection and reputation damage.
4. Crisis Management Expenses:
- This piece will review the all-encompassing financial coverage that is made for cases of losses or transactions made when a crisis is on.
- This involves an outlay of money for forensic audits, security consultation, reputation damage control, credit reporting and identity theft monitoring, ransomware, psychological therapy and relief to the victims by working together with the service providers.
Today’s Cyber Risk Environment
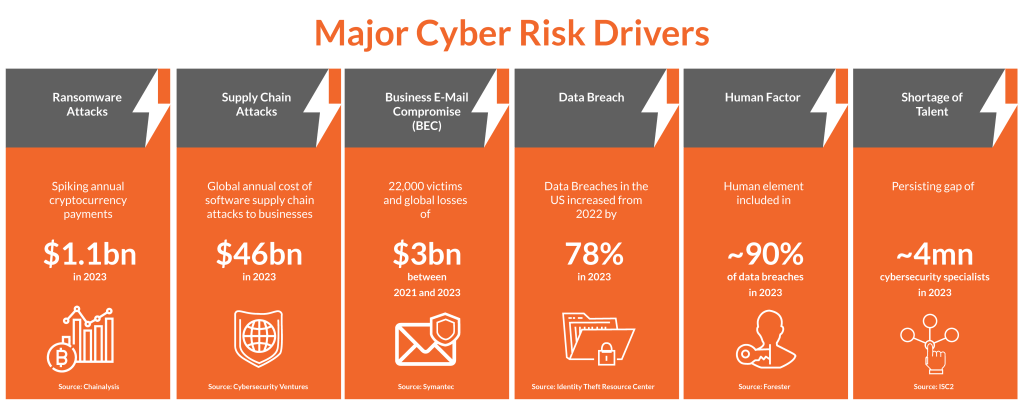
Gathering true statistics on cybercrimes appears challenging for organizations and authorities, given the assumed underreporting, where just a part of the total number of crimes is accounted for. An example is the BKA (German Federal Criminal Police Office), which estimates a range of 91.5% that crime in cyberspace remains unsolved and unexposed. According to Statista, the estimations show that the figure for annual global cybercrime spending will expand fromUS$8.15 trillion in 2023 to US$13.8 trillion by 2028.
Trends in Cyber Insurance Market
In 2023, the global market for cyber insurance was valued at US$14 billion, nearly double the expected growth to an estimated US$29 billion by 2027, according to Munich Re. Various factors drive this growth: increased awareness of the increase in frequency and complexity of cyber-attacks, along with financial impacts; more stringent regulatory requirements, as evidenced by the impending implementation of the Network and Information Security Directive (NIS2) in October 2024, which further highlights the need for robust cybersecurity measures; and the dynamic state of the digital landscape, driven by continuous technological improvements and digitalization in industries.
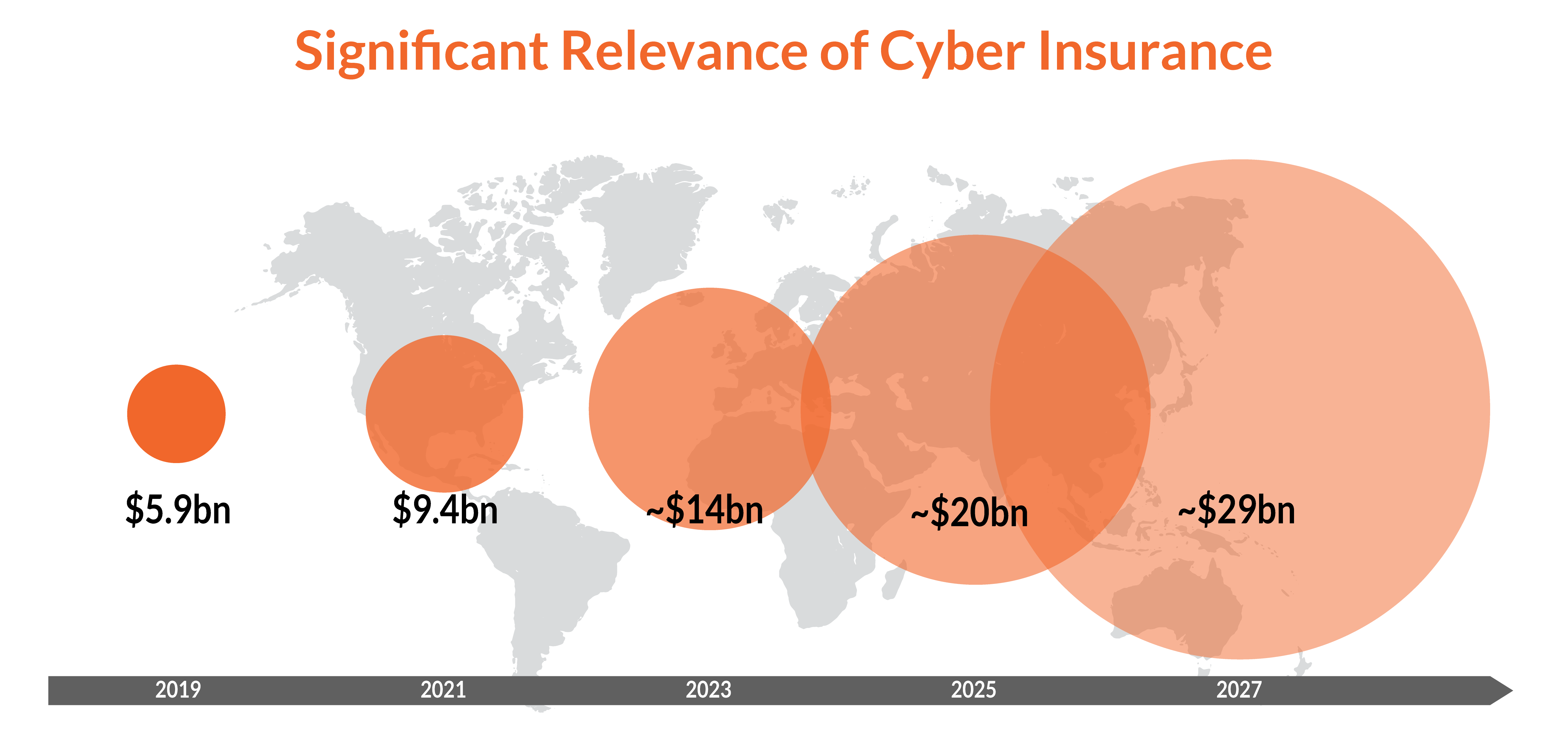 The business increasingly recognizes the need to implement cyber insurance as a component of comprehensive risk management strategies and, thus, the growing demand for cyber insurance. In addition to increasing cybersecurity requirements, supply chain partners are increasingly mandating concrete cyber insurance coverage, and many others are following suit.
The business increasingly recognizes the need to implement cyber insurance as a component of comprehensive risk management strategies and, thus, the growing demand for cyber insurance. In addition to increasing cybersecurity requirements, supply chain partners are increasingly mandating concrete cyber insurance coverage, and many others are following suit.
Despite the significant growth in the cyber insurance market over the last five years, a significant gap exists between economic losses and insured losses. Although reinsurers and even the capital markets have shown interest in cyber risks, a large segment of risks remains uninsured. Interestingly, large corporations form a prominent segment in the cyber insurance market, leaving small and medium-sized enterprises to stand alone and absorb their cyber risks.
One of the greatest challenges for insurers is bridging the gap between economic losses and insured losses. Risk dynamics within a digitized economy mean more risks must be insured. In this respect, insurers are important in covering comprehensive risks and providing innovative solutions to protect the digital landscape and instill resilience in the economy and society.
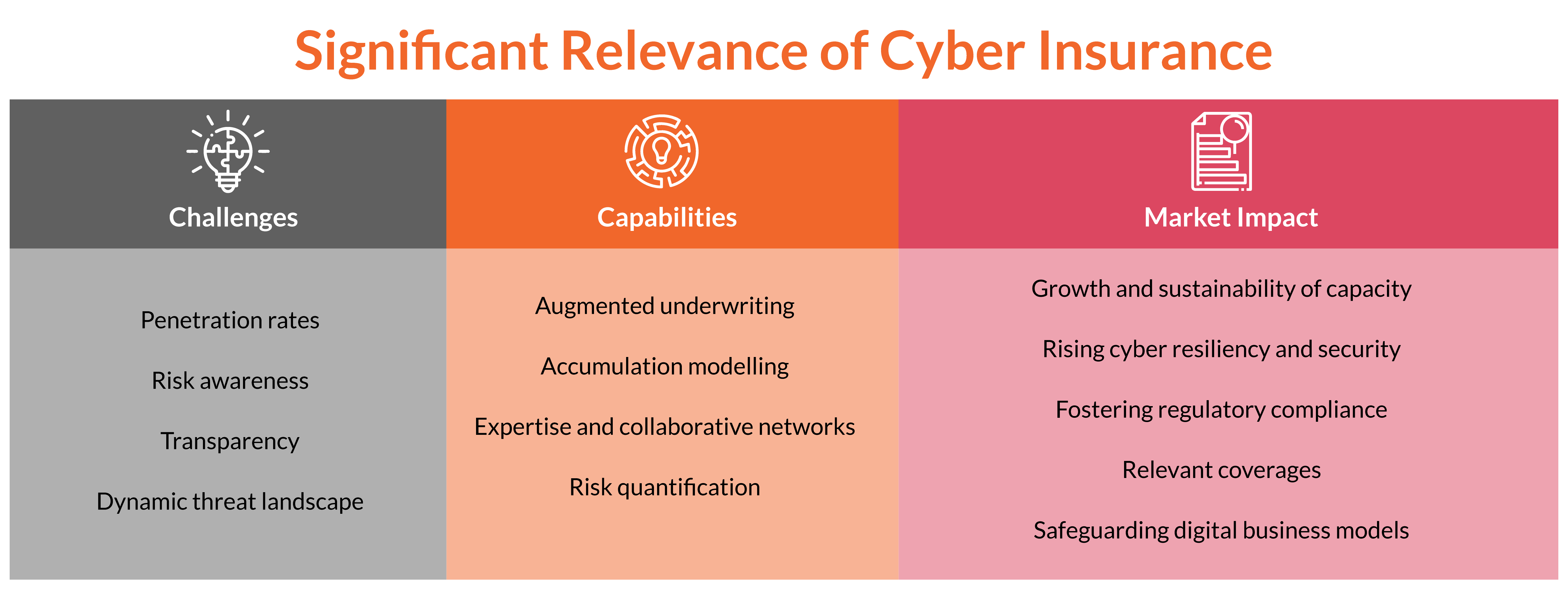
Munich Re continues to uphold its responsibility to address clients’ and insureds’ evolving needs and to meet growing cyber insurance coverage needs. As a reliable partner in risk management, Munich Re continues to prioritize sustainability and sufficiency in its product portfolio. This ensures that insurance cover remains robust and resilient in the face of emerging cyber threats.
Cybersecurity Breaches: A Double-Edged Sword for Finances
When cyber attacks occur, the financial impact can be disastrous. The following are how:
- Loss in Revenue: A cyber attack can bring your operations to a screeching halt, depriving the company of the loss of significant revenue, especially for small businesses.
- Reputational Damage: Trust is hard-earned and easily lost. A cyber breach may drop customer confidence, taking your business years and years to get out of the rat race with a darkened brand.
- Legal Issues: If customer data is compromised, litigations may crop up, and costs accrue for its defense and even settlements.
- Fines from Regulators: If customer data is breached, failure to observe necessary data protection regulations may attract heavy fines from governmental departments.
According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach for a company in 2020 stood at around $3.86 million. These incidents cause not only major turmoil in the financial world but also have enduring implications for the sustainability and reputation of the business.
How Can Cyber Insurance Protect against Cyber Attack Costs?
Let’s explore the value of buying cyber insurance in this digital age. Have you ever considered how your business would deal with a cyber attack?
Imagine a financial safety net against the risks of being online. It can help to pay immediate costs involved in an attack, such as system repairs and restoration, which can very quickly become very expensive. Yet, this is not all. Lawyers’ fees can soar, especially if customer-sensitive data is under attack. Add to that regulatory fines, which depend on where you are.
It does not end there. There is also the less tangible yet equally critical impact on your business. Take, for example, lost revenue due to system downtime or customer trust lost – things that are difficult to quantify but are critical to address.
For example, data from the Ponemon Institute says that the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was approximately $3.86 million, which is a huge financial drag, especially for small businesses. Without cyber insurance, such financial implications would be debilitating.
So, the question is, how prepared is your business to deal with these digital challenges? Maybe it’s time to delve into cyber insurance coverage to measure your risk management.
Top Cyber Insurance Providers to Mitigate Financial Risks
#1 BitSight
BitSight, a leading cybersecurity rating company, analyzes leading firms across several sectors, among which are companies, government agencies, and educational institutions. BitSight’s data and insights equip insurers, investors, enterprises, and governments across the world with the ability to make well-rounded, risk-based decisions.
In pursuit of increased cyber risk management capabilities, The company has recently formed a strategic partnership with Marsh McLennan, a well-known professional service company that specializes in risk, strategy, and people solutions. They are able to combine BitSight’s Security Ratings, data, and analytics with Marsh McLennan’s Cyber Risk Analytics Center. Through this partnership, they will assist organizations in understanding, measuring, and managing their posture in terms of cybersecurity, and in turn enable proactive risk mitigation strategies.
#2 Prevalent, Inc.
Prevalent, Inc. leads the way in managing vendor risk and cyber threat intelligence analytics, offering advanced technologies and highly automated services to help organizations mitigate security threats and risks associated with third and fourth parties. Specializing in vendor risk management for the insurance industry, it helps insurance companies reduce third-party risks and simplify compliance reporting. Through real-time insights on financial, business, cyber, and data privacy, Prevalent’s solutions automate third-party risk assessments, helping security and risk teams minimize risk exposure and ensure full compliance.
#3 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Cisco Systems, a prominent multinational technology conglomerate headquartered in the United States, collaborates with industry leaders such as Apple, Aon, and Allianz to address cyber risks comprehensively. Together, they offer a holistic approach to cyber risk management, integrating cutting-edge security technology, secure devices, cybersecurity expertise, and enhanced cyber insurance solutions.
In February 2018, Cisco, Apple, Aon, and Allianz unveiled a groundbreaking cyber risk management solution tailored for organizations. This innovative solution encompasses improved cyber insurance coverage from Allianz, cyber resilience assessment services from Aon, and state-of-the-art technology from Cisco and Apple. Designed to cater to diverse enterprises, the solution aims to bolster organizations’ ability to manage and defend against prevalent cyber threats, particularly ransomware and other malware-related attacks, which pose significant risks in today’s digital landscape.
#4 Allianz SE
Allianz SE is a highly recognized multinational financial services company based in Germany. It operates worldwide and offers a wide range of insurance and asset management solutions. In the area of cyber insurance, the company provides Allianz Cyber Protect, a fully complete insurance product that addresses organizations in need of data breaches or cyber incidents. Such coverage includes the common costs of cyber incidents and provides access to Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty (AGCS) expert partners.
In late June 2022, Allianz announced a new long-term arrangement with Coalition, a leading U.S.-based cyber insurance and security company. In this arrangement, Allianz agrees to long-term capacity for Coalition’s U.S. cyber insurance programs and to lead Coalition’s U.K. cyber program upon its launch.
#5 Microsoft Corporation
Microsoft Corporation, a multinational technology corporation based in the United States, develops a wide range of software and hardware for computers, consumer electronics, and associated services. On September 29, 2021, Microsoft announced its strategic partnership with At-Bay, a leading cyber insurance company, to develop data-driven cyber insurance for its clients. Within this collaboration, At-Bay carries out comprehensive assessments of the cyber risk profile of each insured company, providing actionable insights to improve its security posture. Through this partnership, Microsoft hopes to promote the development of advanced, data-driven cyber insurance products in the insurance industry, aided by its advanced security offerings to enhance overall cyber risk management.
Benefits that Cyber Insurance offers
1. Expert Advice & Support
- 24/7 hotline access for cyber insurance provides the first available support in the event of a cyberattack.
- It connects businesses to cyber experts for crisis management and forensic investigation for post-breach remediation and prevention.
- Crucial for businesses to stay informed and understand how to recover from cyber threats, guesswork and lack of expertise may cause even more damage.
2. Financial Protection
- Cyber insurance is a means to offset financial losses incurred as a result of a cyberattack.
- Allows businesses to offset costs such as professional services, extortion liability, system restoration, and business interruption losses.
- Businesses must avoid the heavy financial burden of recovery and reinvest the funds to boost their cybersecurity defenses.
3. Data Breach Cover
- Cyber insurance links businesses to professionals who can survey, restore, and secure data compromised during a cyberattack.
- It is critical for businesses to recover from the impacts of data breaches, minimize data theft, and avoid ransom payments.
- Brings businesses protection from expensive data retrieval costs and safeguards sensitive information.
4. Reputation Defence
- Cyber insurance offsets costs associated with public relations to mitigate the reputation damage caused by a cyberattack.
- It enables businesses to maintain trust with clients and customers, particularly for businesses whose reputation is a potential source of income.
- Protects businesses from potential lawsuits and legal expenses arising from data breaches, ensuring speed in reputation recovery.
5. Ideal Cybersecurity Strategy
- Cyber insurance complements an organization’s already implemented cybersecurity strategy and serves as the last line of defense against cyberattacks.
- Brings peace of mind and financial security that allows businesses to operate confidently.
- Enables cybersecurity improvement initiatives and awareness efforts that would reflect a business has commitment toward protecting its clients and customers’ data.
FAQs
1. What is Covered by a Cyber Insurance Policy?
A cyber insurance policy shields organizations from the expenses associated with internet-based threats impacting IT infrastructure, information governance, and policy, often not encompassed by standard liability policies or conventional insurance offerings.
2. Understanding Cyber Insurance and its Functionality
Cyber insurance operates similarly to other insurance types, with numerous providers offering policies alongside business insurance options like errors and omissions, liability, and property insurance.
3. Exclusions from Cyber Insurance Coverage
Cybersecurity insurance policies typically exempt issues attributable to preventable actions, human error, or negligence.
4. Cyber Defense vs. Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance should not substitute effective cyber risk management. While essential for mitigating potential cyberattack damages, it should complement existing security measures and technologies within a comprehensive risk management strategy.
5. Common Exclusions in Cyber Insurance Policies
Common exclusions from cyber insurance policies include bodily injury, property damage, intentional misconduct, ongoing legal proceedings, government orders, personal negligence leading to financial loss, theft of tangible property, loss of cryptocurrency, and more.
6. How to procure Cyber Insurance?
Companies seeking cyber insurance must first undergo a security audit conducted by the insurer’s inspectors under IRDAI guidelines. Following the audit, insurers provide coverage details, terms, and premium amounts based on the company’s annual revenue and susceptibility to cyber threats.
Conclusion
Cyber insurance can be a key component of cyber risk management; it plays an important role to the extent that it is one of the steps to mitigate financial risks from cyber-attacks. It is still only one component of the whole approach to risk management. Customer education and engagement, with the key decision-makers involved, is paramount. More importantly, a Chief Risk Officer (CRO) and a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) are vital, especially if they are cybersecurity champions as the highest organizational priority. Although there are additional problems, including concerns over incomplete risk models and the threat of system-wide attacks, more research is needed to improve market understanding and develop effective solutions to developing cyber risks. On that basis, a better understanding of its market dynamics will position the industry to better serve organizations in navigating the complex landscape of cyber risk and insurance.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]


