Red Hat Revolutionizes Telecom Industry’s Adoption of Open RAN Solutions with NVIDIA GPU Support on Red Hat OpenShift
Red Hat, a leading provider of open-source solutions, has unveiled a groundbreaking initiative to expedite the telecom sector’s transition to open radio access network (RAN) solutions. This strategic move involves the integration of NVIDIA GPUs for 5G virtualized RAN (vRAN) deployments on Red Hat OpenShift, facilitating containerized RAN implementations on standard servers across any cloud environment.
Leveraging NVIDIA GPUs within the Red Hat ecosystem eliminates the necessity for specialized hardware, paving the way for streamlined deployments on Red Hat OpenShift utilizing standard Kernel. This innovative approach drives down the total cost of ownership (TCO) for clients. It fosters rapid network rollouts across diverse cloud infrastructures while laying the groundwork for scalable multi-tenancy and RAN-as-a-service offerings.
The collaboration between Red Hat and NVIDIA underscores a shared commitment to empowering service providers with cutting-edge edge computing capabilities and virtualized RAN functionalities. According to a recent ACG report sponsored by Red Hat, the convergence of 5G core and RAN edge computing on a unified horizontal infrastructure unlocks significant TCO advantages throughout the network ecosystem.
Moreover, the integration of NVIDIA GPUs through the Red Hat-certified NVIDIA GPU Operator enhances the computational capabilities of Red Hat OpenShift, enabling seamless execution of high-performance computing tasks such as machine learning (ML) workloads and RAN applications on the same OpenShift node. This integration heralds a new era of efficiency and scalability in telecom infrastructure management, propelling service providers towards the forefront of technological innovation in the 5G era.
Enhancing Telco Capabilities with Location-Based Services
This partnership equips providers to develop, deliver, and support location-aware applications and services, reducing delays and disruptions in 5G networks. Through Red Hat’s virtualized RAN (vRAN) solutions, telecom companies can achieve scalability and operational efficiency in distributed cloud environments.
Unlocking Growth Potential with 5G Network-as-a-Platform
5G offers communication service providers (CSPs) new avenues for monetization and expansion through a network-as-a-platform model. The end-to-end (E2E) 5G network architecture includes modern components such as Next-Generation Radio Access Network (NG-RAN), incorporating options like Traditional New Radio and disaggregated RAN. It also encompasses multi-access edge computing (MEC), 5G core service-based architecture (SBA), and IMS core and application services layer transitioning into the service-based interface (SBI). These elements are built on an innovative AI/ML-enabled cloud-native telco cloud infrastructure.
Revolutionizing RAN Architecture for Enhanced Efficiency
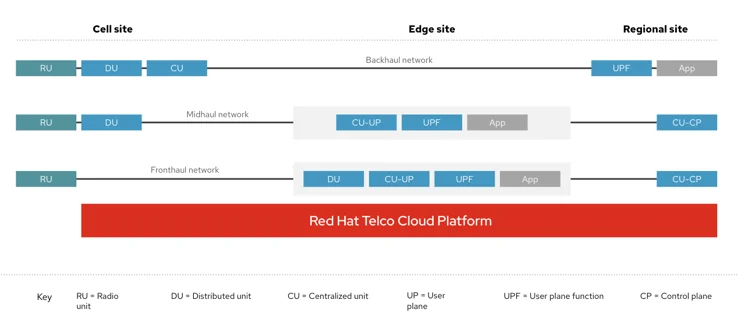
The shift from traditional RAN setups, dominated by proprietary vendors, necessitates addressing the intricacies of BaseBand Unit (BBU) architecture. Red Hat and NVIDIA’s collaborative solutions involve a radical redesign, particularly focusing on virtualizing the BBU. This transformation entails bifurcating the BBU’s functions into two distinct components: the Centralized Unit (CU) and the Distributed Unit (DU).
The DU assumes responsibility for critical real-time processing tasks previously handled by the BBU, such as MAC scheduling, error correction, beamforming, and modulation. Conversely, the CU oversees management and control-related functions. To meet stringent latency requirements, the DU is strategically positioned near the Radio Unit (RU), connected via the Fronthaul network utilizing a Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI) for efficient sample transport.
Recognizing the differing latency tolerances, CUs can be farther away from the RU and DU, often centralized in edge locations. This architecture enables the pooling of multiple CUs for streamlined management. The connection between CU and DU, termed Midhaul, is facilitated through interfaces like F1-C and F1-U.
 Standardizing RAN Virtualization with O-RAN ALLIANCE
Standardizing RAN Virtualization with O-RAN ALLIANCE
Acknowledging the complexity of RAN virtualization and the imperative of vendor interoperability, O-RAN ALLIANCE has spearheaded efforts to establish standardized models for classifying and orchestrating RAN components. This standardized approach ensures vendor neutrality, facilitating efficient slice management, scalability, fault tolerance, and seamless upgrades.
Empowering 5G RAN Innovation with NVIDIA Aerial™ SDK
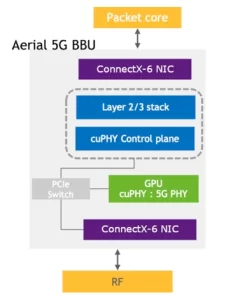
The NVIDIA Aerial™ SDK introduces a comprehensive 5G wireless RAN solution featuring inline L1 GPU acceleration for 5G New Radio (NR) Physical Layer (PHY) processing. It offers a full-stack framework facilitating gNB integration at Layers 2 and 3 (MAC, RLC, PDCP), coupled with robust manageability and orchestration capabilities. Moreover, the Aerial SDK extends support to non-5G signal processing applications, enhancing its versatility.
This groundbreaking SDK streamlines the development of programmable and scalable software-defined 5G RAN PHY, comprising two key components:
- CUDA Baseband (cuBB): The NVIDIA cuBB SDK empowers GPU-accelerated 5G signal processing, notably cuPHY for Layer 1 5G PHY. By harnessing the power of high-performance GPU memory, cuBB delivers unparalleled throughput and efficiency, consolidating all physical layer processing tasks within the GPU.
- DOCA GPUNetIO: This library facilitates GPU-initiated communications, enabling CUDA kernels to interact seamlessly with the DOCA GPUNetIO library. By leveraging GPUDirect-capable network cards such as NVIDIA ConnectX-6 DX or A100X converged accelerators, GPUNetIO facilitates efficient packet transmission and reception, enhancing overall network performance.
Enhanced 5G PHY Processing with cuPHY
 cuPHY comprises a GPU-accelerated 5G PHY layer software library and SDK examples, facilitating GPU-offloaded 5G signal processing for heightened efficiency and performance.
cuPHY comprises a GPU-accelerated 5G PHY layer software library and SDK examples, facilitating GPU-offloaded 5G signal processing for heightened efficiency and performance.
cuPHY-CP serves as the control-plane software, bridging the gap between the layer 1 cuPHY and upper layer stacks, ensuring seamless communication and coordination.
NVIDIA Aerial implements a comprehensive inline offload of the 5G PHY layer (layer 1), leveraging two key innovations: GPUNetIO and GPU Direct RDMA driver within the Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK). These advancements optimize layer 1 processing, delivering superior performance and real-time capabilities on the GPU.
By fully offloading layer 1 to the GPU and eliminating CPU interaction, the need for a real-time kernel running on the CPU is obviated. Consequently, a Linux real-time kernel is only required in the CPU if any portion of layer 1 processing is conducted therein, a scenario not applicable to Aerial’s GPU-optimized solution.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of Red Hat and NVIDIA’s collaboration in RAN architecture?
Red Hat and NVIDIA’s collaboration marks a significant milestone in the evolution of RAN architecture, particularly in the context of 5G networks. Integrating NVIDIA GPUs with Red Hat OpenShift aims to accelerate the adoption of open RAN solutions, offering increased flexibility, scalability, and operational efficiency to telecom providers.
2. How does integrating NVIDIA GPUs with Red Hat OpenShift impact the deployment of virtualized RAN (vRAN) solutions?
Integrating NVIDIA GPUs with Red Hat OpenShift enables containerized deployment of RAN solutions on industry-standard servers across any cloud environment. This eliminates the need for bespoke hardware, reduces total cost of ownership (TCO), and streamlines network deployments, facilitating the transition towards virtualized and cloud-native RAN architectures.
3. What are the key benefits of utilizing NVIDIA GPUs with Red Hat OpenShift for RAN deployments?
By leveraging NVIDIA GPUs within the Red Hat ecosystem, telecom providers can harness GPUs’ computational power and efficiency for various RAN functionalities, including signal processing, machine learning (ML), and AI-driven optimizations. This results in enhanced performance, reduced latency, and improved scalability, ultimately leading to a more robust and agile network infrastructure.
4. How does the collaboration address the challenges of RAN virtualization and vendor interoperability?
The collaboration between Red Hat and NVIDIA focuses on standardizing and optimizing RAN virtualization, thereby addressing interoperability challenges commonly encountered in multi-vendor environments. By adhering to open standards and leveraging GPU-accelerated technologies, the collaboration facilitates seamless integration, management, and orchestration of virtualized RAN components, ensuring compatibility and interoperability across diverse network architectures.
5. What role does the O-RAN ALLIANCE play in the context of RAN virtualization and standardization?
The O-RAN ALLIANCE is a key industry consortium promoting open, interoperable RAN architectures and specifications. Through collaborative efforts with industry stakeholders, including telecom providers, vendors, and technology partners, the O-RAN ALLIANCE works towards defining standardized models for RAN virtualization, cloudification, and orchestration. These efforts align with the broader objectives of enhancing network flexibility, scalability, and innovation in the era of 5G and beyond.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]


