Cloud computing is rapidly reshaping the landscape of banking and finance. Recent studies, such as the O’Reilly survey, reveal that over 90% of organizations across various industries are embracing cloud technology, marking a significant increase from previous years. However, the banking sector has been slower in adopting this transformative technology.
Despite the increasing demand for seamless digital experiences from consumers, the banking and financial services industry has lagged in meeting these expectations. This reluctance to embrace digital transformation can impede institutions from effectively serving their customers. Recent surveys indicate that consumers now place equal importance on the experience provided by a company as they do on its products and services, with 59% expecting higher standards of customer service than before.
This underscores the urgent need for financial institutions to leverage modern technology to enhance customer experiences while reducing operational costs. Many institutions, however, face challenges in achieving this due to the complexity of integrating disparate data sources and modernizing outdated systems.
There’s a growing recognition within the industry of the necessity to modernize. Reports from Gartner reveal that application modernization is a key priority for cloud adoption in banking and investment services. Notably, 70% of banking respondents anticipate increasing their cloud investment in 2022.
Cloud computing is emerging as a pivotal focus for IT leaders, executives, and board members alike. It has the potential to catalyze enterprise transformation, fundamentally altering how financial institutions operate in the future. As the industry evolves, understanding the role of cloud computing becomes paramount in driving innovation and maintaining competitiveness.
Recommended: Top 10 Cloud Reporting Tools for CIOs to Consider in 2024
Power of Cloud Computing for Future Banking Frontiers
The banking landscape is undergoing significant transformation, driven by evolving consumer expectations, emerging technologies, and alternative business models. In anticipation of the Bank of 2030, strategies must be devised to adapt to this evolving environment. Cloud computing is emerging as a focal point for chief information officers, C-suite executives, and board members.
Leaders in banking and capital markets increasingly view the cloud as more than just a technological solution; it represents a destination for storing data and applications and accessing advanced software via the internet.
Cloud can be a catalyst for enterprise business
transformation; a potential game-changer for how FSI organizations will operate in the future. – Deloitte
Major public cloud providers offer a plethora of innovative products and services, enabling banks to implement business and operating models that enhance revenue generation, customer insights, cost containment, product delivery efficiency, and the monetization of enterprise data assets. Furthermore, the cloud presents a significant opportunity to harmonize organizational operations by breaking down silos across various functions such as risk management, finance, regulatory compliance, and customer support. By consolidating vast datasets in one location, organizations can leverage advanced analytics to gain integrated insights.
While initially recognized for its cost-effectiveness and agility, bank leaders are now exploring how cloud computing can be leveraged in both strategic and operational domains. Specifically, they are considering leveraging the cloud to create new business frontiers and optimize organizational efficiencies. By strategically applying cloud technology, banks aim to enhance overall business performance and deliver greater shareholder returns.
Maximizing Value in the Finance Sector through Cloud Computing
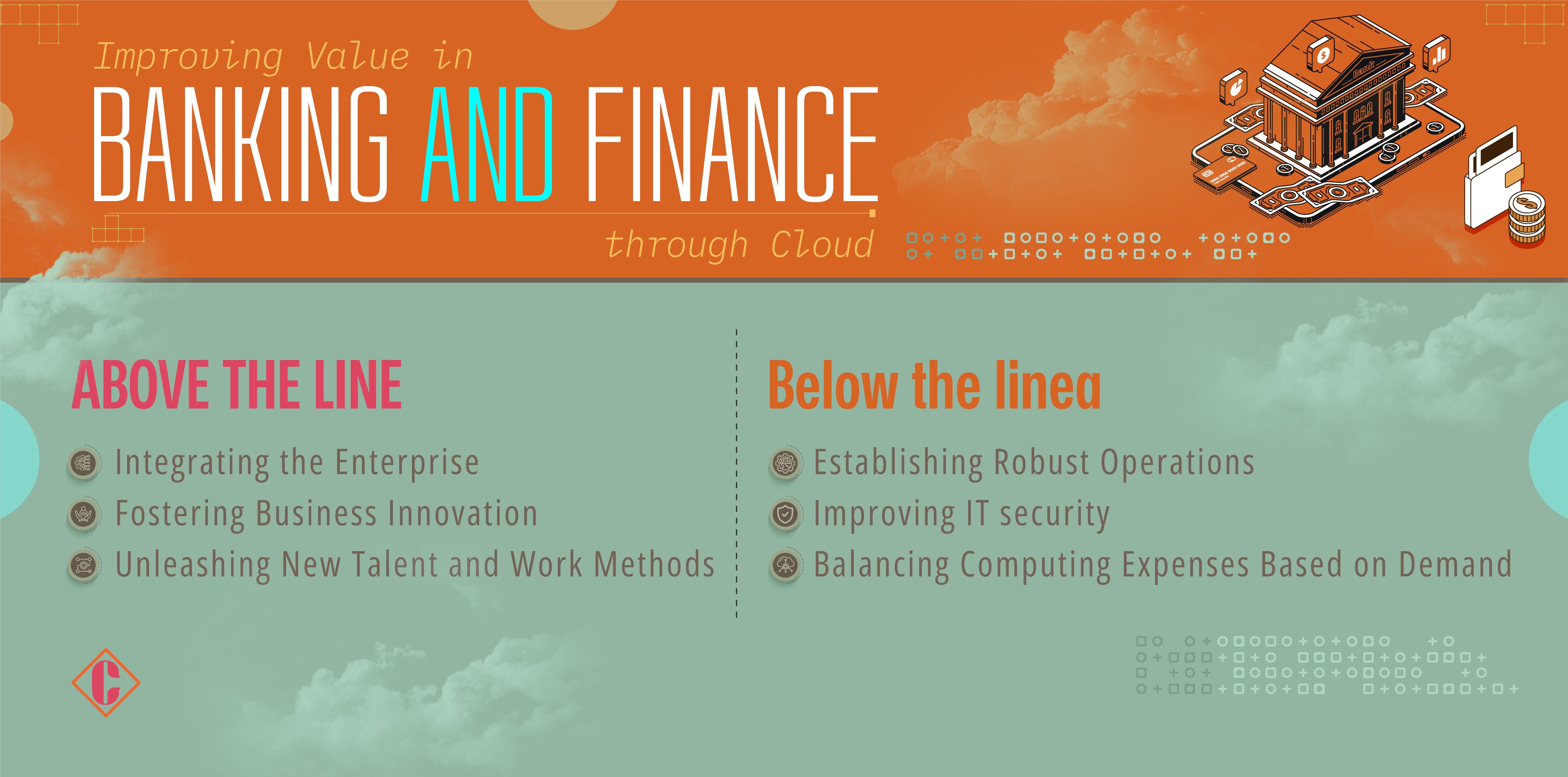 Unlocking New Business Frontiers: Above the Line
Unlocking New Business Frontiers: Above the Line
Cloud transformation unlocks critical sources of value for banks, enabling advancements in new business frontiers.
Integrating the Enterprise
- Facilitates better integration of business units by sharing data, leading to more integrated decisions and faster resolution of customer issues.
- Creates common, interconnected data sets, enabling deeper insights and collaboration through shared platforms and tools, thus accelerating decision-making processes.
Fostering Business Innovation
- Empowers innovation and strategic initiatives to enhance customer experiences, develop new offers, streamline operations, and manage talent by leveraging tools like machine learning, IoT platforms, AR/VR, and natural language processing.
- Utilizes new capabilities to increase revenue, reduce costs, standardize operations, and improve talent retention.
Unleashing New Talent and Work Methods
- Aligns technology with the needs of business units to attract new talent and foster innovative work methods.
- Provides access to ecosystems with new skill sets, fostering process improvements such as automation and human augmentation for increased productivity and organizational integration.
Optimizing the Organization: Below the Line
Cloud transformation also offers significant benefits in optimizing organizational efficiencies.
Establishing Resilient Operations
- Enhances overall resilience by enabling rapid responses to physical outages and disruptions.
- Shifts from reliance on single data centers to replicating data and application services across multiple centers or regions.
Improving IT Security
- Utilizes cloud providers with stringent security standards to enhance IT security.
- Ensures secure environments, comparable to or surpassing on-premises security, through proper implementation and skilled security management.
Balancing Computing Costs as Needed
- Transforms tech spending from heavy upfront capital investments to operational-based models.
- Enables rapid response to market shifts or changes in financial priorities.
- Captures cost efficiencies through dynamic cloud pricing, adjusting computing capacity as required and facilitating precise spending control.
Leveraging Cloud Computing in Banking
Fraud Detection:
Banks leverage cloud computing to analyze vast volumes of data from diverse sources, enhancing their ability to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. This proactive approach enables financial institutions to identify suspicious behavior before it causes any harm.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Cloud-based CRM systems empower banks to manage client interactions and data effectively. This capability allows financial organizations to track customer interactions seamlessly across different channels and times. Additionally, employing the right cloud solutions enables banks to provide personalized services tailored to individual customer needs and preferences.
Data Analysis:
Banks are increasingly turning to cloud computing for advanced analytics to gain insights into patterns and trends in customer behavior. By analyzing how customers interact with financial products, banks can develop innovative solutions that better meet customer demands than ever before.
Cloud Deployment and Operating Models for Financial Services
Deployment Model:
Private cloud: Private infrastructure is operated for a specific bank type. This infrastructure is self-managed by the banks from the premises itself. It gives higher control and increases flexibility therefore it is recommended for banks to host their services from a private cloud.
Public cloud: Public infrastructure is open for the entire banking industry. It allows to share and is owned by the organization which sells the cloud services. It allows banks and financial businesses to reach economies of scale.
Hybrid cloud: Hybrid infrastructure is composed of both private and public clouds that operate for their business use case.
Operational Model:
Virtual Captives: In this model, a dedicated pool of centers and resources is allocated to assist banks with their cloud operations as needed.
Staff Augmentation: Under this model, banks enhance their cloud expertise by hiring individuals with the required skillset internally. This internal team offers flexibility to meet real-time demands efficiently.
Outsourcing Vendors: This approach involves utilizing offshore facilities and personnel to manage cloud operations. Typically, these resources serve multiple banks under this model.
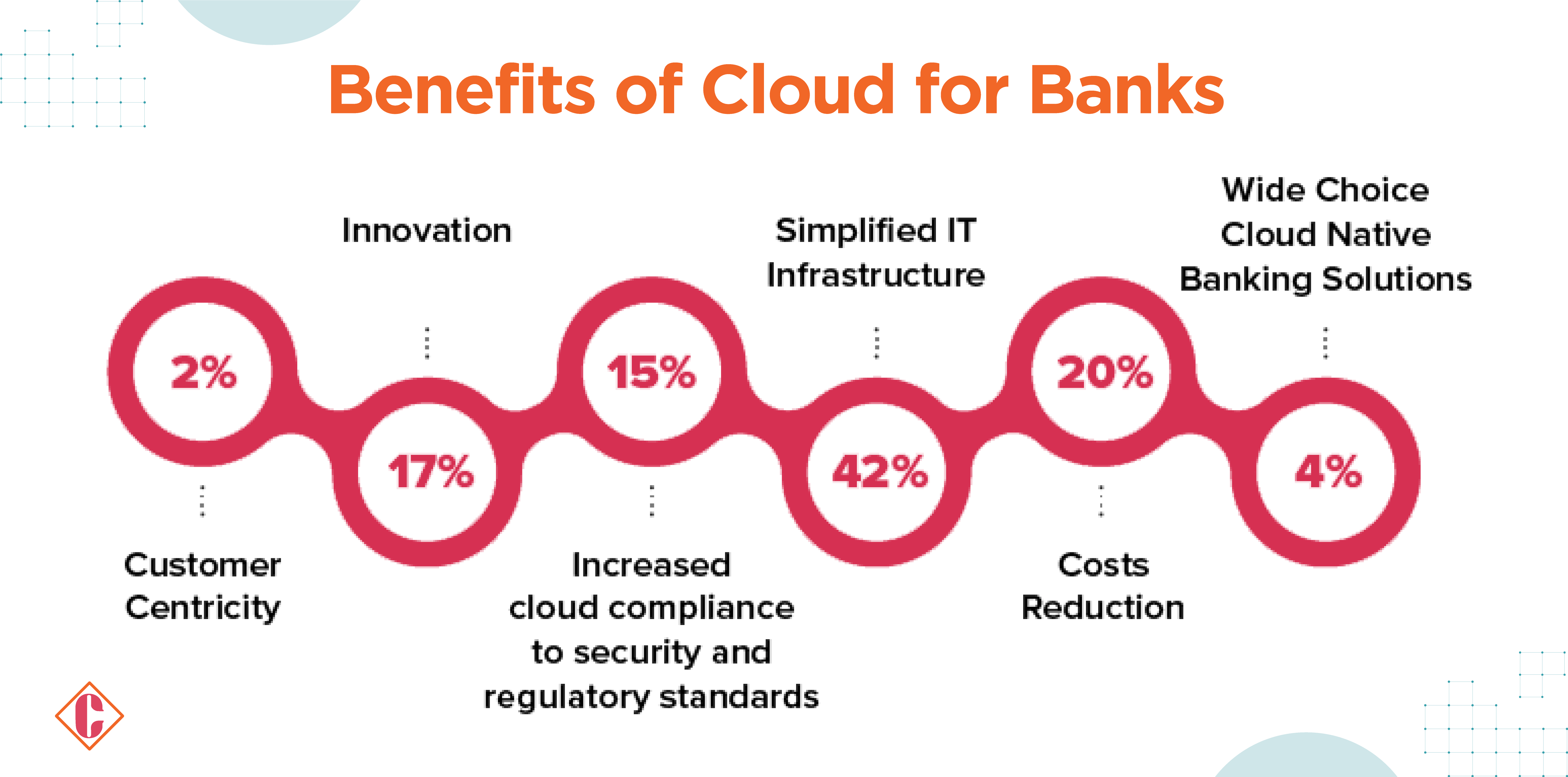
Benefits of Cloud Computing in the Banking Industry
Financial institutions gain significant advantages by embracing cloud computing, including enhanced fraud detection, cost reduction, heightened security, regulatory compliance, improved customer relationship management (CRM), and greater scalability.
 1. Fraud Detection:
1. Fraud Detection:
Cloud computing empowers banks to analyze extensive datasets from various sources to detect and prevent fraudulent activities effectively. This proactive approach allows financial institutions to identify suspicious behavior before it causes harm.
2. Cost Reduction:
Cloud computing offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, enabling financial institutions to minimize data storage costs compared to traditional on-premise systems. By outsourcing administration and maintenance to cloud providers, organizations can reduce equipment, infrastructure, and staffing expenses.
3. Enhanced Security:
Cloud providers adhere to rigorous data privacy and security standards, offering multiple layers of protection against cyber threats and data breaches. This ensures the secure storage of sensitive customer data, addressing the legal obligations of financial institutions.
4. Regulatory Compliance:
Cloud storage providers comply with stringent data privacy and security regulations, alleviating compliance concerns for financial organizations. By leveraging cloud solutions, institutions can ensure adherence to industry-specific regulations effortlessly.
5. Improved CRM:
Cloud-based CRM systems centralize customer data and interactions, enabling banks to deliver personalized services tailored to individual customer needs and preferences. This fosters stronger customer relationships and enhances satisfaction levels.
6. Greater Scalability:
Cloud services offer scalability, allowing financial institutions to adjust computing capacity based on fluctuating demand. This flexibility optimizes operations and prevents resource over-allocation, particularly during peak periods or seasonal spikes in activity.
Risk Management in Cloud Banking Systems
Effective risk management is paramount for financial institutions to safeguard their operations against various types of risks, ensuring optimal financial performance.
McKinsey underscores the importance of managing risks diligently to mitigate potential negative impacts on banks’ stability. Here are examples of the risks faced by financial institutions:
- Regulatory Risk: This risk arises from the possibility of banks violating regulations governing financial services in their operational jurisdictions. Non-compliance could lead to fines, penalties, or even loss of licenses. The use of cloud-based systems amplifies this risk as they may not always comply with local laws and regulations.
- Reputational Risk: Financial institutions face the risk of reputational damage due to negative publicity in traditional media outlets. Negative perceptions about their services and products can tarnish their reputation and erode customer trust.
- Operational Risk: The operational risk stems from inadequate internal controls over organizational processes, potentially resulting in financial losses. Examples include unauthorized access to sensitive data due to lax security measures or technology failures leading to service disruptions.
- Strategic Risk: Strategic risks encompass changes in government regulations or the exit of key players from financial markets. These developments can significantly impact financial institutions’ ability to operate successfully in specific markets, necessitating proactive risk management strategies.
Key Elements in Planning and Implementing Cloud Solutions for Banks
Business Case Development
Cloud solutions offer opportunities for innovation and the rapid development of new capabilities to address business needs. A comprehensive business case should highlight how cloud-delivered solutions can drive customer insights, enhance experiences, reduce costs, and support enterprise operations. It should also include a value-assessment model to analyze changing market dynamics and aid in scenario planning, along with addressing change management considerations.
Solution Design and Execution
Financial institutions must carefully consider the cost and effort involved in migrating workloads to the cloud. Time to market is crucial, particularly for leveraging advanced technologies like data analytics and machine learning. External cloud providers offer capabilities that can expedite development compared to in-house solutions.
Vendor Management
Given the transition to hybrid and multi-cloud environments, banks need to avoid vendor lock-in and ensure flexibility in adapting to marketplace changes. Adopting a multi-vendor/multi-cloud strategy requires a common understanding of architectural components and governance to optimize usage.
Security
Data security is a top priority for banks, and understanding how cloud technology enhances security measures is crucial. Cloud providers offer native security tools, and they share responsibility for securing infrastructure layers with clients. Organizations must anticipate and prepare for security risks in collaboration with cloud providers.
Regulatory Compliance:
Cloud computing can assist banks in meeting regulatory reporting requirements across multiple jurisdictions. Cloud solutions facilitate tasks such as intraday liquidity calculations, risk assessments, and fraud detection. Additionally, cloud platforms provide data-brokering capabilities based on data criticality and regulatory certifications.
In Short
The future of banking and finance is intertwined with the transformative power of cloud computing. Global spending on cloud computing within banking reached $20.9 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow at a 22% CAGR until 2026. Cloud computing offers banks and financial institutions the agility, scalability, and efficiency needed to thrive in an era defined by rapid technological advancement and evolving consumer demands. From enhancing fraud detection and regulatory compliance to enabling personalized customer experiences and facilitating seamless operations, the benefits of cloud adoption are profound and far-reaching.
Looking ahead, the integration of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and quantum computing with cloud solutions holds immense potential to revolutionize financial services further. As pioneers in this digital evolution, banks, and financial institutions must embrace a forward-thinking mindset, leveraging the power of cloud computing to redefine the boundaries of possibility and usher in a new era of banking excellence.
FAQs
1. Why are banks moving to the cloud?
Several factors are driving the shift:
- Enhanced Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in robust security measures, often exceeding what individual banks can manage.
- Operational Efficiency: Eliminating expensive IT infrastructure frees up resources for innovation and customer service.
- Faster Innovation: Cloud environments facilitate the rapid development and deployment of new financial products and services.
- Disaster Recovery: Data backups and redundancy in the cloud offer superior protection against outages and disasters.
2. Are there any risks associated with cloud banking?
Vendor Lock-in: Overreliance on a single cloud provider can limit flexibility and negotiation power.
Data Security Concerns: Ensuring data remains secure within the cloud environment requires careful management and oversight.
Downtime Disruptions: While rare, outages in the cloud can interrupt access to financial services.
3. What skills are banks investing in for cloud success?
Cloud Architecture and Engineering: Designing, building, and managing secure and scalable cloud infrastructure.
Cloud Security: Implementing and maintaining robust security controls to protect sensitive financial data.
DevOps: Automating development, deployment, and operations for efficiency and agility.
Data Analytics: Harnessing cloud data to gain insights and drive informed business decisions.
4. What are the challenges the banking and financial sectors face in adopting cloud computing?
- Lack of Control
- Data Privacy and security
- Regulatory compliance
5. What is the Technology impact of cloud computing on finance and banking?
- Storage: Email archiving and storage of voice and chat
- Reporting and analytics: Leveraging cloud as an analytics platform for real-time customer insights and reporting
- Containers, APIs, and microservices: Exposing data and services through APIs and microservices to enable faster and easier access to data
- Master data management: Providing consistent client views across channels and identifying cross-sell
opportunities
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]



 1. Fraud Detection:
1. Fraud Detection: