Overview of Open Source Intelligence (OSINT)
Open-source intelligence (OSINT) involves gathering information from publicly available sources. Whether conducted by IT security professionals, malicious hackers, or state-sanctioned intelligence operatives, OSINT employs advanced techniques to sift through vast data to achieve specific objectives.
Crowdstrike defines Open source intelligence (OSINT) as the act of gathering and analyzing publicly available data for intelligence purposes.
OSINT acts as a counterpart to operational security (OPSEC), a process through which organizations safeguard public data that, if analyzed, could reveal detrimental truths. Internal security teams conduct OSINT operations on their organizations to bolster operational security. They seek sensitive information not recognized as public, enabling the protection of exposed data and anticipation of potential attacker knowledge. This information is crucial for risk assessment, prioritizing security resources, and refining security practices and policies.
Why is OSINT Essential for Effective Cybersecurity Strategies?
Instances of information leaks in the public domain correlate with misfortunes, often highlighted in media reports of data breaches affecting major companies or the exposure of private communications involving high-profile individuals. The rise of cancel culture, predominantly on social media, is closely linked to the misuse of information shared online.
As Oscar Wilde aptly observed over a century ago,
“Private information is practically the source of every large modern fortune.” His words resonate strongly in today’s context. Conversely, a contemporary truth emerges – “Public information is often the source of many large modern misfortunes.” In our digitally connected era, where information flows incessantly through the cyber landscape, this truth becomes increasingly evident.
The root cause of many misfortunes frequently aligns with instances of public exposure or the inadvertent sharing of information with unintended audiences. Blame is commonly attributed to poor digital hygiene or a lack of education, leading individuals to overshare.
Compounding the issue is software design, which often prioritizes usability over security. Oversight of opt-out settings results in the unintentional leakage of data, exposing user-created content to the widest audience by default. Consequently, the notion of a “private” space in the cloud warrants careful consideration from an information security perspective.
The global prevalence of digital information-sharing platforms has magnified the role of OSINT. Unfortunately, this increased influence can be exploited to extract a wealth of data points related to individuals and organizations.
OSINT Evolution: Bridging Spycraft to IT
The historical roots of Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) trace back to the 1980s when military and intelligence services underwent a strategic shift. During this period, the emphasis moved away from covert activities such as intercepting communications or attempting to uncover hidden secrets through clandestine methods. Instead, efforts were redirected toward seeking intelligence that was openly available or officially published.
Although social media had not yet emerged, there were abundant sources like newspapers and publicly accessible databases containing valuable information. The term OSINT was coined to encompass the practices of gathering intelligence from these openly available sources, marking the inception of OSINT in the realm of spycraft.
Fast-forward to the present day and the principles of OSINT find application in the domain of cybersecurity. Organizations, irrespective of their size, manage vast, public-facing infrastructures across diverse networks, technologies, and hosting services. Information, crucial for security, can be dispersed across employee desktops, legacy on-prem servers, cloud storage, embedded devices like webcams, and even concealed within the source code of active applications.
Security and IT staff in large enterprises often grapple with the challenge of comprehensively knowing about every asset in their domain, whether public or concealed. The complexity amplifies when considering that organizations may inadvertently control or own assets indirectly, including social media accounts. These assets, if falling into the wrong hands, could pose significant risks. The evolution of OSINT from traditional spycraft to its contemporary application in IT reflects a dynamic response to the changing landscape of information gathering.
Application of OSINT in Cybersecurity
The utilization of OSINT in cybersecurity is diverse and contingent on business needs, cybersecurity requirements, and the specific teams involved in collecting OSINT. Threat intelligence teams, in particular, are often assigned the responsibility of gathering open-source intelligence to meet defined goals and objectives set by other security teams or business units.
-
Dark Web OSINT:
- Accessible through TOR (The Onion Router), the dark web offers a high level of anonymization for network traffic.
- Threat actors operate intricate supply chains across dark web markets, forums, and illicit communities on platforms like Telegram.
- Dark Web Threat Intelligence provides critical insights into threat actor tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), initial access brokers, leaked credentials, and infected devices for sale about specific companies.
-
External Attack Surface & Cybersecurity OSINT:
- A common initial step for adversaries in targeted attacks is to gather open-source intelligence about a specific company.
- Sources include corporate and personal social media profiles, business directories, corporate websites, published documents, third-party data sources, news, press releases, domain registry data, publicly available email addresses, and phone records.
- Conducting OSINT on one’s organization reveals potential security gaps, data exposure, and inadvertent disclosure of confidential information by key executives.
-
Geopolitics & Cybersecurity OSINT:
- OSINT plays a crucial role in providing contextual insights into evolving geopolitical risks, influencing the risk profiles of individual organizations.
- Monitoring open-source intelligence sources is invaluable for understanding an organization’s risk within the broader context of global events, such as geopolitical crises like Russia’s actions in Ukraine or potential crises over the Taiwan Strait.
-
Vulnerability Management and OSINT in Cybersecurity:
- OSINT is integral to vulnerability management, monitoring for 0-day exploits and new vulnerabilities disclosed daily by software vendors and researchers.
- Security operations teams or cyber threat intelligence teams actively monitor for newly disclosed vulnerabilities affecting enterprise software applications.
-
OSINT, Google Dorks, and Targeted Cyber Attacks:
- Google Dorks, a more advanced OSINT collection method, allows for highly customizable Google search terms to uncover hard-to-find intelligence sources.
- Both threat actors and security teams leverage Google Dorks for targeted cyber attacks and intelligence gathering.
OSINT: A Dual-Edged Sword
Open-source information, inherently accessible to everyone, serves as a powerful tool for both cybersecurity professionals and malevolent actors. The unrestricted availability of OSINT creates a two-way street, presenting challenges for the security landscape.
-
Social Engineering by Cybercriminals:
- Cybercriminals exploit OSINT for social engineering, collecting personal information from social media profiles and online activities to craft targeted phishing attacks.
- Personalized profiles of individuals are created, enhancing the effectiveness of social engineering attacks.
-
Detection Evasion and Alternate Attack Methods:
- OSINT aids cyber adversaries in evading detection by reviewing publicly disclosed intelligence. Threat actors identify defense lines and explore alternative attack methods.
- Google hacking, or Google Dorking, involves using specific command searches in Google to uncover system vulnerabilities and sensitive information.
-
Google Hacking Techniques:
- Cybercriminals execute targeted searches, such as seeking documents containing specific phrases like “sensitive but unclassified information.”
- Tools are employed to scan websites for misconfigurations or security gaps in their code, which can serve as entry points for future ransomware or malware attacks.
-
Influencing Google Searches:
- Adversaries manipulate Google searches by establishing a network of fake websites containing unreliable OSINT data.
- Misinformation is disseminated to mislead web crawlers, and readers, or distribute malware, showcasing the deceptive potential of OSINT in the wrong hands.
Latest Innovation
Skopenow, a prominent OSINT provider, propels into 2024 with Grid, its revolutionary 360-degree situational awareness solution. This innovation reflects Skopenow’s commitment to proactive threat detection, offering a unified platform for 1,500+ customers in both the public and private sectors. Grid’s key features include comprehensive data integrations, real-time AI-driven insights, precision in data filtering, multi-channel notifications, and a user-friendly interface.
Grid Highlights:
-
- Provides a single-pane-of-glass for optimizing tech stacks and focusing resources on core operations.
- Fuses data from diverse sources for a comprehensive view, serving specialized teams in various sectors.
- Enables timely threat assessments and proactive measures against risks to critical areas.
- Filters extraneous data, ensuring teams access relevant geospatial information for actionable intelligence.
- Delivers instant alerts for emerging threats, facilitating rapid decision-making and response.
- Simplifies data review and insight gathering, minimizing the need for extensive training.
Read more: SKopenow Launches a Complete End-to-End OSINT Platform to Verify Online Information
Key Benefits of Integrating OSINT into Cybersecurity Strategies 3.1 Enhanced Threat Intelligence 3.2 Proactive Threat Detection and Mitigation 3.3 Reputation Management and Brand Protection 3.4 Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
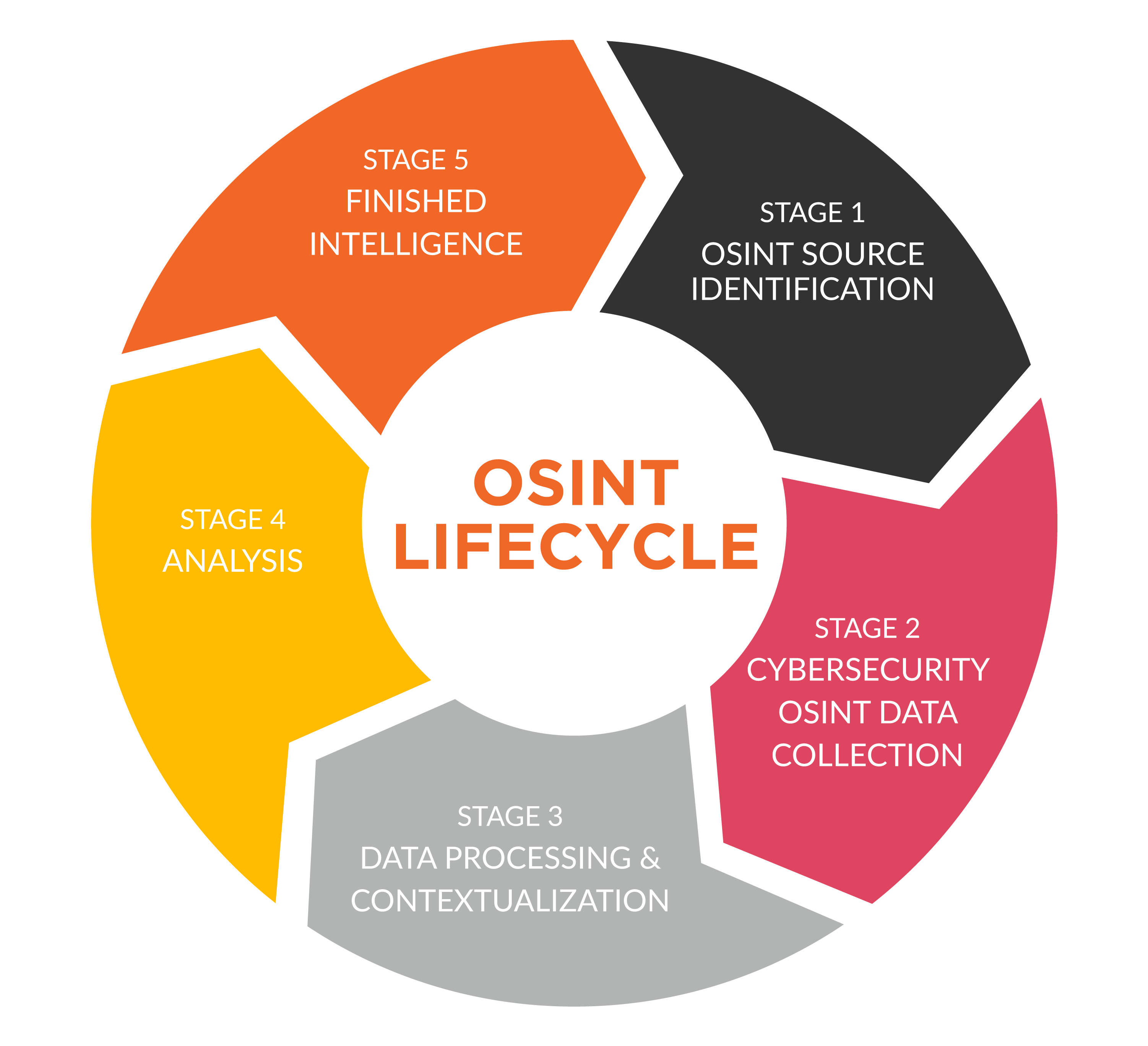
Advanced OSINT Techniques for Improved Decision-Making
The primary challenge in Open Source Intelligence lies in handling the vast and ever-growing volume of public data. Human capacity falls short, necessitating organizations to automate data collection and analysis. Employing mapping tools aids in visualizing and establishing clearer connections among data points.
Leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence, OSINT tools efficiently gather and store large data sets. These tools excel in identifying significant links and patterns within diverse information sources. To navigate this sea of information, organizations must formulate a precise strategy, defining the data sources aligned with their goals. This strategic approach ensures the system is not overwhelmed with irrelevant or unreliable data.
OSINT Collection Strategies: Passive and Active Approaches
Open-source intelligence collection is broadly categorized into passive and active techniques. Passive collection consolidates diverse data into an easily accessible repository. Threat intelligence platforms, empowered by machine learning and artificial intelligence, facilitate data management and prioritization based on defined rules.
On the other hand, active collection employs investigative techniques to pinpoint specific information. This approach supplements cyber threat profiles identified through passive means or supports targeted investigations. Common tools for active OSINT collection include domain or certificate registration lookups to identify ownership and public malware sandboxing for application scans.
Top OSINT Tools
Maltego
SpiderFoot
ZoomEye
Shodan
Censys
BuiltWith
Lampyre
Maltego
Skopenow
Mitigating Open-Source Intelligence Risks
Addressing vulnerabilities in open-source intelligence is crucial, as not every cyber threat involves sophisticated penetrations. Cybercriminals often opt for the path of least resistance to achieve their objectives. If the desired information is publicly accessible, hackers are unlikely to invest months in cracking robust cybersecurity defenses. Instead, they may exploit open channels to obtain sensitive information, facilitating the acquisition of valid credentials or planning intrusions with reduced effort and risk.
Employing Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) tools becomes imperative for organizations to comprehend the extent of information available about their networks, data, and users. Swift identification of such information is essential, enabling its removal before exploitation. OSINT tools play a pivotal role in this critical race to secure sensitive data and fortify defenses against potential threats.
FAQs
1. What is OSINT, and how does it empower cybersecurity?
OSINT, or Open-Source Intelligence, involves collecting information from publicly available sources. Its advantage in cybersecurity lies in providing valuable insights into potential threats and vulnerabilities, aiding in proactive defense strategies.
2. Why should C-suite decision-makers prioritize OSINT in their cybersecurity strategy?
OSINT offers a proactive approach to cybersecurity by leveraging publicly accessible data, allowing decision-makers to stay ahead of potential threats and enhance overall organizational resilience.
3. How can OSINT tools enhance threat detection and response?
OSINT tools enable organizations to gather and analyze information swiftly, enhancing their ability to detect and respond to potential cyber threats in real time.
4. Are there specific industries or sectors that benefit more from the OSINT advantage?
OSINT is versatile and beneficial across various industries, including finance, healthcare, and technology, providing tailored insights into industry-specific threats and vulnerabilities.
5. How does OSINT contribute to risk assessment and management?
OSINT aids in risk assessment by uncovering potential risks, vulnerabilities, and data exposures, allowing organizations to proactively manage and mitigate these risks.
6. How can organizations stay updated on the latest OSINT tools and techniques?
Staying informed about the latest OSINT tools and techniques involves continuous learning through reputable sources, training programs, and industry conferences.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]


