In the modern healthcare industry, data is the cornerstone for the businesses. With approximately 10 billion IoT medical devices, including pacemakers, insulin pumps, and heart rate monitors, generating extensive data, the role of software applications in aiding clinicians has become pivotal. Yet, the traditional method of transmitting this data to centralized data centers or the cloud for processing proves inefficient for real-time healthcare needs.

The healthcare sector faces a data deluge. A Dell survey from 2020 revealed a 900% surge in healthcare and life sciences data within two years, as hospitals connect 10 to 15 devices at patient bedsides. Contemporary health systems and providers deploy fresh tools and care models, aiming to enhance patient services.
This inefficiency is at odds with the urgency of the healthcare industry, where instantaneous and precise solutions are imperative for doctors and patients alike. Enter edge computing in healthcare—a strategic approach involving the relocation of computational power and data processing systems closer to the origin of medical data. This proximity enables swift analysis, crucial for preserving lives and enhancing patient outcomes.
Comparing Cloud Computing and Edge Computing in Healthcare
In healthcare, numerous sensors—embedded in devices like pacemakers, MRI machines, insulin pumps, and ultrasound devices—continuously monitor patient health, generating vast amounts of data requiring substantial computing power for processing and analysis. Organizations have shifted from on-premises data centers to cloud computing, sparing them from hardware maintenance and purchases.
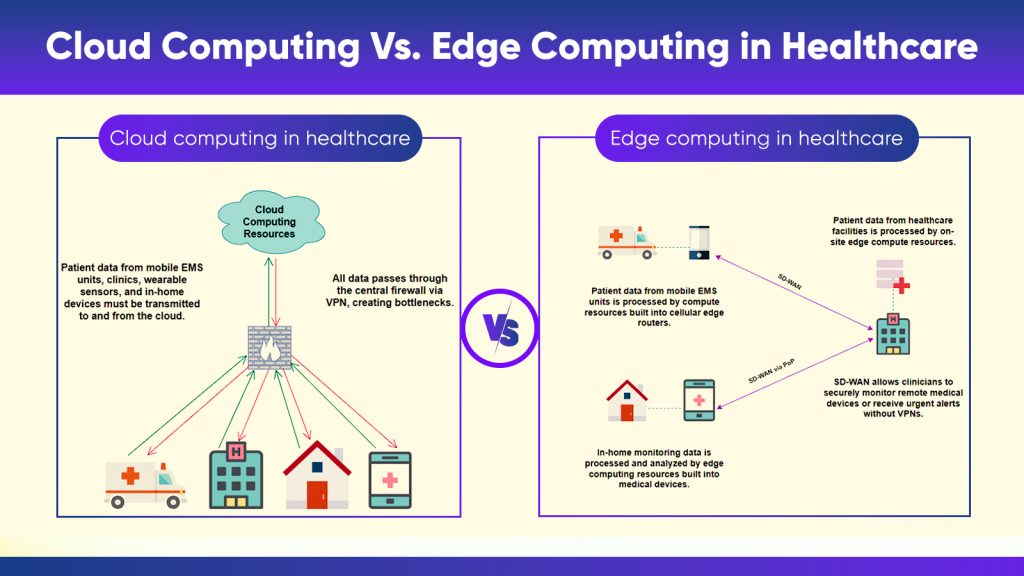
However, cloud computing involves transmitting patient data to and from the cloud, introducing latency and security concerns. For instance, mobile EMS devices and wearable sensors utilize cellular networks to connect to cloud resources, risking data security. Healthcare entities often route data through central firewalls using VPNs to mitigate this, causing transmission delays.
Conversely, edge computing processes patient data locally, markedly reducing transmission time. Data processing occurs almost concurrently with the collection, whether through co-located edge computers in clinics or integrated cellular edge routers in ambulances. This minimizes latency, enhancing application performance and data accuracy.
Processing data at the edge reduces latency and heightens security by keeping data within the local network, simplifying HIPAA compliance. Leveraging SD-WAN technology, clinicians securely access remote patient data without VPNs, enabling faster response to critical issues.
5 Edge Computing Best Practices for Healthcare
Adopting SD-WAN in Healthcare
- Software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN) offers software abstraction for efficient WAN management.
- Decouples network logic from underlying WAN hardware, freeing healthcare organizations from traditional WAN limitations.
- Enables secure data processing and transmission, even in scenarios like ambulance-based data collection, bypassing the hospital’s MPLS backbone.
Implementing Security Measures for Edge Computing
- Edge computing reduces security risks but doesn’t eliminate them; proper security implementation is crucial.
- Zero trust security, founded on “never trust, always verify,” grants access rights based on least privilege and continuously evaluates trust during account access.
- Granular access policies enforced through Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) fortify edge security.
- User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) respond to suspicious behavior by triggering immediate actions, such as identity re-verification.
SASE Integration for Enhanced Security
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) combines SD-WAN with cloud-based cybersecurity services, offering Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) for secure edge-device connections.
- ZTNA ensures limited access based on device needs, reducing attack surfaces and requiring rigorous identity verifications for network traversal.
Introducing Automation in Edge Computing
- Edge computing complexity is mitigated through automation.
- SD-WAN’s software abstraction allows centralized management of extended architecture, deploying network automation scripts and workflows via orchestration platforms.
- Automation extends to big data, machine learning, and AIOps applications on the edge, providing predictive insights and problem-solving capabilities.
Utilizing Vendor-Neutral Platforms
- Vendor-neutral management platforms streamline network architecture management.
- Unifying SD-WAN orchestration, security monitoring, edge device management, and automation behind a single interface simplify administration, enhances reliability, and provides a holistic overview of the network’s health and security posture.
Enhanced Edge Computing Benefits in Healthcare
Edge computing revolutionizes healthcare by offering:
- Improved Remote Patient Care: Wearable sensor data undergoes near-real-time analysis, enabling proactive responses to potential health issues before escalation.
- Speed and Performance: EMS data processed by 5G devices in ambulances allows faster treatment recommendations—real-time data transmission to receiving hospitals aids in better patient preparation.
- Workload Efficiency: Real-time analysis of monitoring data delivers swift insights into diagnostic and treatment options. Automated data prioritization reduces handoff delays and miscommunications among clinicians.
- Security: On-site processing of patient data ensures HIPAA compliance and deters interception without relying on sluggish VPNs.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: Edge machine learning and big data applications minimize transmission latency, bolstering diagnostic precision and yielding faster results.
- Cost Savings: Edge-deployed big data applications furnish valuable insights, aiding waste reduction and cost-saving strategies without compromising care standards.
Future Outlook
As healthcare embraces the transformative potential of edge computing, the future appears promising and dynamic. This technological shift heralds an era of unprecedented advancements, offering a glimpse into a healthcare landscape that prioritizes proactive and personalized patient care. In addition, the integration promises to revolutionize healthcare delivery by fostering a seamless fusion of real-time data analysis, swift responses to emergent situations, and heightened security measures. Improved diagnostic accuracy, efficient workflows, and cost-effective strategies will redefine the standards of care while ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory frameworks.
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]


