IT service delivery is a mechanism that allows organizations to provide users seamless access to essential IT services, encompassing applications, data storage, and critical business resources. It is a comprehensive process that spans the entire lifecycle of services, covering design, development, deployment, operation, and eventual retirement. The numerous professionals involved at different stages are integral to IT service delivery excellence. The benchmark for evaluating the efficacy of this delivery lies in the metrics outlined within the Service-Level Agreement (SLA).

An IT Service Management (ITSM) framework is at the core of this efficient operation, exemplified by the widely recognized IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL). This framework delineates the processes, people, and products essential for effective IT service delivery. It ensures adherence to established regulations, compliance standards, governance requirements, and industry best practices.
Implementing a formalized system for IT service delivery yields substantial benefits for organizations dealing with large-scale or intricate software and hardware deployments. It accommodates diverse system needs, accommodates dynamic IT configuration changes, meets high uptime demands, and addresses increasingly sophisticated user expectations. Furthermore, as technology evolves, business units are presented with alternative options beyond the confines of dedicated IT teams. These options include leveraging public cloud hosting and embracing software-as-a-service (SaaS) products.
Key Elements of IT Service Delivery
- Service level management: SLM forms the cornerstone, ensuring that IT services consistently meet performance benchmarks by crafting and vigilantly monitoring service level agreements (SLAs).
- Financial management for IT services: It operates at the core of budgeting and overseeing costs tied to the sustenance and delivery of diverse IT services.
- Capacity management: Capacity management supervises IT servers, networks, and storage, ensuring an adequate resource pool for present and future service demands.
- Availability management: It stands as a guardian, ensuring the timely availability of IT services while prudently managing associated risks.
- IT service continuity management: Continuity management is crucial in developing and executing processes that sustain service continuity during system failures or disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
IT Service Delivery Manager (SDM)
A service delivery manager supervises various functions aimed at providing exceptional customer service. Their tasks encompass budget management, progress monitoring, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), conducting client surveys, and resolving issues as they arise. The role of an IT Service Delivery Manager is multifaceted, often entailing a myriad of responsibilities, some of which may conflict. Understanding the pivotal functions of an SDM is crucial to discerning whether your business could benefit from a dedicated professional in this role.
The SDM mediates between IT engineers and end users, translating customer requests into engineering language. Ideally, the SDM offers additional insights and support, a point we’ll explore shortly. Many companies merge IT responsibilities, often blending the roles of SDM and technical support. This means the SDM might handle tasks such as hardware installation, troubleshooting IT issues, liaising with vendors, and more. The rationale behind this consolidation might be to optimize human resources or streamline time and cost. However, the common outcome tends to be frustration among employees and end users.
Key Challenges in IT Service Delivery
- Undefined KPIs: Clear KPIs are essential for measuring service delivery success and guiding improvement efforts. The absence of these benchmarks hinders informed decision-making and satisfaction enhancement.
- Stakeholder Communication Gap: Aligning IT services with business objectives necessitates effective communication and engagement with key stakeholders. The lack of this interaction hampers collaboration across teams and departments.
- Rigidity in Adaptation: IT service delivery must be adaptable to evolving business needs. Inflexibility leads to stagnation, failing to meet dynamic end-user requirements and hindering company progress.
- Contextual End-User Support Gap: Tailored support for individual user needs is crucial but challenging for IT teams. Inadequate support can breed user frustration and reluctance to engage with IT services.
Essential IT Service Delivery Resources
- Help Desks: Centralizes user service requests, offering resources and support for prompt issue resolution, easing communication between end users and IT teams. Automation features enhance issue resolution efficiency.
- IT Service Catalogs: Showcases available services and resources to end users, facilitating requests for new tools/services and aiding decision-making. Helps IT teams track service requests for a better understanding of service needs.
- Digital Adoption Platforms (DAP): Utilizes interactive guides and in-app tutorials to introduce new technologies, aiding onboarding, training, and collecting user feedback. Simplifies IT delivery by automating complex tasks.
- Knowledge Base Management: Provides instructions and resources for troubleshooting, empowering users and teams to solve issues independently and swiftly. Enables users to access support autonomously.
- Log Management: Standardizes collection, storage, and management of IT service delivery information. Aids in identifying ongoing issues, responding to incidents, and detecting anomalies swiftly, supporting capacity planning.
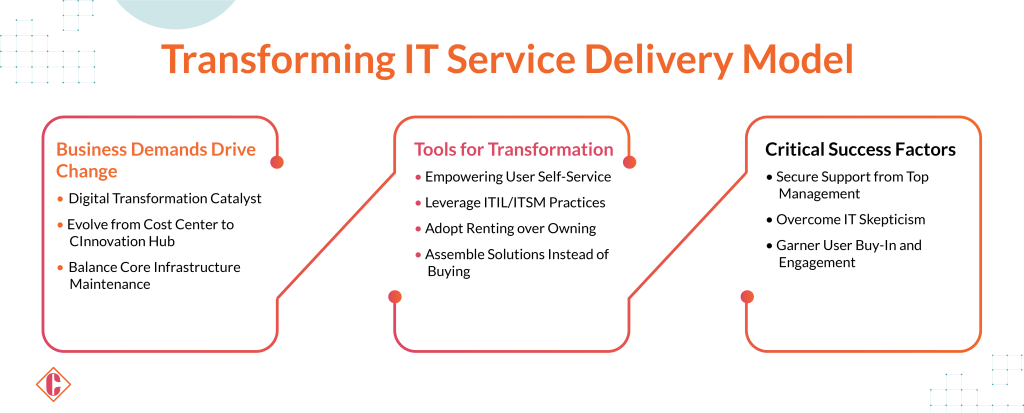
Transforming the IT Service Delivery Model
Amidst the surging demands of digital transformation across various industries, technology leaders face a pressing need to redefine the IT service delivery model. Companies use IT to compete and improve customer service, raising business expectations. Consequently, IT departments must shift from being perceived as cost centers to revenue-generating entities.
 The responsibility lies upon CIOs, CTOs, and senior IT managers to synchronize with the escalating needs of enterprises.
The responsibility lies upon CIOs, CTOs, and senior IT managers to synchronize with the escalating needs of enterprises.
Ron McIntyre, CTO at Delmar International Inc., shares about evolution over stagnation, emphasizing the necessity of adaptation to evolving paradigms. Delmar’s strategic initiatives, including migrating its Microsoft Dynamics AX ERP environment and transitioning email to cloud-based Office 365, embody a five-year transformation journey to meet dynamic business requirements. Understanding the key tools and methodologies is vital in managing expanded responsibilities in navigating this evolution.
The Shift to User Self-Service:
A pivotal transformation sees IT departments relinquishing their traditional role as technology gatekeepers, transitioning towards enabling rather than impeding business growth. Embracing a customer-centric approach, the focus shifts towards delivering value and service. It empowers users through self-service avenues like IT vending machines, secure device lockers, and portals for acquiring cloud services.
Liberating IT Time through ITSM:
IT Service Management methodologies, particularly leveraging ITIL processes, emerge as pivotal in liberating resources and redirecting focus toward innovation. By optimizing service delivery processes, IT departments can reallocate support staff towards value-added initiatives, fostering a culture of continual improvement.
Maximizing Existing Assets:
A strategic shift within IT service delivery involves leveraging existing cloud and on-premises assets, favoring a blended approach over new acquisitions. Like digital bartending, this approach encourages repurposing existing resources to address emerging needs, minimizing reliance on proprietary solutions and fostering interoperability among systems.
Embracing a Rental Mindset:
The trend towards ‘renting’ IT assets instead of owning them emerges, leveraging cloud platforms to facilitate agile test and development environments. This approach mitigates the ‘IKEA effect,’ where ownership may lead to resistance to change, fostering adaptability and innovation within IT landscapes.
Benefits of Partnering with IT Service Delivery Experts
The increasing demands and heightened user expectations exert significant pressure on internal IT teams, burdening them with IT service delivery responsibilities. This strain leads to prolonged lead times, poor end-user experiences, damaged reputations, and diminished team morale.
Effectively managed IT service delivery yields numerous advantages, including cost reduction, enhanced customer and employee experiences, expanded market reach, workflow automation, and data utilization for improved cost-efficiency.
Consequently, an increasing number of organizations opt to collaborate with third-party experts to streamline and optimize their IT service delivery. This strategic partnership provides dedicated support, enabling the enhancement of key performance indicators (KPIs) while liberating internal resources to concentrate on strategic initiatives.
Partnering with IT service delivery offers the following benefits:
- Access to Expert Knowledge: Internal teams, burdened with diverse responsibilities, struggle to keep pace with the rapid evolution of technologies and best practices in IT service delivery. Engaging a reputable vendor facilitates the design of strategic approaches aligned with business objectives, establishing pertinent KPIs, and resolving intricate IT issues. Additionally, it assumes responsibility for daily operations, continuously optimizing processes to meet user expectations and enhance cost-efficiency.
- Reduction in Operating Costs: Hiring and training new personnel to manage IT service delivery incurs substantial costs and time investments. Partnering with a third-party provider grants immediate access to an experienced team, eliminating recruitment overheads, administrative tasks, equipment procurement, and additional office space expenses. This approach ensures swift deployment without administrative intricacies or prolonged onboarding periods.
IT Service Delivery Partners
Businesses rely heavily on robust and efficient IT infrastructure to thrive. However, managing complex IT systems in-house can be resource-intensive, diverting focus from core operations. This is where IT service delivery partners come in. The IT service delivery partner encompasses a range of players with specialized strengths. Here’s a brief overview of some key categories:
1. Managed Service Providers (MSPs): These all-rounders handle the day-to-day operations of your IT infrastructure, from network management and server maintenance to security monitoring and user support. Think of them as your outsourced IT department, ensuring smooth tech sailing.
A few of the MSPs:
Accenture
Wipro
Capgemini
Cognizant
2. Cloud Service Providers (CSPs): Cloud giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer a robust suite of cloud-based solutions, from computing and storage to data analytics and artificial intelligence. Partnering with a CSP unlocks scalability, agility, and access to cutting-edge technologies.
A few CSPs:
Google Cloud
RedHat
AWS Cloud
IBM Cloud
Microsoft Azure
3. Cybersecurity Providers: With cyber threats lurking around every corner, these specialized partners fortify your defenses. They offer solutions like intrusion detection, vulnerability management, and incident response, keeping your data and systems safe from harm.
A few Cybersecurity Providers:
Palo Alto Networks
Cisco
Crowdstrike
McAfee
Best Practices for Achieving IT Service Delivery Excellence
-
Ensure Proactive and Empathetic Service Delivery
Active and empathetic service delivery ensures customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Proactive issue detection and resolution through specialized tools help IT teams prioritize transformation initiatives, avoiding reactive support scenarios that impede business functions. Additionally, empathetic engagement with users during issue resolution ensures timely solutions aligned with user needs, fostering a positive experience and driving user satisfaction.
-
Develop an Adaptive Service Catalog Framework
Achieving service delivery excellence demands adaptability in the face of evolving technologies. A comprehensive catalog, aligned with sales and delivery departments, facilitates swift adaptation to client requirements, optimizing service delivery for success.
-
Embrace Metrics and Iterative Approaches
Focusing on DORA metrics and Net Promoter Scores is crucial for maximum service efficiency. Implementing methodologies like value stream mapping aids in identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, fostering a proactive approach for service elevation. Continuous iteration and measurement against anticipated improvements enable consistent service enhancement and uphold world-class service quality.
-
Standardize Processes and Understand Business Needs
Effective service delivery begins with standardized processes and documentation for the organizations. Standardization ensures consistency, aligning with security policies and streamlining training and onboarding. Understanding and aligning each department’s needs with overall strategic goals enables IT to create a service portfolio that enhances organizational flexibility and innovation.
-
Adopt a User-Centric Approach and Assemble Fitting Teams
Leveraging a user-centric approach in organizing development teams works best for excellence in IT service delivery. Establishing product teams for end-to-end delivery of features fosters adaptability and responsiveness to customer needs. Ensuring that IT decisions align with organizational goals and customer needs centers the decision-making process, facilitating adaptive and responsive service delivery.
-
Avoid Ad Hoc Execution and Document Complaint Resolutions
Planning and adhering to predefined service delivery plans are essential for effortless service delivery. Ad hoc execution often results in dissatisfaction and attrition, emphasizing the importance of structured operating procedures. Addressing complaints systematically, documenting resolutions, and following a CAPA process ensure transparent, proactive updates, minimizing future occurrences of similar issues.
In a Nutshell
With increasing technological advancements, the significance of IT service delivery is the backbone of organizational success. The evolving trends in IoT, augmented reality, 5G technology, and ethical digitization showcase the continual pursuit of innovation and efficiency. Embracing these trends while navigating the challenges requires a holistic approach, combining technological advancements with a strategic focus on user-centricity, adaptability, and leveraging expertise. Ultimately, achieving IT service delivery excellence demands a harmonious blend of cutting-edge technology, agile methodologies, and a relentless commitment to meet evolving user needs in the ever-changing digital realm.
FAQs
1. What are the key pillars of IT service delivery excellence?
-
- People: Hire and retain a skilled and motivated IT team.
- Process: Implement standardized and efficient IT processes.
- Technology: Leverage the latest technologies to automate tasks and improve service delivery.
- Culture: Foster a customer-centric culture with a focus on continuous improvement.
2. What are the benefits of partnering with an IT service provider?
-
- Access to specialized expertise and resources.
- Improved scalability and agility to meet changing needs.
- Reduced costs and increased efficiency.
- Enhanced focus on core business operations.
- Peace of mind and reduced risk of IT-related disruptions.
3. How can organizations align IT service delivery excellence with business objectives?
Aligning IT service delivery with business objectives involves understanding business needs, actively engaging with stakeholders, designing IT services that support strategic goals, and measuring the impact of IT services on business outcomes. This alignment ensures IT investments contribute directly to organizational success.
4. How can organizations measure IT service delivery excellence?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as service availability, response time, incident resolution time, user satisfaction scores, adherence to SLAs, and cost-effectiveness of service delivery methods are crucial metrics for measuring excellence in IT service delivery.
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]


