According to the latest Google Cloud Cybersecurity report, attackers are preparing to launch multi-pronged cyberattacks on nations and organizations. The prominent cyberattack groups are well-versed with AI technologies such as Generative AI (GenAI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) when it comes to exploiting vulnerabilities in mature cloud ecosystems. Google Cloud’s cybersecurity report specifically mentions the rise of GenAI-as-a-service and paid LLM services to assist attackers in cybercrime operations. We have already witnessed the destructive force of ransomware-as-a-service in recent months. In 2024, these AI-as-a-services, along with serverless services, would create bigger hurdles for CIOs, CISOs, and security managers. Extortion operations will grow in 2024 without disruptions in the security marketplace.
Cybercrime Busters: Top 5 Cybersecurity Insights for Enterprise Storage
Google Cloud’s Cybersecurity Forecast 2024 gathered insights from Google Cloud’s security leaders. The report majorly focuses on the role of new technologies that are accelerating cyberattacks against cloud users. In a rapidly evolving genAI and LLMs, security leaders and managers can deploy threat intelligence solutions to defend against expanding surface attacks.
Here are the top key takeaways from Google Cloud’s Cybersecurity Forecast 2024 report, highlighting the advancing use of GenAI-as-a-service and serverless services in 2024 and its potential impact on IT infrastructure and security readiness.
Cyberattackers are Getting Better with AI and LLMs for Social Engineering, Phishing, and SMS-based Scams
Google Cloud leaders have identified next year’s Summer Olympics in Paris as the biggest target for cybercrimes in 2024.
Access to Gen AI and LLMs is burning the candle at both ends for cybersecurity professionals. While organizations prepare to adopt AI and LLMs for interpreting big data, cybercriminals are using the same technology to set up organized ransomware attacks. Voice Cloning, Infostealer malware on YouTube videos, and password generators could blow away all existing threat intelligence frameworks in 2024.

Phil Venables, CISO of Google Cloud on AI, shared his insights with CIO Influence through an email statement.

Phil said, “AI is already providing a tremendous advantage for our cyber defenders, enabling them to improve capabilities, reduce toil, and better protect against threats. We expect these capabilities and benefits to surge in 2024 as the defenders own the technology and thus direct its development with specific use cases in mind. In essence, we have the home-field advantage and intend to fully utilize it. On the other hand, while our frontline investigators saw very limited use of attackers using AI in 2023, in 2024 we expect attackers to use generative AI and LLMs to personalize and slowly scale their campaigns. They will use anything they can to blur the line between benign and malicious AI applications, so defenders must act quicker and more efficiently in response.”
Looking into 2024, there is every possibility that AI will help cybercriminals find vulnerabilities in the existing digital infrastructure at a blitzkrieg pace. As AI develops at an uncontrolled pace, criminals are finding innovative ways to target high-value assets without an iota of fear of getting caught and prosecuted.
Importance of AI-based DevSecOps Security in Singaporean Businesses
Google Cloud leaders have identified next year’s Summer Olympics in Paris as the biggest target for cybercrimes in 2024. In addition to launching phishing and social engineering attacks, cybercrime groups could also spear out misinformation and disinformation campaigns coinciding with other geopolitical events linked to the European and American nations. The European Parliament elections and India’s 2024 Lok Sabha elections would emerge as the prime targets in 2024. However, the global security community should expect cybercrime to explode around the Summer Olympics in 2024.
Ticketing systems, retail e-commerce platforms, payment gateways, and social media channels — cybercriminals could target the foundations of financial infrastructure as well as public security systems.
Cybercriminal groups are already leveraging new-age technologies for their attacks. In 2024, Google Cloud experts believe these attacks could gain more steam with GenAI-powered capabilities for personalized and scaled phishing. Social engineering attacks could be carried out using deep fake assets such as AI-generated voice and video for banking KYC and authentication. As generative AI tools become more accessible for democratized communities, attackers would use these to craft error-free messages and emails with better contexts and legitimate information about the victims. No-code and LLM-generated software could emerge as the most potent anti-social tool to execute automated cyberattacks over time.
So, CIOs and CISOs should be ready to face a barrage of AI-powered cyber crimes such as deep fakes and voice cloning. These attacks would be far better organized, hyper-targeted, and more devastating than any of the previously reported incidents. To combat these attacks, security leaders must find a way to stay ahead of the attackers. Gen AI and LLMs could augment their ability to transform organizations against shoring attacks in 2024.
Cyber Espionage by The Big Four: Rise in Zero-Day Attacks and Extortion Demands
Chinese links with cyber espionage and security device zero-day vulnerabilities are unmistakable. Other nations that are equally contributing to the growing clout of cyber criminals are Russia, North Korea, and Iran. These are referred to as The Big Four, in the Google Cloud report for CISOs.
Latest Report Identifies the Biggest Cybersecurity Threats Affecting India
According to Sophos, the average ransomware demand and payout is $1.54 million in 2022. As per Astra’s report, the cost is higher– approximately $1.84 million. Victims largely belong to the software applications, finance and banking services, healthcare, manufacturing, and education industries. According to Trend Micro, the financial services industry reported the most number of ransomware attacks in 2022-2023. For the same industry, the rate of attacks grew from 55% in 2022 to 64% in 2023, as per Sophos.
Zero-day attacks are newly discovered events that link to unknown errors and vulnerabilities at the victim’s side. It derives the name from the fact that security professionals have “zero days” to fix these errors to prevent cyber attackers from exploiting them and demanding a ransom.
According to Fortinet, the term “zero-day” comes from the world of pirated digital media. State-sponsored attackers scan zero-day vulnerabilities to launch cyberwarfare against their enemy nations. Hacktivists also chase these vulnerabilities to seed wiper malware and kinetic operations. Hybrid cloud applications and Edge devices are most likely to be infected with these vulnerabilities.

The Google Chrome attack in 2021 and 2022 carried out by North Korean hackers is one of the biggest reported instances of zero-day exploits. According to analysts, hackers installed spyware and remote access malware on victims’ browsers and OS to steal data. Log4Shell and Stuxnet are other examples of zero-day attacks in the post-COVID period.
Earlier this year, Mandiant analyzed 55 zero-day (0-day) vulnerabilities and 81 0-day threats in 2021.
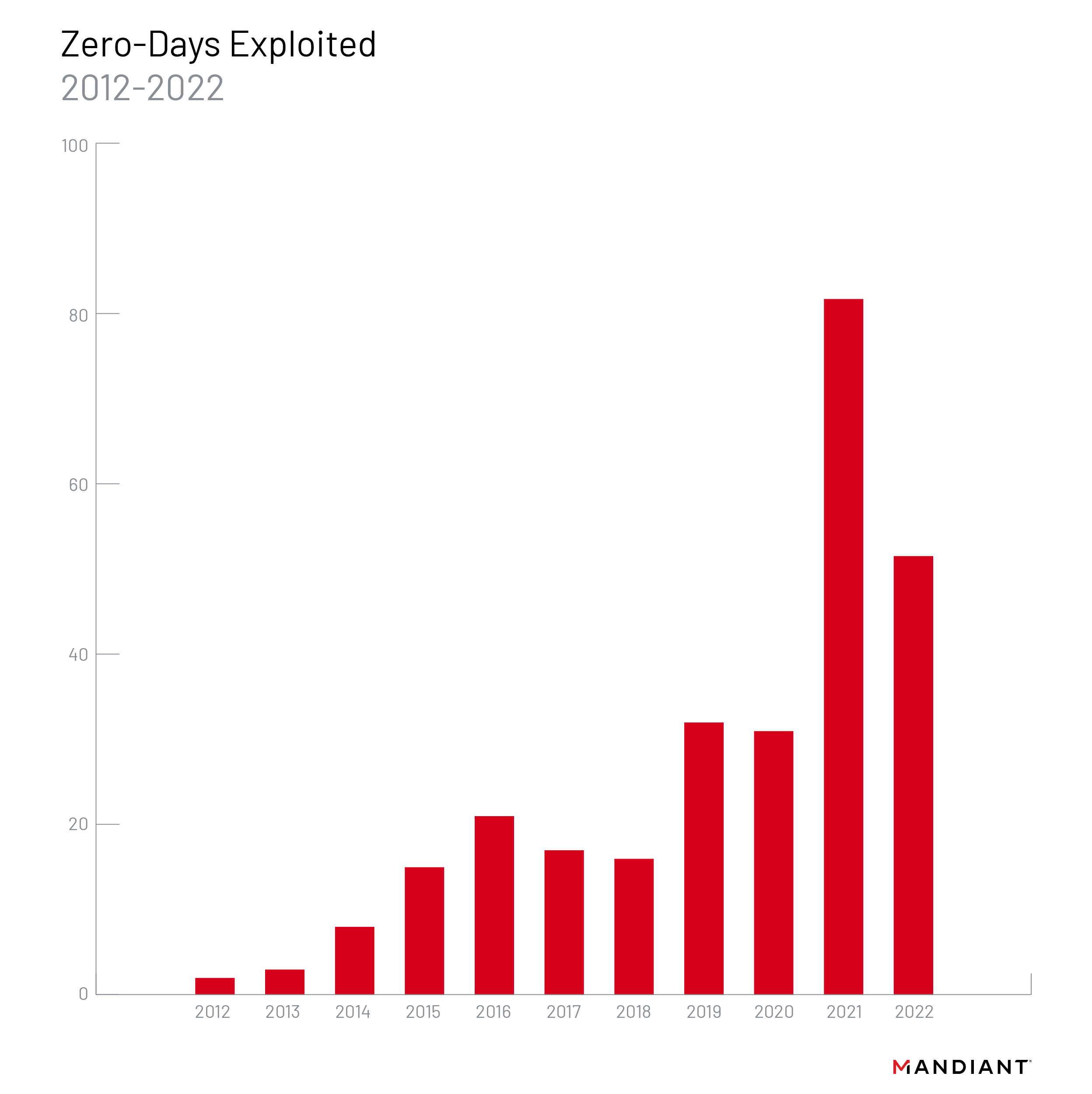 75% of these incidents were linked to ransomware operations. Google Cloud’s Cybersecurity Forecast 2024 report expects growth in 0-day attacks in 2024. The stakes will be very high as attackers (state-sponsored as well as cybercriminal groups) go after zero-day vulnerabilities in Generative AI-powered software marketplaces. Operating systems, browsers, remote workplace applications, and IoT-connected devices are most vulnerable to these attacks.
75% of these incidents were linked to ransomware operations. Google Cloud’s Cybersecurity Forecast 2024 report expects growth in 0-day attacks in 2024. The stakes will be very high as attackers (state-sponsored as well as cybercriminal groups) go after zero-day vulnerabilities in Generative AI-powered software marketplaces. Operating systems, browsers, remote workplace applications, and IoT-connected devices are most vulnerable to these attacks.
Sandra Joyce, VP of Mandiant Intelligence, Google Cloud said, “China, Russia, North Korea, and Iran each wield distinct cyber capabilities driven by their geopolitical needs in the short and long term. As tensions rise globally, especially in hotspots in the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and East Asia, these actors will undoubtedly be leveraged, so focused preparation will really be the key. In 2023, we also saw the time between discovery to exploitation of Zero Days – even on the criminal side – drop rapidly. We are simply going to have to move faster, and be smarter if we want to stay ahead of these threat actors.”
Security managers should have a strong risk management strategy against 0-day exploits. An AI-powered zero-day vulnerability testing and reporting solution can prevent such incidents in 2024. AI solutions for patch management, anomaly detection, and zero trust architecture would emerge as mainstays in the CIO’s security management and threat intelligence arsenals.
Biggest Challenge for CIOs: Thwarting the Attacks on Hybrid and Multi-cloud Environments
According to Palo Alto Network’s State of Cloud Native Security Report 2023, 68% of organizations fail to identify or detect a security threat within 60 minutes. 76% of respondents blamed the number of point tools (ever-growing!) within their cloud environments for causing “blind spots.” It’s a constant struggle for CIOs to consolidate the point tools and identify the best security architecture for thwarting cyber attacks on their assets.
Disruptive hacktivism, cyber kinetics, and zero-day exploits would be targeting hybrid and multi-cloud environments. The report mentions the collaboration between Mandiant and VMware to remediate 0-day vulnerabilities embedded on guest virtual machines (VMs). Despite a negligible impact on the IT systems, the attack modus operandi is a warning for IT security operators and cloud architects who are yet to secure their cloud environments from evolving threats and vulnerabilities within and outside networks and VMs.
Preventing crypto mining would be another challenge for CIOs in 2024. These attack groups use serverless services and automation to form a cartel of cyber criminals for enterprises and societies worldwide. A wider footprint across rogue nations provides these attackers with stealth cover for carrying out international espionage through sleper botnets and AI-masked DDoS ransomware agents.
The Google Cloud Cybersecurity Forecast 2024 also named the growing prevalence of cyber crimes a major headache for security teams in 2024. Fake social media messages, job postings spoofed pop-up alerts, impersonated brand emails and websites, and countless other tactics would the IT security organizations busy next year.
AI and SecOps: The Great Integration to Combat Serverless Services Attacks
Serverless services are part of the cloud-native computing approach for managing code, running advanced programs, and integrating applications. According to Palo Alto’s State of Cloud Native Security Report 2023, 77% of respondents from the security and DevOps industry plan to deploy new or updated code to production weekly. 70% of respondents reported planned use of serverless architecture and computing increase in the next 24 months.
More serverless applications mean more permissions.
Attackers exploit these when victims fail to bring all their cloud assets spread across multiple cloud platforms, versions, and regions under one roof. AI and SecOps integration can solve this challenge.
Four interesting results could be derived from Google Cloud’s latest set of predictions for 2024. CIOs and CISOs should prepare for the AI-led cybercrime world. This can be achieved by:
- Improving threat intelligence systems
- Using AI and Machine Learning (AIOps)
- Availing cyber insurance
- Consolidating Security Operations (SecOps) across the private cloud, multi-cloud, on-premise, and hybrid environments.
Sunil Potti, VP & GM of Google Cloud, mentioned the future developments leading to the convergence of cloud and enterprise SecOps in 2024.
Sunil said, “Right now, we see organizations running their data in a combination of multi-cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments – and while it is unrealistic to expect these organizations to host their assets solely in one place, it does make unified, comprehensive security operations and overall risk management particularly challenging. In 2024, I expect we’ll see more convergence in cloud and enterprise security operations as customers increasingly demand integrated risk and threat management across all their cloud and on-prem silos – all powered via a modern, AI-infused platform.”
Here the challenge is the lack of AI skills and training resources. According to AMD, 46% of IT leaders state their organization isn’t prepared to implement AI within the next few years. AMD’s survey found that IT professionals are growing skeptical about the role of AI tools in breaching existing security infrastructures. 67% of IT leaders said that AI tools could introduce new types of risks in the security and data governance domains. These risks could be linked to inexperienced teams that are unfamiliar with the evolving norms of AI data training and storage.
In a Nutshell
A key outcome of the Google Cloud report on cybersecurity pointed to the use of technologies to evade the detection of threats that target edge devices and multi-cloud applications. The report mentions the rising cyber insurance premiums and the need to broaden the coverage to meet the ambitious cyber security goals in 2024. While insurance companies broaden the coverage for expanding threats and exploits, CIOs should come up with a customized integrated AI-powered SecOps framework to match the shifting tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) and defend against cyber adversaries.
As we prepare for the New Year 2024, we should be aware of the overwhelming nature of cyber attacks launched using new technologies and services for phishing, ransomware, and social engineering.




