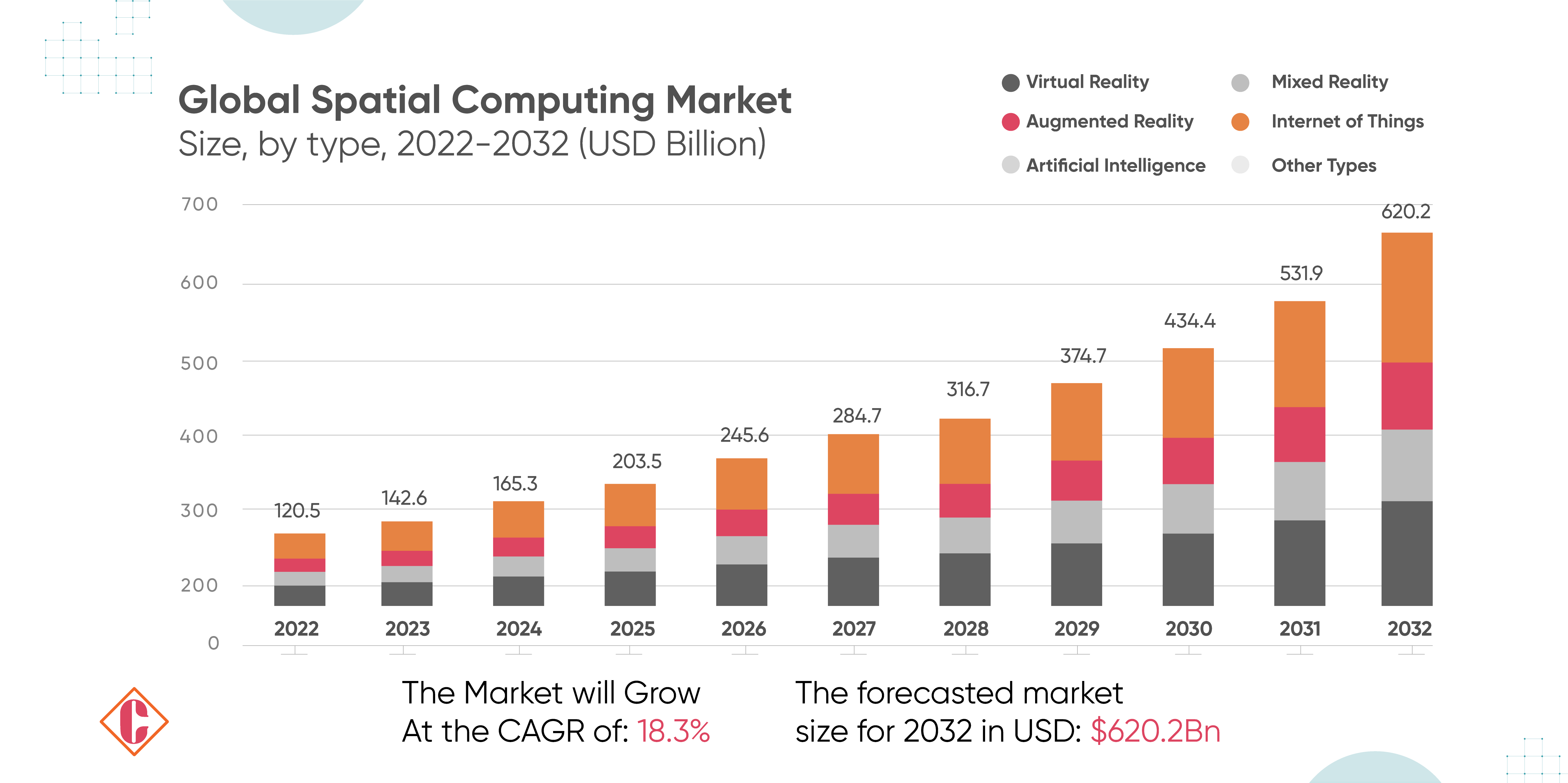
Spatial computing, encompass technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR), the spatial computing market is expected to grow at an annual rate of 18.30%, rising from $124 billion in 2023 to $620 billion by 2032. This growth constitutes approximately 4% of the global IT revenue, a substantial share of the $3.1 trillion total. According to the Market Research Report for Spatial Computing, businesses can strategically harness this growth. Europe anticipates an annual growth rate of 20%, while Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa expect a remarkable 25.1% annual growth between 2023 and 2032.
To capitalize on this spatial computing revolution, businesses must understand and leverage its opportunities, reshaping the landscape of services and digital interactions. Organizational leaders face critical challenges as these new platforms emerge and mature. Understanding spatial computing, its benefits, challenges, and applications for adoption is essential for effectively navigating this transition.
Defining Spatial Computing
What is Spatial Computing?
Key Components and Technologies
At the core of spatial computing are the core components of this transformative technology, which makes seamless integration between digital content and the physical world possible. This is at the core of development in applications redefining the digital landscape, making spatial computing one of the most pivotal elements in the evolution of interactive technologies.
Foundational Technologies
- AR and MR: The former is a technology overlapping digital information and rendering immersive experiences through the combination of virtual and physical worlds.
- AI and ML: Artificial intelligence enhances the accuracy of 3-D mapping and object identification, whereas machine learning algorithms like CNNs assist devices in making sense of their visual data and orientation.
- Computer Vision: It does object, people, and spatial structure recognition through visual data processing with the aid of algorithms like SURF and SIFT for object localization and tracking.
Interaction and Mapping Technologies
- Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM): Enables devices to create real-time maps of unknown environments, which is very important in navigation for AR and robotics.
- Natural interfaces with gesture recognition and NLP: Allow users to interact smoothly with digital overlays by using gestures and possible commands to control contents.
Development and Visualization Tools
- Unity 3D and Unreal Engine: These engines make it possible to create realistic 3D environments and, thus, limitless possibilities in virtual training and architectural visualization.
- ARKit and ARCore: integrated programming frameworks that help realize extremely engaging AR apps in a bid to bridge the gap between the worlds that computers generate and end-users.
Hardware and Sensors
- Camera Sensors and IoT Devices: These digitize three-dimensional data and offer further interconnectivity for spatial computing environments.
- Immersive User Interfaces: A head-mounted display offers intuitive and engaging user interactions with digital content, as do other physical controls in the case of spatial computing.
Also Read: How Can Modern Day CIOs Measure the ROI of their AI Initiatives
Applications and Use Cases
Manufacturing
Manufacturing was among the first industries to adopt spatial computing. XR devices assist assembly line workers by displaying virtual instructions during part assembly. Technical scans enable quality assurance associates to detect flaws before products are shipped, significantly impacting the bottom line. For instance, Lockheed Martin reduced some costs by 93% through the introduction of augmented reality.
Product Development
Designers and engineers have long used CAD programs to conceptualize new products. Spatial computing enhances this process by bringing 3D renderings off the monitor and into the physical world. MR headsets facilitate cross-continental collaboration for automotive designers at Volvo, allowing teams in Sweden, California, and China to interact with the same model simultaneously.
Retail
Retailers are incorporating XR into their physical spaces alongside AR apps like Amazon’s. For example, the Chinese clothing boutique Lily installed an AR display in a Shanghai train station. Commuters can try on clothes using their avatar and purchase items by scanning a QR code, all without entering the store.
Architecture and Design
Spatial computing provides architects with new opportunities for exploration. Augmented reality allows precise placement of windows to optimize natural light at different times of the day and harmonizes designs with the surrounding environment. Researchers at a Spanish university used AR to construct a vaulted brick structure without forms or guides, enhancing safety through real-time AR-enabled structural monitoring.
Workforce Training
Spatial computing offers a safe environment for trial-and-error learning, crucial in high-stakes fields. At the University of Cambridge, medical students use real scalpels on virtual patients, with mixed-reality headsets providing real-time feedback. This hands-on experience builds muscle memory and shortens reaction times, which are critical advantages for future medical professionals.
Benefits of Spatial Computing
Optimizing Productivity and Efficiency
- Enterprise Processes: Spatial computing aligns programming to the way humans think through the designing of new physical work flows and auto generation of digital twins. This gives reduced employee training time and allows enhancement of how physical facilities are planned.
- Manufacturing: Spatial computing enabled a 20% increase in productivity from manufacturing in 2023 as it streamlines design, assembly as well and maintenance processes.
- Healthcare: In 2023, spatial computing applications have enhanced the efficiency of the work in healthcare by over 30%, which has improved patient care and training.
Advanced Training and Simulations
Spatial computing transforms education, making learning truly interactive, intuitive and inclusive by enhancing knowledge transfer.
Improved Customer Engagement and Brand Experiences
- Retail: Spatial computing changes retail cushioned through virtual try-on and virtual showroom experiences, which increases impressively customer engagement and satisfaction.
- Entertainment: The VR and AR technologies are also used in the entertainment sector administratively; for instance, 70% of the new video games will contain elements of spatial computing by 2024 end.
Innovative use cases in other sectors
- Urban Planning and Smart Cities: spatial computing allows the development of smart cities on urban planning through designing and visualization tools; for instance, the ARC helps in planning buildings for smart cities.
- Automotive: Innovations such as augmented reality dashboards and advanced driver assistance systems are revolutionizing the experience of driving from both inside and outside vehicles.
New Challenges Brought by Spatial Computing
Spatial computing represents a new field in technology. It consists of many technologies and devices. With every new paradigm, as has been the habit, come special challenges.
Virtual Air Rights
Bringing spatial computing to real world raises questions of “virtual air rights.” More precisely, ownership and control of the air space that surrounds people. Who gets to put up advertisements? Who controls what audio plays in shared spaces? The greater the implications of virtual air rights, the more boundless they are—significant for every person.
Talent and Workforce Implications
Spatial computing will impact not only the nature of work but also the kinds of talent that companies require. Companies have to connect with a new generation of workers who grew up as digital natives. Generation Alpha, born when digital interactions are as real as those in the physical world, will be especially influential. What this new generation of workers and citizens brings to the table are completely different expectations of how to engage digitally—immersed in both gaming and virtual world-building through Minecraft and Roblox.
Gen Alpha adjustment
Business leaders need to enter their world of mixed reality if they are going to engage and retain the youngest customer demographic. Understanding these digital pursuits and this entrepreneurial spirit is necessary for companies wanting to hire, retain, and train professionals who will maneuver an evolving technological landscape; future success will depend on engaging with this generation on their terms.
Spatial Computing Innovations
Apple Vision Pro
Recently, Apple released the Apple Vision Pro, which realized its entry into spatial computing devices. The device allows attendants to interact with digital content using unobtrusive eye and hand motions, interacting naturally. This invention mirrors their commitment to innovations that create increased interrelation between physical and natural atmospheres.
Also Read: The Rise of Quantum Computing in Enterprise IT
AWS Spatial Computing
AWS offers cloud-based services to developers to create, build, and deploy space applications across augmented reality, virtual reality, and 3D technologies. It democratizes spatial computing with accessible development tools for more people.
Top Spatial Computing Companies
Apple
Meta
Microsoft
Magic Leap
Unity Technologies
Qualcomm Technologies
Nvidia
Final Thoughts
As technology improves, spatial computing devices will grow and become more efficient in energy requirements, accelerating their adoption. Spatial computing is not about creating a substitute, that is a virtual world, for our real world. In the words of Alan Kay, it changes our relationship with technology. It enables us to move away from static devices and puts the focus back on the world around us; all the while, technology integrates into the background seamlessly.
Spatial computing also warrants interest from a broad stakeholder community. C-suite executives, especially the Chief Information Officer, Chief Technology Officer, Chief Information Security Officer, and Chief Marketing Officer, are extremely important in setting directions and driving adoption within organizations. Cross-functional R&D, marketing, sales, and innovation units drive the full potential of spatial computing toward value creation and competitive advantages.
With innovations springing up in an increasingly competitive environment, spatial computing will be critical if a CIO or any other IT leader wants to get ahead—using the technology to drive innovation, enhance efficiency, and unlock new avenues of growth and success.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to psen@itechseries.com]


