Managing multiple cloud services can sometimes feel like trying to juggle a dozen balls while balancing on a unicycle. If you’re deep into the world of cloud computing, you’ve likely come across Software Defined Cloud Interconnection (SDCI) and Network as a Service (NaaS). These aren’t just trendy tech terms—they’re game-changers for how businesses are connecting their cloud environments, data centers, and networks. But what do they really mean, and why are they so important?
Also Read: CIO Influence Interview with, Corinne Koppel, Global Oracle Practice Lead, IBM Consulting
For companies embracing hybrid and multi-cloud architectures, SDCI is quickly becoming the go-to solution for private cloud connectivity. And with good reason: Gartner predicts that by 2027, 30% of enterprises will use SDCI services to connect to public cloud providers, up from less than 10% in 2022. This shift highlights the growing need for more agile, predictable, and high-performance cloud connections—something traditional internet-based interconnects can’t always deliver.
To understand where SDCI and NaaS fit into the picture, let’s take a step back. In the late 1990s, running networking hardware in-house was a major headache. It was expensive, and even second-hand equipment didn’t come c****. Plus, you had to deal with wiring and hire skilled tech teams to keep everything working, which put a huge strain on IT budgets and staff.
Then came cloud computing, which helped ease some of these burdens by shifting basic storage and connectivity to centralized third-party servers. This marked the start of large-scale virtualization, bringing down hardware costs and making maintenance a bit more manageable.
Fast forward to today, and we have NaaS and SDN as key players in this landscape. Yet, many people mix these terms up, often using SDN when they really mean NaaS. So, what sets them apart, and why should you care? Let’s break it down and explore how these technologies can make cloud management simpler and more effective.
What is SDCI?
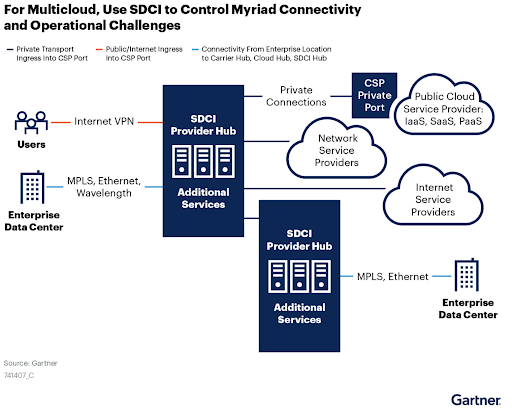
Understanding How SDCI Operates
SDCI providers offer a network of geographically distributed and interconnected physical points of presence (PoPs) that allow customers to create a dedicated network segment, known as the middle mile.
Customers can streamline network traffic by directing it to the nearest PoP, utilizing dedicated bandwidth from the underlying infrastructure. This setup can be tailored to specific user needs, applications, performance standards, and security requirements for both site-to-cloud and site-to-site connections.
Offered as a service, SDCI can be seamlessly integrated into existing software-defined workflows for deployment and management.
Also Read: One-Time Password Malware Poses a Serious Threat to Your Device Security
Benefits of SDCI
- Flexibility: SDCIs support site-to-cloud and site-to-site connectivity for various location types, including offices, branches, and data centers. Connectivity can utilize any transport type, such as satellite, internet, MPLS, or 5G/LTE, for last-mile connections.
- Visibility: Configured with SD-WAN, SDCI enables comprehensive monitoring and control of network traffic through the SD-WAN fabric, reducing blind spots. Traffic is swiftly shifted from the public internet to the SDCI provider’s secure backbone, ensuring end-to-end visibility and reliable monitoring from source to destination.
- Management and Analytics: Integrating SDCI with an SD-WAN overlay provides centralized management through a single-pane-of-glass interface. This allows for automated circuit deployment, end-to-end security segmentation, and network policy management, along with complete visibility and underlay monitoring.
- On-demand Connectivity: SDCI’s software-defined model enables the provisioning of new connections within minutes, significantly faster than the days or weeks needed for deploying a traditional dedicated backbone or physical network components.
- Agility: SDCI offers on-demand connectivity, straightforward management through SD-WAN fabric, and compatibility with any cloud or data center. This flexibility and cost-effectiveness allow enterprises to expand, contract, or adjust their network as goals and conditions change.
- High Performance: Unlike internet traffic that may pass through multiple hops and providers, potentially increasing latency, SDCI provides dedicated pathways exclusive to an enterprise’s data. This isolation ensures faster transmission speeds and lower latency, delivering a reliable, high-performance network experience.
- Lower Costs: The pay-as-you-go model of SDCI reduces capital expenditure (CapEx) and offers long-term flexibility compared to traditional network providers. Direct integrations with cloud service providers allow SDCI vendors to offer lower data egress rates, passing cost savings on to customers.
What is NaaS?
Integrating SDCI and NaaS for Enhanced Network Efficiency
The combination of SDCI and NaaS offers businesses a robust, cost-effective networking strategy. SDCI lays down the infrastructure for connectivity, while NaaS manages the services that run on that infrastructure. Think of SDCI as creating the highways and NaaS as the vehicles navigating those routes.
For instance, if a company operates applications across AWS, Azure, and an on-premises data center, SDCI ensures secure, high-speed connections between these locations. NaaS then oversees bandwidth allocation, security, and VPNs, maintaining seamless operations without the need for additional hardware.



