The global data storage market has seen remarkable growth, valued at USD 186.75 billion in 2023 and expected to rise to USD 774.00 billion by 2032, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.1% according to Fortune business insights. This surge reflects the expanding role of data in driving business operations, innovation, and decision-making. North America, a key player in this growth, accounted for USD 78.98 billion in market value in 2023, solidifying its position as a leader in data storage innovation.
Data storage has evolved beyond simple archiving. It is now a critical function, ensuring secure, efficient, and scalable access to digital information for future use. Rapid advancements in storage technology, especially in the adoption of Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Nonvolatile Memory Express (NVMe) devices, are transforming the landscape. These high-speed, durable solutions outperform traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), meeting the growing demand for faster and more reliable data storage.
This technological shift opens new opportunities for storage vendors, enabling them to offer cutting-edge solutions that align with the increasing need for data-intensive applications. As businesses continue to prioritize high-performance storage systems, the sector is poised for unprecedented growth.
Also read: Data Storage and AI: Bridging the Gap with Data Orchestration
Why Are Organizations Moving from On-Premises to Cloud?
As data storage needs evolve, organizations are increasingly shifting from traditional on-premises infrastructures to cloud-based environments. This migration allows businesses to transition their digital operations from physical, locally maintained servers to the cloud, where they can leverage the enhanced capabilities of cloud providers. Key benefits such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency drive this change, aligning closely with the growing data demands of modern enterprises.
Cloud migration offers organizations the ability to dynamically scale storage and computing power based on demand, unlike the fixed capacity of on-premises servers. This adaptability is crucial for businesses handling large volumes of data, as it provides the infrastructure necessary to support real-time analytics, AI, and other data-driven processes. Moreover, cloud platforms reduce capital expenditure by eliminating the need for expensive hardware upgrades and maintenance, shifting costs to a more predictable operational model.
This shift to cloud solutions directly ties into the broader context of data storage trends. As businesses grapple with the explosion of data, cloud-based storage solutions are emerging as the most viable option to ensure agility, performance, and future-proofing in a fast-paced digital landscape.
Understanding Cloud Data Warehousing
What is a Cloud Data Warehouse?
A cloud data warehouse is a centralized, cloud-hosted repository designed to store, manage, and process vast volumes of data. Unlike traditional on-premises databases, a cloud data warehouse leverages cloud computing to offer enhanced flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. This allows organizations to manage and analyze data efficiently, regardless of location.
Cloud data warehouses enable the integration of data from various sources, facilitating comprehensive analytics and reporting. By harnessing the power of the cloud, businesses can optimize data storage, improve decision-making through real-time insights, and ensure data integrity and security. This evolution in data management offers a cost-effective and scalable solution, meeting the growing data demands of modern enterprises.
Key features
High-Performance Architecture with Massively Parallel Processing (MPP)
Cloud-based data warehouses optimized for large-scale data projects leverage MPP architectures to ensure efficient handling of vast data volumes. MPP involves multiple servers working in parallel, distributing processing and I/O workloads to execute high-performance queries with maximum efficiency.
Optimized Storage through Columnar Data Models
These MPP architectures typically employ columnar storage, offering greater flexibility and cost-effectiveness for analytical workloads. By storing data in columns rather than rows, columnar databases significantly accelerate aggregate queries, a critical function in reporting and business intelligence.
Key Business Drivers for Adopting Cloud Data Warehouses
Cost Efficiency
Cloud data warehouses eliminate the need for significant investments in hardware, maintenance, and dedicated personnel. Companies no longer require additional physical storage space for expanding data, as cloud providers offer flexible, on-demand pricing models. This pay-as-you-go approach allows businesses to procure storage and compute power only when needed, minimizing costs during periods of low demand. As a result, organizations reduce networking and hardware expenses while potentially lowering their dependence on server rooms.
Storage Flexibility
One of the most compelling advantages of cloud data warehouses is their ability to scale storage dynamically in response to business needs. Unlike traditional methods that required businesses to estimate and purchase storage in advance, cloud solutions offer seamless expansion without the need for pre-planning or procurement. This adaptability ensures that companies can adjust storage capacity in real time, addressing unpredictable data growth without operational disruptions.
Enhanced Data Security
Cloud data warehouses offer superior security measures compared to on-premises solutions. With no physical infrastructure on-site, the risk of physical theft is eliminated. Additionally, cloud providers implement advanced encryption, rigorous internal controls, and security protocols to safeguard sensitive information from external threats and cyberattacks. These measures ensure that businesses can maintain robust data protection while meeting compliance requirements.
Also Read: Cloud and AI: Data management and data protection are primary pain points for CIOs and CISOs
Real-Time Data Insights
Cloud data warehouses enable businesses to process and stream data in real time, providing a crucial edge in dynamic markets. With advanced computing capabilities, companies can integrate multiple data sources effortlessly, allowing for automatic adjustments to data volumes. This seamless integration enhances the accuracy of business intelligence, supporting swift and informed decision-making.
Seamless Data Integration
As data volumes increase, businesses require efficient data integration for analytics and business intelligence. Cloud data warehouses excel in this area, offering seamless compatibility with third-party data integration tools. Processes such as data cleansing, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) mapping, and transformation become more efficient, allowing organizations to integrate structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from various cloud platforms and sources. This integration capability empowers users to build tailored data warehouses that align precisely with business needs.
Cloud Data Warehouse vs. Traditional On-Premises Data Warehouse
Criteria |
Cloud Data Warehouse |
Traditional On-Premises Data Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Hosted on the cloud, eliminating the need for physical hardware. | Requires significant investment in physical servers and hardware. |
| Scalability | Instantly scalable to meet fluctuating demands. | Scaling requires purchasing, installing, and maintaining new hardware. |
| Cost Model | Operates on a pay-as-you-go subscription model. | Involves substantial initial capital outlay and ongoing maintenance costs. |
| Accessibility & Collaboration | Accessible from any location, allowing real-time collaboration. | Limited to on-site access, making remote collaboration challenging. |
| Maintenance & Management | Managed by cloud providers, minimizing internal resource allocation. | Requires dedicated personnel for hardware maintenance and management. |
| Disaster Recovery | Automatic backups with easy recovery in case of data loss. | Backup and recovery systems are often manual and costly to manage. |
| Implementation Time | Rapid deployment with minimal upfront setup. | Lengthy setup process involving procurement and installation of hardware. |
Accelerating Efficiency with Cloud Data Warehouse Automation
Cloud data warehouse automation is transforming the way businesses manage their data environments by streamlining the entire data lifecycle. Modern data integration platforms now offer automated solutions that significantly enhance the speed and efficiency of data management, enabling businesses to access analytics-ready data much faster than traditional methods. This automation leverages a model-driven approach, empowering data engineers to design, deploy, and manage cloud data warehouses with greater agility.
Key features driving this productivity boost include:
- Real-Time Data Ingestion and Updates: The ability to ingest and update enterprise data in real-time, ensuring that cloud data warehouses always reflect the most current information.
- Automated Workflow Management: Using a model-driven approach, these platforms continuously refine and optimize data warehouse operations without manual intervention.
- Enterprise-Grade Data Sharing: Secure data catalogs allow businesses to share trusted, enterprise-ready data marts seamlessly across teams, supporting more effective decision-making.
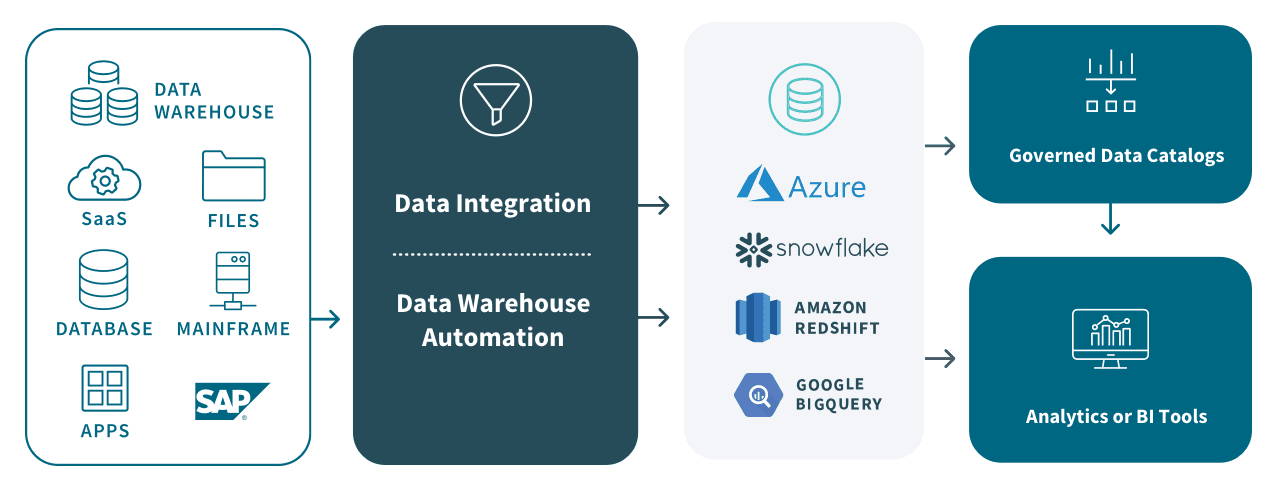
Cloud Data Warehouse Vendors
Amazon Redshift
BigQuery
Snowflake
Azure Synapse Analytics
Teradata
Cloudera Altus
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Cloud Data Warehouses
- Cloud Data Warehouses are More Expensive Many assume cloud data warehouses are costlier than on-prem solutions due to subscription fees. However, cloud offerings eliminate upfront capital investments and ongoing maintenance costs. They provide elasticity, cheaper storage, and cost transparency, allowing better control over expenses. Organizations following best practices can achieve significant savings and revenue growth.
- Cloud Data Warehouses Lack Security and Compliance Concerns about cloud security are common, especially in regulated industries. However, cloud providers now meet rigorous standards like SOC2, PCI, HIPAA, and GDPR. Providers also manage security and compliance updates, ensuring ongoing regulatory adherence.
- All Data Warehouse Migrations Are the Same Migrating to the cloud can be complex, requiring replication, optimization, and re-architecture. A hybrid-cloud strategy with an existing vendor can simplify migration, minimize disruptions, and distribute workloads across on-prem and cloud environments.
- Misconception: Cloud Migration Must Be All-or-Nothing Companies often feel pressured to fully migrate to the cloud. A hybrid-cloud approach allows for selective migration, letting organizations balance cloud scalability with the control and security of sensitive on-prem workloads.
- Misconception: Cloud Warehouses Reduce Control Some believe cloud data warehouses lack the control of on-prem solutions. However, modern cloud platforms offer advanced features like failover, automated backups, and high availability. Rather than replacing DBAs, cloud systems free them to focus on high-value tasks like performance tuning and system integration.
Considerations for Cloud Data Warehouse Migration
Migrating to a cloud data warehouse is a strategic decision that requires careful planning. Evaluating key factors will ensure a smooth, cost-effective migration aligned with your business objectives.
Key considerations when migrating your data warehouse to the cloud:
1. Data Relevance and Prioritization
- High-Value Data: Focus on frequently accessed datasets that drive business value. Prioritizing these ensures a streamlined migration.
- Legacy Data: Older or less-used datasets can be archived or kept on-prem until necessary, reducing the migration load.
2. Data Integrity and Quality
- Data Consistency: Ensure data is clean and validated to avoid bringing errors into the cloud.
- Deduplication: Eliminate duplicate data to save on storage costs and prevent confusion during cloud operations.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
- System Interactions: Consider how your data integrates with current applications. Ensure integrations are either maintained or reconfigured for cloud compatibility.
- API and Endpoint Support: Verify that your cloud environment can support existing API connections and external data exchanges.
4. Security and Compliance
- Sensitive Data Protection: Ensure robust security measures are in place for migrating sensitive or personal data to the cloud.
- Regulatory Compliance: Check that your migration complies with industry regulations governing data storage and processing.
5. Cost Management
- Storage Costs: Cloud pricing is typically based on data volume, so avoid migrating unnecessary data to keep costs down.
- Migration Expenses: Some data, especially large or complex datasets, may be costly to migrate. Weigh the benefits of moving this data against the associated costs.
Conclusion
The adoption of cloud data warehouses is on the rise, projected to grow at a CAGR of nearly 15%. To capitalize on this trend, business leaders must refine their cloud strategies and harness the advantages of an evolving cloud ecosystem. By doing so, organizations can leverage the power of business intelligence and integrate emerging technologies such as edge computing and AI/ML. This strategic approach will enhance their capacity to enter new markets and deliver significant competitive advantages.
Cloud data warehouses signify a crucial advancement in data management, providing unmatched scalability, flexibility, and performance. As businesses increasingly depend on vast amounts of data, embracing cloud data warehousing becomes essential for deriving insights, fostering innovation, and sustaining a competitive edge. By comprehending the architecture, benefits, use cases, and future trends of cloud data warehousing, organizations can make informed decisions that fully exploit its potential, ultimately achieving their data-driven objectives.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to psen@itechseries.com]


