Test data management is often overlooked but vital for testing success. It is used in complex projects that are critical to optimize. QA teams require varied test data for better coverage. Test data management excels at separate storage, which is essential for proper management and setup.
SDLC Partners report states that QA professionals dedicate more than 30% of their testing time to handling faulty test data. On average, they invest 5 to 15 hours per week in managing test data-related tasks, amounting to at least one day per week lost to provisioning issues.
What is Test Data Management?
Test data management involves planning, creating, and maintaining datasets for testing to ensure they are relevant, formatted, and available. Testing data encompasses input values, which may require application testing with an eye on simulating real-world user scenarios. Test scripts are often used to automate value selection and system response assessment.
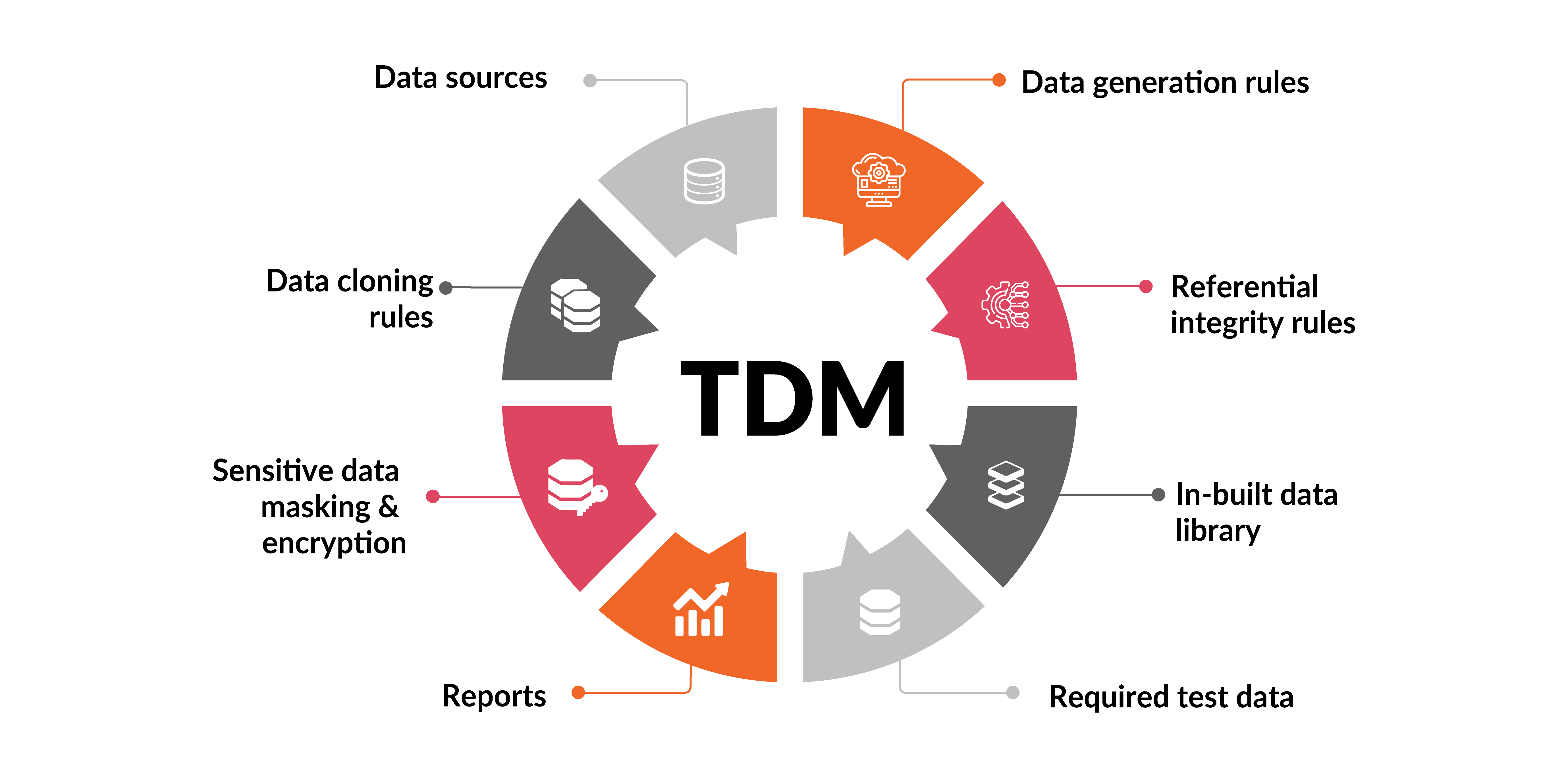 Test data are input values used during testing to implement various applications, such as software, web, mobile apps, and APIs. Testers write scripts that generate such input values to simulate real user actions and observe system responses.
Test data are input values used during testing to implement various applications, such as software, web, mobile apps, and APIs. Testers write scripts that generate such input values to simulate real user actions and observe system responses.
Characteristics of Test Data Management
 What Test Data Management Tools Can Do?
What Test Data Management Tools Can Do?
Test Data Management has several crucial functions ingrained in the process. It helps organizations with:
1. Coordinating Data Sources
These tools aid in coordinating data from all sources, including production, versioning copies, and the rest.
2. Discovery and Management of Sensitive Data
Test data management tools help to discover and manage sensitive data. They allow CIO and CISO teams to use security features such as data masking, authorization, authentication, and finely tuned data access management.
3. Compliance with Regulations
These tools allow organizations to quickly meet compliance and data privacy regulations through features like compliance masking and audit logs.
4. Multicloud Distribution
Test data management tools allow the distribution of test data across multiple cloud environments, enabling agile development and automated testing.
Key Indicators of Quality Test Data
When monitoring test data quality, there are four key aspects to consider:
1. Relevance: Test data must truly represent the situations being tested. Inappropriate data will yield wrong results, such as logins that test incorrect user identification and password details.
2. Availability: Test data must be readily available and accessible. Test data should be available for testing activities, and access rights should be assigned to the relevant personnel.
3. Updates: Test data should reflect the software’s change. As the software changes, so does the test data, ensuring accuracy and relevance for testing purposes.
4. Compliance: Test data must comply with regulatory practices when testing. Production data is convenient but often contains sensitive information regulated by GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI rules. Compliance should be in place to avert data privacy issues.
Significant Test Data Management Challenges
The following are the significant obstacles that an effective test data management process faces:
1. Access to Test Data: Enterprise data can be far-flung and disbursed across various sources, making it hard for teams to access the required data for their tests in the shortest time possible.
2. Down-Subsetting Test Data: Consolidating large datasets into smaller, more focused subsets is essential to undertake comprehensive testing while keeping costs down.
3. Data Privacy Data Protection: Test environments must comply with stringent data privacy regulations, and masking sensitive information promptly can be daunting.
4. Maintaining Referential Integrity: To ensure that test data is valid, One must maintain consistency across data in various databases and tables.
5. Adequate Test Data Availability: Adequate test data availability ensures comprehensive testing coverage and low defect density.
6. False Positives and False Negatives: Test data can cause false positives or negatives, adversely affecting the software’s quality and efficiency.
7. Reusing Test Data: Efficiently reusing test data is important for several purposes, such as regression testing and verifying fixes to defective software.
8. Data Overwrites: The accidental overwriting of test data must be prevented because overwritten data can be corrupted, and re-provisioning and re-running tests can be time-consuming.
Best Practices for Effective Test Data Management
Test data management is sometimes challenging to manage in an agile environment. Maintaining the following best practices is advisable:
- Work on data security
- Real data should be kept separate from test data.
- Application security should be emphasized.
- Implement automated processes for data management.
- Use a centralized repository for data refreshment.
- Data analysis should be done regularly to update promptly.
Best Test Data Management Tools
#1 Delphix
Delphix, a test data management platform, helps populate test environments with accurate and amendable test data. Delphix offers benefits including powerful masking capabilities, version control for data sets and virtual test data provisioning. The platform also integrates several tools and data sources with a user-friendly interface.
The
Delphix offers:
- Data control tower
- Continuous data
- Continuous compliance
- Elastic data
- Sources
- Integration
#2 Broadcom Test Data Manager
Broadcom Test Data Manager can locate, design, secure, create and provision ‘fit for purpose’ test data. This data is for the efficient, cost-effective test cycles needed to deliver applications faster. This tool can also enhance the quality of production data by filling gaps in test data coverage and creating all the data needed to cover continuous testing requirements fully.
Features:
- Sensitive data identification
- Synthetic test data generation
- Storing and reusing existing data
- creating virtual copies of test data
#3 DATPROF
Datprof is one of the test data management tools that helps simplify and streamline the data creation and representation of the test data process.
Features of Datprof allow:
- Generate diverse datasets that are accurate
- Enhance software testing efficacy
- Allow random generation
- Support a wide range of data types
#4 IBM InfoSphere Optim
IBM InfoSphere Optim Test Data Management helps create and manage a nonproduction data-making process more effectively and efficiently. Better testing approaches help Optim Test Management identify problems faster, reducing the risks involved in application failures that result from test data errors and inconsistencies. It optimizes all stages of application testing.
Features:
- Manages data at the business-object level
- Accesses data analysis capabilities
- Enforces test data management policies
- Automates data comparisons and analyzes results
#5 Tricentis
Tricentis identifies and resolves some of the most common problems of test data management. This test data management tool’s built-in structure aligns the development team with the operations, tools required, and software tests planned.
Features:
- Seamless integration with the JIRA cloud
- Visual test data management dashboard
- Offers a paid version called qTest Enterprise for enterprise-level services
- Allows test data management for multiple software at once
#6 Informatica Test Data Management
 Informatica Test Data Management Tool provides automated data subsetting, connectivity, masking, and test data generation capabilities. It also helps detect sensitive data locations automatically.
Informatica Test Data Management Tool provides automated data subsetting, connectivity, masking, and test data generation capabilities. It also helps detect sensitive data locations automatically.
Offerings:
- A non-production dataset that completes the requirements of the development team.
- Integrated sensitive data discovery that increases the security of test data.
#7 K2view
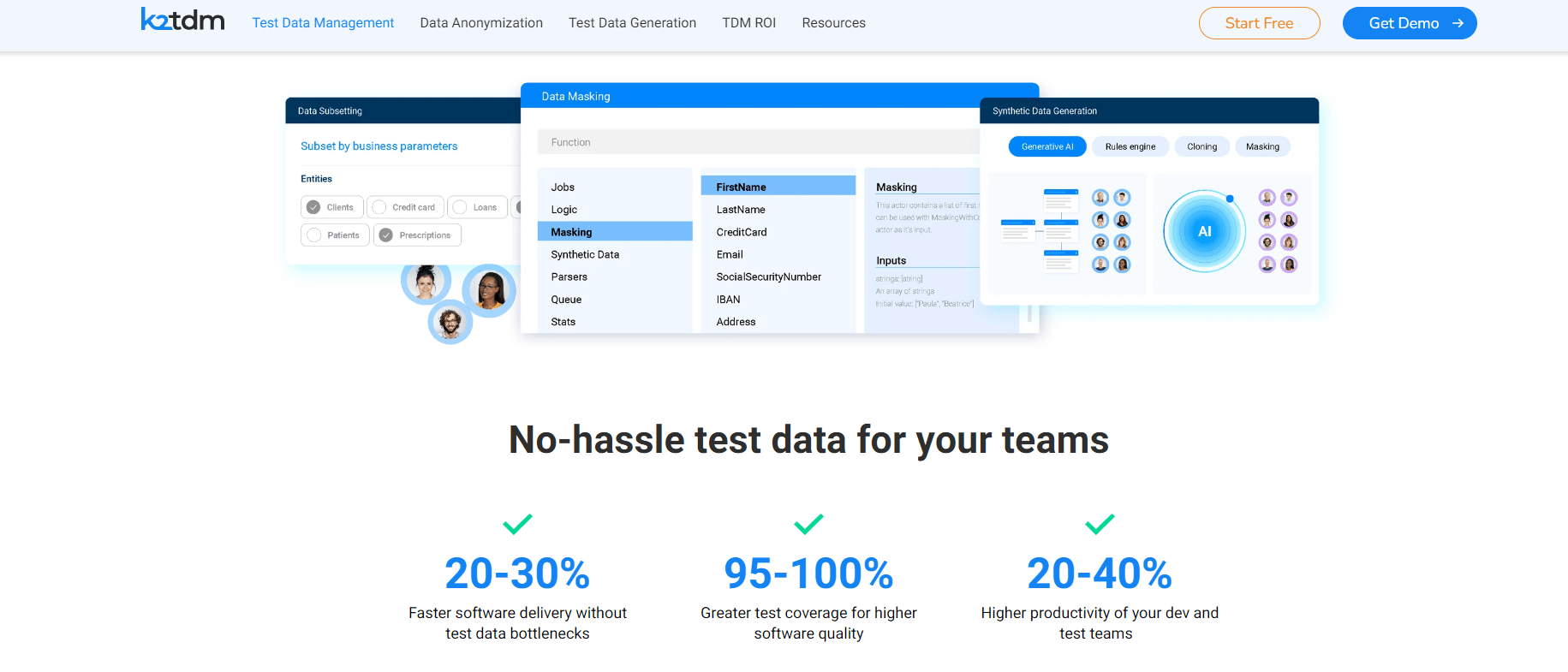 K2View is a leading test data management solution for complex environment enterprises. Testers can quickly provision test data subsets on demand from any number and type of production source while preserving referential integrity. Extensive API-enabled integration into DevOps CI/CD automation pipelines.
K2View is a leading test data management solution for complex environment enterprises. Testers can quickly provision test data subsets on demand from any number and type of production source while preserving referential integrity. Extensive API-enabled integration into DevOps CI/CD automation pipelines.
Features:
- Self-service provisioning
- Any data source
- In-flight data masking
- Synthetic data generation
- CI/CD pipeline integrations
#8 Solix
Solix automatically creates test data subsets for development, testing, patching, masking, outsourcing and training. The test data management tool also creates and manages clone production data subsets from large databases. The clone production is created according to the rules defined by the organization. It helps reduce time and infrastructure costs by up to 70%.
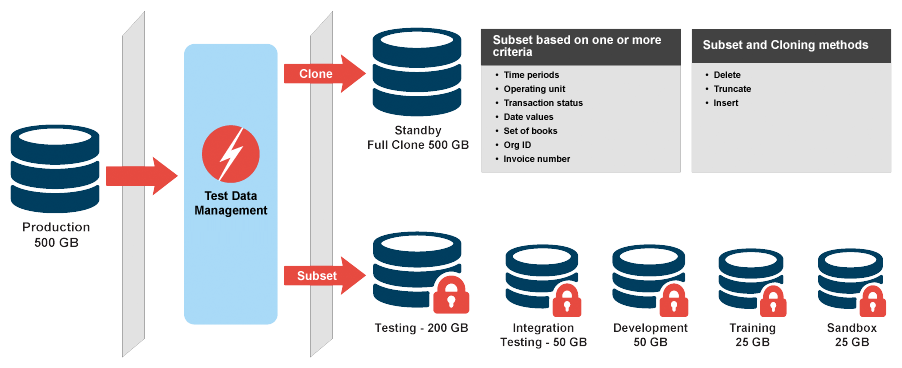 Features:
Features:
- Configure subset creation
- Multiple subset functions, including space reclamation
- Out-of-box support for popular applications
- Secure sensitive data
#9 AVO Automation
AVO Automation is the only test data management platform that delivers production-like test data with enterprise-level scalability. The tool prioritizes staying compliant with ever-evolving data privacy regulations and focuses on providing AI/ML-based synthetic data.
Products:
- Ai/ML Test Data
- Data Discovery
- Data Obfuscation
#10 BMC
BMC AMI DevX Data Studio provides capabilities to help users understand large amounts of data. Its simplified interface makes it easy to compare and identify the impact of changing data.
Benefits:
- Increases data integrity based on referential integrity or application relationships
- Mask sensitive test data to enable better application quality
Final Thoughts
In most cases, the testing team responsible for creating test data does not have direct access to the production data. When the production data is provided, it is a pile of raw data. The raw data cannot be used directly for testing purposes. The data needs filtration, and tailored data is then used. Good-quality data is expected for good-quality software testing. The average data will not provide sufficient results. To overcome this problem, a test data management process or solution is used.
In addition, Agile and DevOps reduce the duration of each testing cycle. This helps create high-quality data and reduces cost, time, and effort. It also enhances customer satisfaction and trust.
FAQs
1. What role does DevOps play in Test Data Management?
DevOps in test data management automates test data collection, delivery and management by integrating a DevOps pipeline. It speeds up testing by enhancing cooperation between testing and development teams. When DevOps pipelines are embedded in test data management, enterprises can manage the large amounts of data generated during testing.
2. How is test data management aligned with the software development life cycle?
Test data management plays a vital role in the software development life cycle. It starts with creating test data and continues until tests are executed. Automating test data management improves agile software delivery and expands regression testing coverage.
3. What are the types of test data?
There are four common types of test data being used, it includes:
- Data Subsets
- Masked data subsets
- Production data copies
- Synthetic data
4. What are the advantages of test data management?
- Better application of data with fewer defects.
- Improved data quality with clean and accurate test data.
- Data availability and accessibility can be achieved quickly with the automation process.
- More protected data with synthetic data generated that mimics real data but protects privacy.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]



 What Test Data Management Tools Can Do?
What Test Data Management Tools Can Do?