Over 70% of organizations struggle with security debt, with nearly half facing “critical” levels. The State of Software Security 2024 report highlights third-party code, especially from open-source libraries, as a major culprit, accounting for two-thirds of critical debt. Remedying third-party flaws takes 50% longer, but agile development teams can cut critical security debt by 4x.
Veracode, a leading figure in intelligent software security, has just released its annual State of Software Security (SoSS) 2024 report, offering insights into the critical issue of security debt within applications. This report defines security debt as unresolved flaws persisting for over a year, found in 42% of applications and impacting 71% of organizations. Alarmingly, 46% of these organizations are plagued by severe, long-standing vulnerabilities constituting ‘critical’ security debt, posing significant risks to business integrity, confidentiality, and availability.
Findings reveal that 63% of applications contain flaws in their first-party code, while 70% harbor issues within third-party code imported via external libraries. This underscores the importance of comprehensive testing throughout the software development life cycle. Remediation rates differ by flaw type, with fixing third-party flaws taking 50% longer, half of these being resolved after 11 months compared to seven months for first-party flaws.
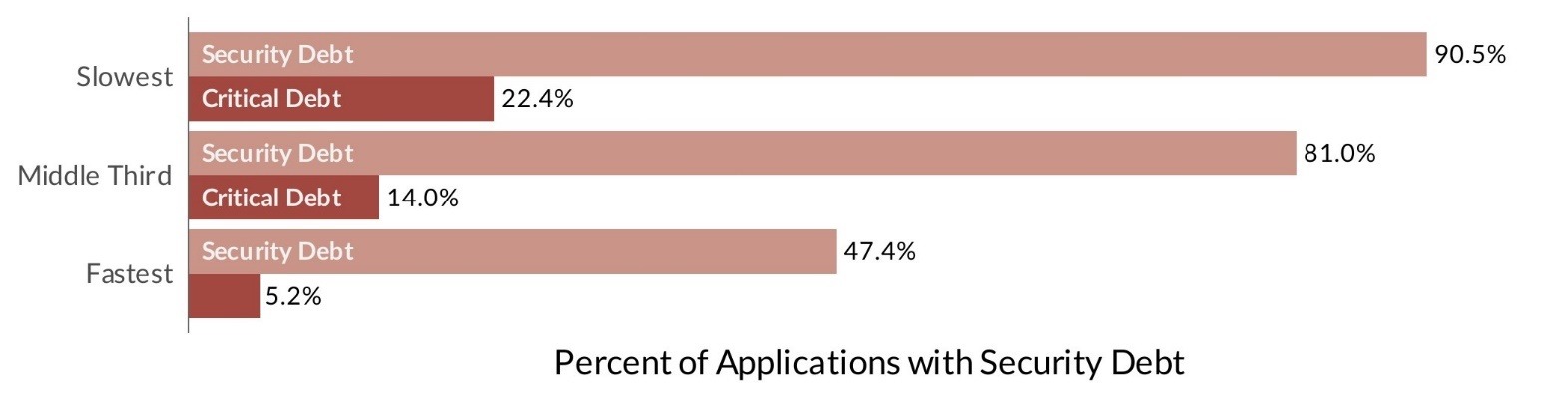
Despite these challenges, there’s a positive trend: high-severity security flaws have halved since 2016, signaling advancements in software security practices and the tangible impact of speedy remediation of critical security debt. Teams that swiftly address flaws can slash critical security debt by 75%, reducing its prevalence from 22.4% to just over 5% in applications. Furthermore, these proactive teams are four times less likely to allow critical security debt to accumulate in their applications.
“While we continue to see improvements in the security landscape, these findings are a wake-up call for organizations to address their security debt head-on. By prioritizing flaw remediation, focusing on third-party code security, and adopting efficient development practices, organizations can significantly reduce their security debt and enhance the overall state of software security across the board.” – CHRIS ENG, Chief Research Officer at Veracode
Navigating AI’s Impact on Software Development and Supply Chains
As technology evolves, the intersection of Artificial Intelligence and software development presents both opportunities and challenges. The SoSS 2024 report underscores a notable concern in this landscape. Chris Eng warns, “Despite AI’s expedited processes in software development, it doesn’t inherently guarantee secure code.” Research findings reveal a staggering 36% of code generated by GitHub CoPilot contains security flaws, raising alarms about the prevalence of insecure code within the software supply chain. This widespread issue poses significant risks to organizations, contributing to the accumulation of security debt over time.
Strategic Risk Management: A Crucial Imperative
Veracode’s investigation underscores the pivotal importance of prioritizing risks effectively within software security management. The research reveals a concerning limitation in remediation capacity among teams, with only 64% of applications possessing the necessary resources to tackle critical security debt effectively. Surprisingly, a mere two out of ten applications exhibit a monthly fix rate surpassing ten percent of all security flaws, indicating a systemic failure in prioritizing critical vulnerabilities.
Merely three percent of all flaws constitute critical security debt, representing the primary risk exposure for applications. By directing concerted efforts toward addressing this subset, organizations can achieve optimal risk mitigation.
Chris emphasizes, “AI opens new avenues in software security, enabling organizations to scale remediation efforts and address the extensive backlog of security debt and emerging vulnerabilities more efficiently. Veracode Fix utilizes AI-generated code edits to tackle the majority of CWEs (Common Weakness Enumeration) rated from medium to very high severity, ushering in a new era of proactive security management.”
FAQs
1. What exactly is security debt, and why is it a significant concern for organizations?
Security debt refers to unresolved vulnerabilities or flaws in software applications that accumulate over time. It becomes a concern for organizations because these unaddressed issues pose risks to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their systems and data. Left unattended, security debt can lead to potential breaches, financial losses, and damage to the organization’s reputation.
2. How does third-party code contribute to security debt, and what steps can organizations take to mitigate this risk?
Third-party code, especially from open-source libraries, contributes to security debt because it introduces vulnerabilities that may go unnoticed or unaddressed by the organization. To mitigate this risk, organizations can implement thorough code reviews and security testing procedures for third-party dependencies. Additionally, staying informed about known vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and promptly applying patches or updates can help reduce the security debt associated with third-party code.
3. What are the key findings of Veracode’s SoSS 2024 report regarding remediation speed and its impact on critical security debt?
Veracode’s SoSS 2024 report highlights that faster remediation of security flaws significantly reduces critical security debt within applications. Development teams that address flaws promptly can reduce critical security debt by up to 75%. This emphasizes the importance of prioritizing and accelerating the remediation process to mitigate security risks effectively.
4. How does AI influence software development and security, and what are the implications highlighted in the report?
AI plays a significant role in software development by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and enhancing decision-making processes. However, the report highlights a concerning trend where AI-generated code may contain security flaws. This poses risks to organizations as insecure code generated by AI tools, such as GitHub CoPilot, could contribute to security debt. Organizations need to be vigilant and implement measures to ensure that AI-generated code undergoes thorough security testing and review before deployment.
5. What strategies does Veracode recommend for prioritizing and addressing security debt effectively?
Veracode recommends that organizations prioritize the remediation of critical security flaws to effectively reduce security debt. By focusing on addressing the three percent of flaws that constitute critical security debt, organizations can achieve maximum risk reduction. Additionally, leveraging AI-driven tools, such as Veracode Fix, can help organizations scale their remediation efforts and address security debt more efficiently by automating code edits and addressing common vulnerabilities.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]