Introduction
Benefits of Using 5G in IoT
-
Higher Transmission Speeds:
With transmission speeds reaching 15 to 20 Gbps, accessing data, files, and programs on remote applications is significantly faster. Utilizing the cloud more extensively reduces reliance on internal device memory, prolonging sensor longevity. This enables the integration of various sensors capturing high-definition images and real-time motion, among other data types.
-
Increased Device Connectivity:
5G’s impact on IoT is evident in the ability to connect more devices to the network. All connected devices can communicate in real time, facilitating information exchange. For instance, smart homes feature numerous connected devices enhancing convenience and enjoyment through smart appliances, energy management, security systems, and entertainment devices. In industrial settings, thousands of connected devices streamline manufacturing processes, ensuring safety and security. The concept of building smart cities becomes feasible on a large scale.
-
Reduced Latency:
Latency, the time between issuing a command to a smart device and its execution, is significantly reduced with 5G, approximately ten times less than with 4G. Lower latency allows for increased sensor utilization in industrial plants, facilitating machinery control, logistics management, and remote transport operations. Additionally, healthcare professionals can remotely intervene in surgical operations with precision instrumentation managed from remote locations, thanks to lower latency provided by 5G technology.
Leveraging 5G for IoT Applications: Transforming Industries
In envisioning a new digital frontier, developers have conceptualized a world where groundbreaking applications of 5G technology intersect with the Internet of Things to revolutionize various sectors.
1. Remote Healthcare:
5G networks pave the way for remote healthcare solutions, enabling doctors to diagnose and treat patients in remote areas through telemedicine. With the potential for remote surgeries and real-time patient monitoring, healthcare outcomes could significantly improve, particularly for underserved populations lacking access to traditional medical facilities.
2. Remote Work Enablement:
The advent of 5G facilitates seamless remote work experiences, where professionals can deliver media-rich presentations from home without interruption. High-speed connectivity ensures productivity remains unhindered, fostering efficiency and flexibility in work environments.
3. Autonomous Driving and Traffic Management:
Autonomous driving, powered by 5G connectivity, holds promise in reducing accidents and alleviating traffic congestion. Smart transportation systems, enabled by IoT sensors and 5G networks, optimize traffic flow and enhance road safety, transforming the future of urban mobility.
4. Smart Grids and Energy Management:
5G-enabled smart grids offer solutions to eliminate brownouts and blackouts globally. Through real-time monitoring and data analysis, utilities can optimize energy distribution, detect faults promptly, and ensure a reliable power supply, contributing to energy efficiency and sustainability.
5. IoT Sensors for Enhanced Safety and Efficiency:
Ubiquitous IoT sensors, supported by 5G connectivity, play a pivotal role in various applications. These sensors facilitate vehicle parking and collision avoidance, monitor electrical systems to prevent fires, and enable remote patient health monitoring, underscoring their significance in preventing disasters and improving safety.
Enterprises stand to benefit from 5G’s capabilities in managing data with network slicing for private networks. This approach offers secure methods for data management, ensuring integrity and access control. The deployment of 5G networks holds immense potential to propel industries forward, enhancing productivity and efficiency across diverse sectors.
Additionally, 5G-enabled IoT solutions must accommodate a wide range of requirements, from low bandwidth applications to ultra-high bandwidth demands, all while enduring harsh environmental conditions and prolonged operational lifespans. Selecting the right technology partners becomes crucial in effectively leveraging the capabilities of 5G networks for IoT applications.
Security, Privacy, and Regulatory Concerns with 5G-Enabled IoT
While 5G promises a revolution in the IoT landscape, it also raises significant concerns regarding security, privacy, and regulatory compliance. Here’s an overview of the key issues and potential solutions:
Security
- Increased Attack Surface: More connected devices exponentially expand the attack surface, attracting malicious actors.
- Complex Network Infrastructure: 5G’s network slicing and edge computing introduces complexity, potentially creating vulnerabilities.
- Data in Transit and at Rest: Sensitive data needs robust encryption throughout its journey.
- Device Security Flaws: Many IoT devices have weak security measures, making them easy targets.
Privacy
- Data Collection and Use: Unclear data collection practices and unauthorized usage can violate user privacy.
- Surveillance and Tracking: Increased sensor deployment raises concerns about mass surveillance and individual tracking.
- Biometric Data: The use of biometric data for authentication poses unique privacy challenges.
- Lack of User Control: Limited user control over data collection and usage can lead to misuse.
Regulation
- Data Protection Laws: Existing laws may not adequately address new data types and use cases in the IoT.
- Global Coordination: Lack of harmonized regulations across countries can hamper trade and create confusion.
- Standardization: Clear standards are needed for security, privacy, and interoperability.
- Accountability and Enforcement: Mechanisms are needed to hold responsible parties accountable for breaches and misuse.
Potential Solutions
- Security by Design: Prioritize security throughout the design and development lifecycle of IoT devices and networks.
- Zero Trust Model: Implement a “never trust, always verify” approach to access control and data handling.
- End-to-End Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to protect against unauthorized access.
- Identity Management: Establish robust authentication and authorization protocols for devices and users.
- Data Minimization: Collect and store only the data necessary for specific purposes.
- User Consent and Transparency: Inform users about data collection practices and obtain explicit consent.
- International Cooperation: Collaborate on developing and enforcing harmonized regulations for data protection and privacy.
- Standardization Organizations: Develop clear standards for security, privacy, and interoperability across the IoT ecosystem.
- Independent Oversight: Establish independent bodies to audit compliance and investigate privacy violations.
Unlocking New Horizons with 5G for IoT
The emergence of 5G technology represents a significant leap forward for IoT, offering many opportunities for businesses to enhance their operations. With 5G, IoT applications that rely on rapid data analysis and real-time decision-making can realize tangible benefits through continuous high-speed communication channels. This heightened connectivity not only facilitates seamless data transmission but also enables swift response times, ultimately bolstering operational efficiency and productivity.
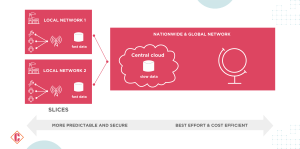 5G empowers IoT applications to tailor network characteristics according to their specific needs, providing unprecedented flexibility and adaptability. Technologies such as LTE-M and NB-IoT further enhance this flexibility by offering functionalities that optimize coverage and battery consumption. As 5G networks evolve, businesses will gain even greater control over service levels, data processing locations, and other critical parameters, thereby enhancing the capabilities of their IoT deployments.
5G empowers IoT applications to tailor network characteristics according to their specific needs, providing unprecedented flexibility and adaptability. Technologies such as LTE-M and NB-IoT further enhance this flexibility by offering functionalities that optimize coverage and battery consumption. As 5G networks evolve, businesses will gain even greater control over service levels, data processing locations, and other critical parameters, thereby enhancing the capabilities of their IoT deployments.
In addition to these advancements, complementary technologies such as network edge computing hold promise in further revolutionizing IoT capabilities. By decentralizing computing resources and running applications on distributed cloud servers closer to IoT devices, edge computing reduces latency and enhances data processing efficiency. This decentralized approach ensures faster response times and enables real-time decision-making, thereby maximizing the effectiveness of IoT solutions.
Impact of IoT on the Job Market
The introduction of 5G technology facilitates real-time communication and data exchange among vehicles, infrastructure, and pedestrians. 5G’s low latency and high bandwidth accelerate the adoption of autonomous vehicles, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and smart traffic management. By 2025, GSMA estimates that over 20% of 5G-enabled devices will be in the transportation sector.
1. Increased Demand for Technical Skills:
IoT adoption drives demand for professionals skilled in IoT development, data analytics, cybersecurity, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence. The design, development, and management of IoT devices and networks require specialized expertise.
2. Emergence of New Job Roles:
The rise of IoT creates opportunities for new job roles such as IoT architects, data scientists, IoT security specialists, and connectivity experts. Various industries seek professionals with specialized knowledge in IoT technologies.
3. Prioritization of Cybersecurity:
The proliferation of connected devices increases the risk of data breaches and cyber threats. Organizations prioritize cybersecurity to protect IoT networks and safeguard sensitive data, necessitating the expertise of cybersecurity professionals.
4. Adaptation of Existing Roles:
Existing job roles evolve to incorporate IoT skills and knowledge. Professionals in manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and other sectors need to upskill to effectively leverage IoT technologies in their respective domains.
5. Changing Skill Requirements:
Traditional job roles may require additional technical competencies as IoT technologies advance. Continuous learning becomes essential for employees to remain competitive in the evolving job market.
Conclusion
5G’s advancements in speed, capacity, and responsiveness hold potential for B2B IoT applications, enabling automation, efficiency, and innovation. However, this interconnected landscape also amplifies cybersecurity concerns, necessitating robust measures to mitigate risks. B2B decision-makers must prioritize security by design, integrating it across the entire IoT ecosystem. Embracing zero-trust principles, implementing robust encryption, and staying vigilant with threat intelligence are essential strategies to safeguard sensitive data and assets. Investing in skilled professionals proficient in IoT security is crucial for navigating the evolving threat landscape. In addition, proactive cybersecurity is no longer optional but essential for IoT success in the era of 5G. By taking decisive action, businesses can harness the transformative power of 5G while safeguarding their assets and data.
FAQs
1. How does 5G revolutionize the Internet of Things?
5G acts as the nerve center for your IoT network, monitoring everything from HVAC systems to water levels with ultra-fast responsiveness. This opens a vast market for 5G IoT monitoring devices and empowers AI-driven industries to seamlessly integrate intelligence into connected systems.
2. What benefits does 5G bring to IoT?
Get ready for lightning-fast speeds, immense data capacity, and near-instantaneous responses. This translates to real-time insights, improved operational efficiency, and data-driven decision-making across industries.
3. How does IoT benefit organizations?
Imagine real-time visibility into your assets and resources, leading to reduced costs, enhanced operations, and predictive insights. IoT empowers you to monitor, manage, and optimize everything from end to end, all while gaining valuable data for strategic decisions.
4. How will 5G fuel the rise of IoT devices?
Current IoT devices often struggle with limited bandwidth and delayed responses. 5G solves these challenges with unprecedented data rates and massive traffic capacity, paving the way for an explosion of interconnected devices and an era of unparalleled digital transformation.
5. Is 5G secure for IoT?
While 5G unlocks potential, it also expands the attack surface. By prioritizing security by design, zero-trust principles, robust encryption, and continuous threat intelligence, you can ensure a secure and thriving IoT ecosystem.
[To share your insights with us as part of editorial or sponsored content, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]


