Generative AI is transformative for organizations, spanning image recognition to cybersecurity. In cybersecurity, its prowess lies in leveraging existing data to produce novel artifacts, enabling secure application development assistants and resilient security operations chatbots. The promise is immense: enhanced security, optimized resources, and adept defense against emerging threats.

As GenAI and Large Language Models (LLMs) commandeer the tech discourse, reshaping industries and igniting debates, a prudent perspective is indispensable amid burgeoning hyperbole. A recent report by Israeli venture firm Team8, “Generative AI and ChatGPT Enterprise Risk,” echoes this need for balance.
Highlighting realistic technical, compliance, and legal risks posed to corporate boards and cybersecurity personnel, the report underscores operational and regulatory vulnerabilities while tempering premature concerns. One such debunked apprehension is the fear of private data exposure through GenAI applications like ChatGPT.
Applications and Benefits of GenAI in Security
The line between social engineering threats and genuine media is blurring in cybersecurity. Attackers are leveraging sophisticated forms of artificial intelligence, particularly generative AI, to create convincing fake articles, images, videos, and audio. The emergence of these well-crafted attacks poses new security risks, exploiting human vulnerabilities such as trust and emotional response.
1. Generating Attack Simulations
Utilizing Generative AI, realistic attack simulations can be crafted to train security analysts and evaluate the efficacy of security systems. These simulations facilitate the creation of lifelike scenarios for analysts to hone their skills.
2. Identifying Potential Threats
Generative AI’s capacity to analyze extensive data enables the detection of potential threats by recognizing data patterns and anomalies that might signal an impending attack.
3. Creating Predictive Models
Generative AI empowers the development of predictive models, foreseeing future attacks. This proactive approach assists organizations in preemptively mitigating potential threats.
4. Automating Security Tasks
Generative AI streamlines security operations by automating repetitive tasks like log analysis and threat hunting. This automation liberates human experts to focus on more critical responsibilities.
5. Enhancing Endpoint Resilience
Leveraging Generative AI bolsters endpoint resilience against attacks. By pinpointing vulnerabilities and implementing stringent security measures, it becomes more arduous for attackers to breach endpoints.
6. Malware Detection Advancements
An area of significant impact within cybersecurity, Generative AI revolutionizes malware detection. Creating synthetic malware samples aids in training machine-learning models to detect novel and unidentified malware strains.
7. Vulnerability Assessment Innovations
Generative AI’s utility extends to vulnerability assessment, crafting synthetic data sets to gauge the efficacy of assessment tools and techniques in identifying system vulnerabilities.
8. Cybersecurity Training Integration
Generative AI becomes instrumental in cybersecurity training, enabling synthetic data sets to educate employees on identifying and responding to diverse cyber threats, ensuring heightened awareness and preparedness.
Risks Associated with GenAI Adoption
Understanding the spectrum of potential risks associated with GenAI in an enterprise setting is critical. Categorizing these risks into technological extensions of existing risks, legal and regulatory concerns, and novel threats is essential for comprehensive risk assessment.
Enterprises must proactively mitigate potential negative impacts of GenAI while ensuring secure, compliant, and responsible usage. For instance, organizations might limit data sharing when utilizing third-party GenAI SaaS platforms or explore on-premise alternatives.
#1 Specific Concerns: Data Privacy and Confidentiality
The high-risk nature of GenAI usage involves potential threats to non-public enterprise data, intellectual property, and sensitive information. Transmitting confidential data externally could trigger legal compliance issues, potentially violating regulations like CCPA, GDPR, or HIPAA. While data submitted to platforms like ChatGPT might be retained for a limited period, inherent storage and processing risks persist, impacting organizations’ risk tolerance.
#2 Enterprise, SaaS, and Third-party Security Risks
GenAI’s wide adoption poses risks related to third-party integrations, potential data breaches, and the concentration of security threats on these platforms. Concerns extend to reliance on third-party security and quality assurance, emphasizing the need for robust security measures amid evolving threats.
#3 AI Behavioral Vulnerabilities
The threat of behavioral vulnerabilities in AI systems, leading to unauthorized access or compromised functionalities, highlights potential risks for non-public enterprise data and model operators. Maliciously crafted inputs might manipulate AI behavior, posing security challenges and exploiting vulnerabilities in GenAI systems.
#4 Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The legal and regulatory landscape introduces medium-level threats, particularly regarding compliance with data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, PIPEDA, CCPA). Instances of regulatory action against specific GenAI usage (e.g., ChatGPT in Italy) raise concerns about liability and compliance in consumer-facing communications.
#5 Threat Actor Tactics
Threat actors leverage GenAI for sophisticated malicious activities, including phishing, fraud, and social engineering. This necessitates reassessment and enhancement of security awareness training and controls to combat evolving threat strategies.
#6 Ethical and Regulatory Developments in AI
The ethical considerations surrounding AI influence legal frameworks, encompassing safety, fairness, transparency, and accountability. CISOs are pivotal in anticipating and mitigating potential ethical and regulatory impacts, aligning AI usage with evolving ethical principles and ESG risks related to labor practices and environmental impact.
Securing the Use of Generative AI: A CISO’s Directive
CISOs and their teams are responsible for ensuring the secure utilization of generative AI within their organizations. This involves a strategic approach across four critical domains:
- Defending with Generative Cybersecurity AI: CISOs are tasked with leveraging GenAI to bolster security measures, optimize resource utilization, counter emerging attack methodologies, and potentially reduce operational costs. Initiating experiments with “generative cybersecurity AI,” such as deploying chat assistants within security operations centers (SOCs) and application security, is an initial step.
- Collaboration with Organizational Counterparts Engaged in GenAI: Effective collaboration with legal, compliance, and various business departments is pivotal. Formulating user policies, providing comprehensive training, and establishing guidelines collaboratively minimize unauthorized GenAI usage, thereby mitigating risks associated with privacy breaches and copyright infringements.
- Application of the AI TRiSM Framework: Implementing the AI Trust, Risk, and Security Management framework becomes imperative. This framework guides the development of proprietary and third-party applications utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI, ensuring a structured and secure approach.
- Strengthening Methods for Assessing Unpredictable Threats: CISOs must reinforce methodologies to effectively assess exposure to unpredictable threats. The evolving nature of malicious actor behavior utilizing GenAI necessitates continuous control efficacy measurement and adaptation.
3. Impact of GenAI on Cybersecurity Defenses
- Leveraging Generative Cybersecurity AI for Defense
- Collaboration and Alignment with Organizational Counterparts Engaging in GenAI
4. Navigating Risk: The AI TRiSM Framework
- Understanding AI Trust, Risk, and Security Management (AI TRiSM)
- Implementing AI TRiSM in GenAI-Centric Strategies
Splunk’s Approach to CISOs and Generative AI
The role of CISOs in navigating the complex landscape of generative AI remains a pivotal challenge. Splunk acknowledges the dual nature of generative AI — a tool and a potential threat, as highlighted in the CISO Report. While the debate continues on its applications in security and the threat landscape, one undeniable fact emerges: Generative AI is here to stay.
 AI Empowers Cyber Adversaries: A Stark Reality
AI Empowers Cyber Adversaries: A Stark Reality
Understanding that what serves for good can be exploited for evil, the company recognizes that AI, including generative AI, can potentially become a weapon for cyber adversaries. CISO Report indicates that 70% of CISOs foresee generative AI creating an asymmetrical battlefield tipped in favor of cyber adversaries. Top concerns include faster and more efficient attacks, voice and image impersonations for social engineering, and an expanded attack surface in the supply chain.
While some concerns are theoretical, backed by media reports or researchers’ proofs of concept, real-world evidence has yet to validate extensive use in cyber attacks. However, CISOs are not passive observers but actively preparing resilient cyber defenses.
AI Fills Cyber Defense Gaps: A Strategic Utilization
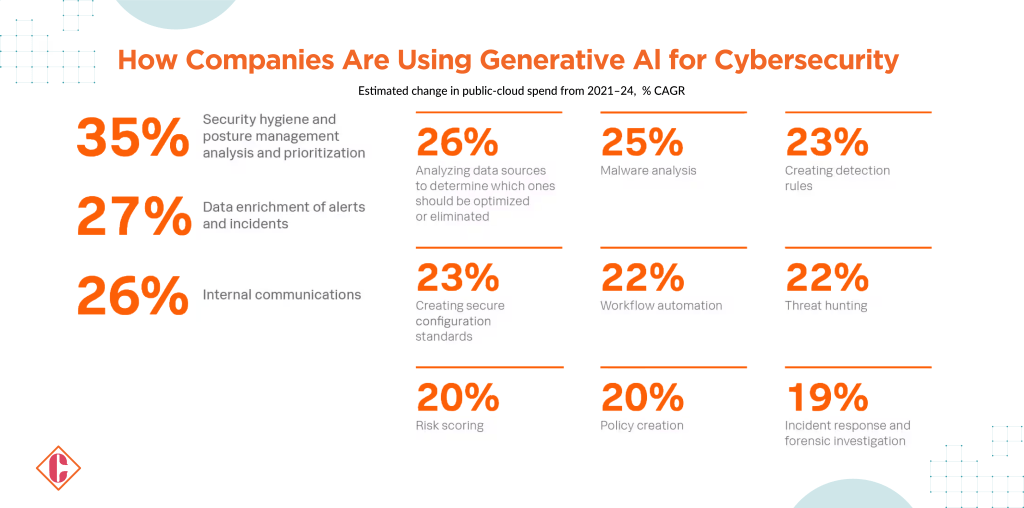
Recognizing the potential for generative AI in cyber defense, CISOs are already harnessing its capabilities. According to the report, 35% of CISOs use AI for positive cybersecurity functions, and 61% either plan to implement it in the next 12 months or express interest in doing so.
Generative AI addresses challenges across strategic and technical domains. CISOs are keen on deploying AI for security hygiene, from generating inline documentation to asset and inventory collection. Its potential extends to quality assurance, prioritizing data sources, malware analysis, threat hunting, incident response, and forensic investigations.
Splunk’s comprehensive approach empowers CISOs to explore AI’s potential in documentation creation and solving intricate challenges previously believed to be exclusive to human intelligence.
Building Out, Building Better: Augmenting Talent with AI
Addressing AI replacing jobs, Splunk’s CISO Report reveals that 86% of CISOs believe generative AI will bridge existing skills gaps and talent shortages within security teams. Rather than replacing jobs, AI is seen as a tool to augment security professionals, filling labor-intensive and time-consuming functions. It offers the ability to supplement staff with automation, ranging from documentation to basic ticket triage.
CISOs view AI, including generative AI, as an augmentation strategy rather than a threat to job security. Automation, already implemented extensively by 93% of CISOs, paves the way for innovative use cases in the future.



 AI Empowers Cyber Adversaries: A Stark Reality
AI Empowers Cyber Adversaries: A Stark Reality