Data is the foundation for innovation, growth, and competitive advantage in this evolving business environment. However, its potency is only realized when safeguarded and strategically managed. The nexus of data privacy, security, and protection forms the bedrock upon which organizations build compliance, fortify networks, and unlock new avenues for growth. Fortified by automated capabilities within a robust data fabric, data governance propels enterprises toward assured compliance and security. This framework orchestrates the seamless flow of sensitive data, safeguarding its integrity as it traverses diverse endpoints within a distributed data ecosystem.

Executives across industries comprehend the pivotal role of data in propelling digital transformation, pioneering analytics-driven revenue streams, and ensuring operational excellence. Yet, the perennial challenge persists: while data’s potential for value creation remains universally acknowledged, its realization often falters due to ineffective governance frameworks. The issue often arises from a disconnect within organizational structures. The C-suite often underestimates the potential impact of robust data governance strategies. Consequently, governance initiatives are limited to procedural policies handled by IT support functions, hindering their organizational effectiveness.
The estimated size of the Data Governance Market in 2023 stands at USD 2.73 billion, with a projected growth of approximately USD 6.71 billion by 2028, indicating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 19.72% within the forecast period (2023-2028) as per the report of Mordor Intelligence.
Technological interventions, while promising, do not singularly resolve this problem. Solutions like data lakes and governance platforms play a crucial role, yet they fall short without an underpinning of quality assurance governance. The absence of robust governance deprives organizations of data-driven prospects and squanders valuable resources. Substantial chunks of time within analytics teams, including skilled data scientists, are consumed by data processing and rectification—a hurdle that impedes scalability and dampens employee productivity.
Read more: Optimizing Data Management with Databricks: A Comprehensive Guide for CIOs
Why Automated Data Governance
Data lineage and traceability are pivotal elements post-deployment of data products, such as dashboards and machine learning models. Particularly significant in regulated industries, auditability demands a comprehensive view of the data’s journey, from its origin in transactional systems to its final iteration supporting business decisions. This retrospective insight ensures compliance and accountability, which are essential in meeting industry standards. In addition, enabling end-users to access and comprehend data sources and transformations expedites their dashboard customization process, saving valuable time.
The stringent impact of non-compliance is evident, with the EU imposing substantial fines totaling $1.2 billion for breaches of the GDPR law since January 28, 2021, underscoring the critical importance of robust data governance in contemporary business environments.
Facilitating self-service data consumption is imperative for organizations aspiring to leverage data’s disruptive potential. A robust governance framework is fundamental in simplifying data access. It empowers authorized users to efficiently locate and utilize quality, governed data through metadata-driven catalogs. Conversely, the absence of centralized governance fosters reluctance to data sharing between business units, reinforcing silos. This compels IT teams to safeguard individual data repositories, spawning shadow IT and escalating system complexities.
Establishing a robust foundation for effective data governance remains challenging for many organizations; however, some have succeeded. One such instance involves a prominent global retailer struggling to derive value from its data while managing governance solely within IT for an extended period. As part of a sweeping analytics transformation initiative, the retailer made a strategic shift by involving the entire senior executive leadership team in data governance.
Each executive leader must be allocated specific data domains or business-data subject areas from the CFO to the CMO. Some domains, like consumer transactions and employee data, spanned multiple functions or lines of business. Through extensive education and involvement, these leaders can become advocates for data governance within their assigned domains. They can appoint representatives as data-domain owners and stewards, aligning governance efforts directly with priority analytics use cases.
In an agile approach, these leaders expedited identifying critical data, focusing on its potential value delivery. Regular check-ins with the CEO and senior leadership ensured alignment with overarching organizational objectives. This agile approach significantly accelerated the establishment of priority data domains within months, a feat that would typically take years. Consequently, it reduces data scientists’ time on data cleanup, expediting the delivery of analytics use cases. This initiative continues to evolve and expand.
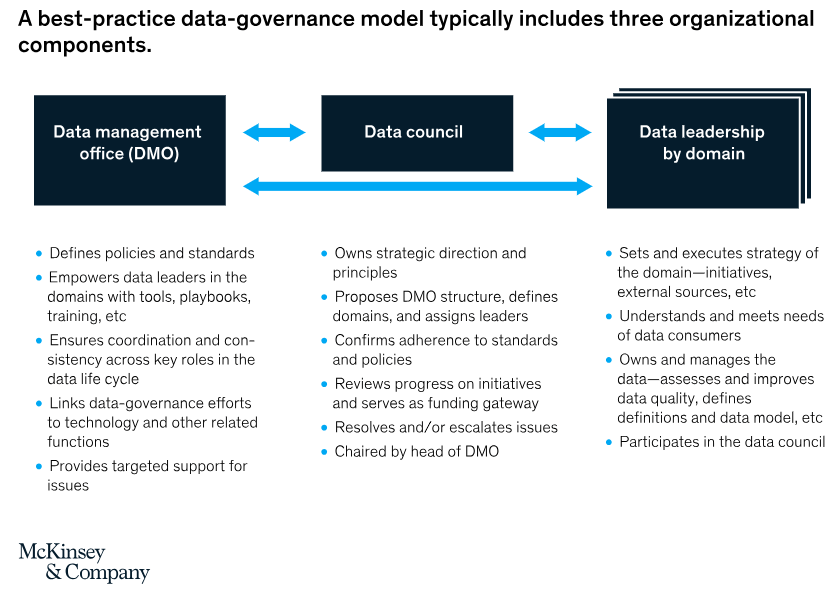 This example illustrated by McKinsey & Company underscores the need to reevaluate the organizational framework for effective data governance. A typical governance structure entails three primary components:
This example illustrated by McKinsey & Company underscores the need to reevaluate the organizational framework for effective data governance. A typical governance structure entails three primary components:
- A central Data Management Office (DMO), usually led by a Chief Data Officer (CDO), defines targeted data strategy and governance standards.
- Governance roles are structured around specific data domains where daily governance activities are executed.
- A Data Council acts as a nexus between domain leaders and the DMO, aligning data strategy with corporate objectives, sanctioning funding, and addressing pertinent issues.
Data Governance Success Story in Financial Services: ING
Among the notable success stories in data governance lies ING, a Dutch banking giant serving 39.3 million customers, corporate clients, and financial institutions across 40 countries. Ferdinand Scheepers, ING’s Chief Architect, envisioned revolutionizing data governance within the company’s hybrid cloud environment.
To realize this vision, ING aimed to govern its cloud data consistently with on-premises operations, necessitating adherence to diverse regulations and business policies across global jurisdictions. Scheepers laid out specific goals:
- Empower ING’s data citizens with swift, uncomplicated access to governed data and associated toolsets.
- Establish robust governance and privacy measures across a complex global ecosystem.
- Ensure compliance with evolving business policies and multi-jurisdictional regulations.
Creating a data fabric solution emerged as the linchpin in implementing a unified corporate operating model at ING. This solution streamlined data management and applications across operational countries, addressing key challenges:
- Scaling data governance for a global operation, minimizing friction for data scientists.
- Collaborative efforts between IBM and ING resulted in a standard, intelligent metadata tier facilitating seamless discovery, governance, and data security. This allowed business analysts and data scientists to collaborate effectively with data stewards in crafting data access policies.
- Leveraging an orchestrator, IBM and ING consistently enforced data protection, privacy, and compliance policies within an open hybrid cloud environment adaptable to ING’s diverse landscape.
Implementing data virtualization bridged existing on-premises investments, eliminating data silos and enabling on-demand access to pertinent data across any cloud or on-premises setup. This approach optimizes costs while ensuring an appropriate level of governance.
The data fabric empowered ING to provide a uniform user experience, fostering collaboration, enhancing application management, and optimizing licensing and IT expenditures.
Read more: Future of Data Integration: How AI is Changing the Blueprint for Businesses.
Empowering Data Governance through Technological Synergy: IBM’s Comprehensive Solutions
A potent data governance strategy hinges on a purpose-built technological framework to achieve comprehensive governance, ensure data quality and foster collaboration. Integrating data governance with data integration and entity resolution amplifies its value.
Embedded within a contemporary data fabric, data governance creates an immersive end-to-end user experience centered on metadata and active policy management. This approach grants users seamless access, manipulation, and data analysis without the need for intricate knowledge of its physical format or location, obviating the need for data movement or replication.
IBM’s data fabric technology components facilitate the automatic application of industry-specific regulatory policies to data assets, ensuring enterprise-wide security:
- An AI-augmented data catalog empowers business users to effortlessly comprehend, enrich, and access pertinent data.
- A metadata and governance layer fosters visibility and collaboration across data, analytics, and AI initiatives in any cloud environment.
- Dynamic and consistent data masking at granular levels ensures confidentiality.
- The creation of anonymized training data and test sets maintains data integrity.
 IBM Cloud Pak for Data, designed with a data fabric architecture, enables faster outcome prediction by streamlining data collection, organization, and analysis across diverse landscapes, enhancing productivity and reducing complexity.
IBM Cloud Pak for Data, designed with a data fabric architecture, enables faster outcome prediction by streamlining data collection, organization, and analysis across diverse landscapes, enhancing productivity and reducing complexity.
- IBM Knowledge Catalog offers intelligent governance through advanced data discovery, quality management, automated data lineage, cataloging, and protection capabilities. Leveraging active metadata enables self-service access to reliable data for insights and regulatory compliance.
- IBM Watson Query streamlines governance policy applications across data sources, swiftly delivering data to end applications without manual intervention, data movement, or replication.
- Databand, an IBM company, provides data observability capabilities, allowing the identification and resolution of data and machine learning pipeline errors and poor quality, addressing challenges at the data source.
- IBM Match 360 with Watson consolidates data from disparate sources using ML and governance capabilities, simplifying the user experience for business users by providing a comprehensive view across entities.
- IBM Security Guardium Insights offers compliance capabilities and workflows, facilitating quick compliance policy enforcement, centralizing data activity, and providing robust data security features for monitoring and reporting in hybrid-cloud environments.


